
-
 Bayer proposes class settlement for weedkiller cancer claims
Bayer proposes class settlement for weedkiller cancer claims
-
Gauff, Rybakina cruise into Dubai last 16

-
 Greenland entrepreneur gambles on leafy greens
Greenland entrepreneur gambles on leafy greens
-
Father of US school shooter goes on trial on murder charges

-
 Iran, US agree on 'guiding principles' for deal at Geneva talks: Iran FM
Iran, US agree on 'guiding principles' for deal at Geneva talks: Iran FM
-
Warner Bros. gives Paramount one week to outbid Netflix

-
 Russians, Belarusians allowed to compete under own flags at 2026 Paralympics: IPC tells AFP
Russians, Belarusians allowed to compete under own flags at 2026 Paralympics: IPC tells AFP
-
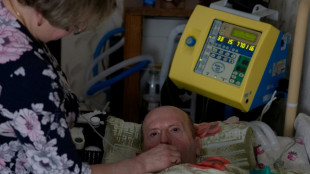
Ukrainian wife battles blackouts to keep terminally ill husband alive
-
 Pollock handed first England start for Ireland visit
Pollock handed first England start for Ireland visit
-
Oil prices fall back as 'hopeful' Tehran responds to Trump

-
 Arteta welcomes Madueke and Saka's competition for places
Arteta welcomes Madueke and Saka's competition for places
-
France and India hail growing ties as Modi hosts Macron

-
 Warner Bros. says reopening talks with Paramount on its buyout offer
Warner Bros. says reopening talks with Paramount on its buyout offer
-
Slalom showdown Shiffrin's last chance for Milan-Cortina medal

-
 Protesters march in Kosovo, as ex-president's war crimes trial nears end
Protesters march in Kosovo, as ex-president's war crimes trial nears end
-
No pressure on India opener Abhishek after two ducks, says coach

-
 Sakamoto eyes figure skating gold in Olympic farewell
Sakamoto eyes figure skating gold in Olympic farewell
-
Pereira 'trusts' Forest owner Marinakis despite three sackings this season

-
 AI 'arms race' risks human extinction, warns top computing expert
AI 'arms race' risks human extinction, warns top computing expert
-
Israeli bobsleigher dismisses Olympics 'diatribe' by Swiss TV commentator

-
 Supreme leader says Iran can sink US warship as Geneva talks conclude
Supreme leader says Iran can sink US warship as Geneva talks conclude
-
Australia, Ireland out of T20 World Cup as Zimbabwe qualify after washout

-
 Greece experts to examine Nazi atrocity photos find
Greece experts to examine Nazi atrocity photos find
-
Los Angeles mayor calls for 2028 Olympics chairman to step down over Epstein files

-
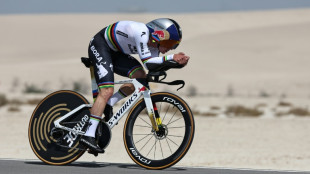 Evenepoel takes UAE Tour lead with time-trial win
Evenepoel takes UAE Tour lead with time-trial win
-
Oil prices rise as Trump ramps up Iran threats

-
 EU investigates Shein over sale of childlike sex dolls
EU investigates Shein over sale of childlike sex dolls
-
Bangladesh's new PM, political heir Tarique Rahman

-
 Rain threatens to knock Australia out of T20 World Cup
Rain threatens to knock Australia out of T20 World Cup
-
US civil rights leader Jesse Jackson dies at 84: family

-
 Trump's new envoy arrives in South Africa with relations frayed
Trump's new envoy arrives in South Africa with relations frayed
-
Jesse Jackson: civil rights lion sought 'common ground'

-
 Iran, United States hold new talks in Geneva
Iran, United States hold new talks in Geneva
-
Tariq confident Pakistan can bounce back after India drubbing

-
 Being back in the USA 'feels amazing', says Vonn
Being back in the USA 'feels amazing', says Vonn
-
New Zealand cruise into Super Eights at T20 World Cup

-
 Moscow, Kyiv meet for US-brokered talks after fresh attacks
Moscow, Kyiv meet for US-brokered talks after fresh attacks
-
Exhilarating Italy aim to sign off with giant-killing at T20 World Cup

-
 Samra hits 110 for Canada against New Zealand at T20 World Cup
Samra hits 110 for Canada against New Zealand at T20 World Cup
-
'Made in Europe' or 'Made with Europe'? Buy European push splits bloc

-
 Slovakia revamps bunkers with Ukraine war uncomfortably close
Slovakia revamps bunkers with Ukraine war uncomfortably close
-
Sydney man jailed for mailing reptiles in popcorn bags

-
 'Like a Virgin' songwriter Billy Steinberg dies at 75
'Like a Virgin' songwriter Billy Steinberg dies at 75
-
Who fills Sexton vacuum? Irish fly-half debate no closer to resolution

-
 Japan hails 'new chapter' with first Olympic pairs skating gold
Japan hails 'new chapter' with first Olympic pairs skating gold
-
Russian prosthetics workshops fill up with wounded soldiers

-
 'Not just props that eat': Extras seek recognition at their own 'Oscars'
'Not just props that eat': Extras seek recognition at their own 'Oscars'
-
Bangladesh PM-to-be Tarique Rahman and lawmakers sworn into parliament

-
 At least 14 killed in spate of attacks in northwest Pakistan
At least 14 killed in spate of attacks in northwest Pakistan
-
Peru Congress to debate impeachment of interim president


The music industry is battling AI -- with limited success
The music industry is fighting on platforms, through the courts and with legislators in a bid to prevent the theft and misuse of art from generative AI -- but it remains an uphill battle.
Sony Music said recently it has already demanded that 75,000 deepfakes -- simulated images, tunes or videos that can easily be mistaken for real -- be rooted out, a figure reflecting the magnitude of the issue.
The information security company Pindrop says AI-generated music has "telltale signs" and is easy to detect, yet such music seems to be everywhere.
"Even when it sounds realistic, AI-generated songs often have subtle irregularities in frequency variation, rhythm and digital patterns that aren't present in human performances," said Pindrop, which specializes in voice analysis.
But it takes mere minutes on YouTube or Spotify -- two top music-streaming platforms -- to spot a fake rap from 2Pac about pizzas, or an Ariana Grande cover of a K-pop track that she never performed.
"We take that really seriously, and we're trying to work on new tools in that space to make that even better," said Sam Duboff, Spotify's lead on policy organization.
YouTube said it is "refining" its own ability to spot AI dupes, and could announce results in the coming weeks.
"The bad actors were a little bit more aware sooner," leaving artists, labels and others in the music business "operating from a position of reactivity," said Jeremy Goldman, an analyst at the company Emarketer.
"YouTube, with a multiple of billions of dollars per year, has a strong vested interest to solve this," Goldman said, adding that he trusts they're working seriously to fix it.
"You don't want the platform itself, if you're at YouTube, to devolve into, like, an AI nightmare," he said.
- Litigation -
But beyond deepfakes, the music