
-
 Smith added to Australia T20 squad, in line for Sri Lanka crunch
Smith added to Australia T20 squad, in line for Sri Lanka crunch
-
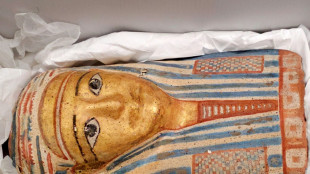
Australian museum recovers Egyptian artefacts after break-in
-
 India forced to defend US trade deal as doubts mount
India forced to defend US trade deal as doubts mount
-
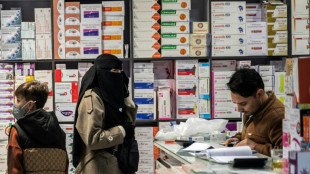
Bitter pill: Taliban govt shakes up Afghan medicine market
-
 Crunch time for Real Madrid's Mbappe-Vinicius partnership
Crunch time for Real Madrid's Mbappe-Vinicius partnership
-
Rio Carnival parades kick off with divisive ode to Lula in election year

-
 Nepal 'addicted' to the trade in its own people
Nepal 'addicted' to the trade in its own people
-
Asian markets sluggish as Lunar New Year holiday looms

-
 'Pure extortion': foreign workers face violence and exploitation in Croatia
'Pure extortion': foreign workers face violence and exploitation in Croatia
-
Nepal launches campaigns for first post-uprising polls

-
 What to know as South Korea ex-president Yoon faces insurrection verdict
What to know as South Korea ex-president Yoon faces insurrection verdict
-
'Train Dreams,' 'The Secret Agent' nab Spirit wins to boost Oscars campaigns

-
 Rubio visits Trump's 'friend' Orban ahead of Hungary polls
Rubio visits Trump's 'friend' Orban ahead of Hungary polls
-
Kim unveils housing block for North Korean troops killed aiding Russia: KCNA

-
 Accused Bondi killer Naveed Akram appears in court by video link
Accused Bondi killer Naveed Akram appears in court by video link
-
Art and the deal: market slump pushes galleries to the Gulf

-
 Job threats, rogue bots: five hot issues in AI
Job threats, rogue bots: five hot issues in AI
-
India hosts AI summit as safety concerns grow

-
 'Make America Healthy' movement takes on Big Ag, in break with Republicans
'Make America Healthy' movement takes on Big Ag, in break with Republicans
-
Tech is thriving in New York. So are the rents

-
 Young USA Stars beat Stripes in NBA All-Star tourney final
Young USA Stars beat Stripes in NBA All-Star tourney final
-
New anti-government chants in Tehran after giant rallies abroad: reports

-
 'The Secret Agent' nabs Spirit Awards win in boost to Oscars campaign
'The Secret Agent' nabs Spirit Awards win in boost to Oscars campaign
-
Pantheon Resources PLC Announces AGM Arrangements & Corporate Update

-
 Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth Olympic crown
Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth Olympic crown
-
Morikawa wins at Pebble Beach despite Scheffler heroics

-
 Germany's Hase and Volodin tango to Olympic pairs figure skating lead
Germany's Hase and Volodin tango to Olympic pairs figure skating lead
-
Rayo thrash Atletico who 'deserved to lose' as Betis cut gap

-
 Napoli salvage point after Malen twice puts Roma ahead
Napoli salvage point after Malen twice puts Roma ahead
-
Lyon down Nice to boost Ligue 1 title bid with 13th straight win

-
 LeBron still unclear on NBA future: 'I have no idea'
LeBron still unclear on NBA future: 'I have no idea'
-
Shelton battles back from brink to beat Fritz, take Dallas crown

-
 Great Britain celebrate best-ever Winter Olympics
Great Britain celebrate best-ever Winter Olympics
-
Brignone wins second Milan-Cortina gold as Klaebo claims record ninth

-
 Arteta concerned over Arsenal's mounting injury list
Arteta concerned over Arsenal's mounting injury list
-
In fuel-starved Cuba, the e-tricycle is king

-
 Shaidorov still spinning after outshining Malinin for Olympic gold
Shaidorov still spinning after outshining Malinin for Olympic gold
-
Late Gruda goal grabs Leipzig draw versus Wolfsburg

-
 'Ultra-left' blamed for youth's killing that shocked France
'Ultra-left' blamed for youth's killing that shocked France
-
Canada wrap up perfect Olympic ice hockey preliminary campaign

-
 Historical queer film 'Rose' shown at Berlin with call to action
Historical queer film 'Rose' shown at Berlin with call to action
-
Wales' Tandy tips hat to France after Six Nations hammering

-
 Quadruple chasing Arsenal rout Wigan to reach FA Cup fifth round
Quadruple chasing Arsenal rout Wigan to reach FA Cup fifth round
-
2026 S-Class starry facelift

-
 What they said as India beat Pakistan at T20 World Cup - reaction
What they said as India beat Pakistan at T20 World Cup - reaction
-
Away-day blues: England count cost of Scotland Six Nations defeat

-
 'Wuthering Heights' debuts atop North America box office
'Wuthering Heights' debuts atop North America box office
-
Rayo thrash Atletico who 'deserved to lose'

-
 Kok beats Leerdam in Olympic rematch of Dutch speed skaters
Kok beats Leerdam in Olympic rematch of Dutch speed skaters
-
India rout bitter rivals Pakistan by 61 runs at T20 World Cup


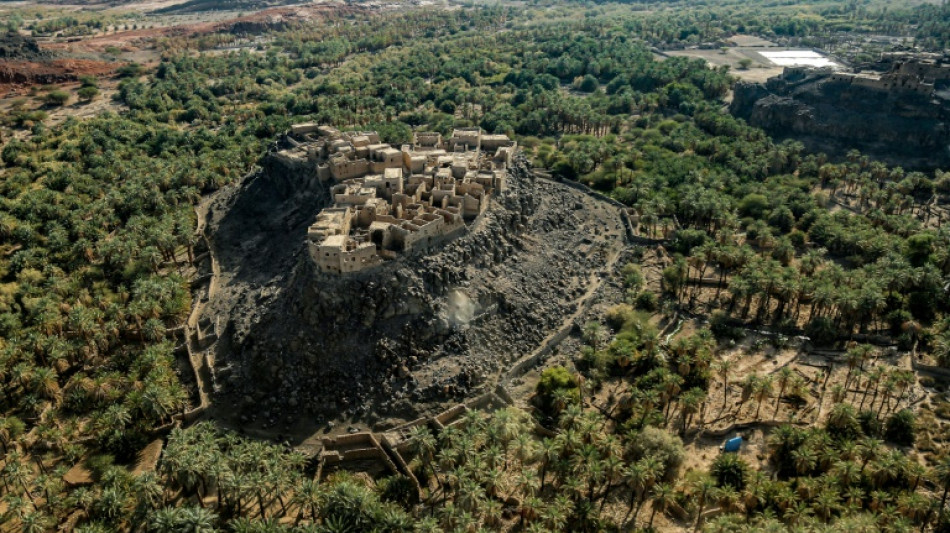
4,000-year-old town discovered hidden in Arabian oasis
The discovery of a 4,000-year-old fortified town hidden in an oasis in modern-day Saudi Arabia reveals how life at the time was slowly changing from a nomadic to an urban existence, archaeologists said on Wednesday.
The remains of the town, dubbed al-Natah, were long concealed by the walled oasis of Khaybar, a green and fertile speck surrounded by desert in the northwest of the Arabian Peninsula.
Then an ancient 14.5 kilometre-long wall was discovered at the site, according to research led by French archaeologist Guillaume Charloux published earlier this year.
For a new study published in the journal PLOS One, a French-Saudi team of researchers have provided "proof that these ramparts are organised around a habitat", Charloux told AFP.
The large town, which was home to up to 500 residents, was built around 2,400 BC during the early Bronze Age, the researchers said.
It was abandoned around a thousand years later. "No one knows why," Charloux said.
When al-Natah was built, cities were flourishing in the Levant region along the Mediterranean Sea from present-day Syria to Jordan.
Northwest Arabia at the time was thought to have been barren desert, crossed by pastoral nomads and dotted with burial sites.
That was until 15 years ago, when archaeologists discovered ramparts dating back to the Bronze Age in the oasis of Tayma, to Khaybar's north.
This "first essential discovery" led scientists to look closer at these oases, Charloux said.
- 'Slow urbanism' -
Black volcanic rocks called basalt concealed the walls of al-Natah so well that it "protected the site from illegal excavations", Charloux said.
But observing the site from above revealed potential paths and the foundations of houses, suggesting where the archaeologists needed to dig.
They discovered foundations "strong enough to easily support at least one- or two-storey" homes, Charloux said, emphasising that there was much more work to be done to understand the site.
But their preliminary findings paint a picture of a 2.6-hectare town with around 50 houses perched on a hill, equipped with a wall of its own.
Tombs inside a necropolis there contained metal weapons like axes and daggers as well as stones such as agate, indicating a relatively advanced society for so long ago.
Pieces of pottery "suggest a relatively egalitarian society", the study said. They are "very pretty but very simple ceramics", added Charloux.
The size of the ramparts -- which could reach around five metres (16 feet) high -- suggests that al-Natah was the seat of some kind of powerful local authority.
These discoveries reveal a process of "slow urbanism" during the transition between nomadic and more settled village life, the study said.
For example, fortified oases could have been in contact with each other in an area still largely populated by pastoral nomadic groups. Such exchanges could have even laid the foundations for the "incense route" which saw spices, frankincense and myrrh traded from southern Arabia to the Mediterranean.
Al-Natah was still small compared to cities in Mesopotamia or Egypt during the period.
But in these vast expanses of desert, it appears there was "another path towards urbanisation" than such city-states, one "more modest, much slower, and quite specific to the northwest of Arabia", Charloux said.
P.Costa--AMWN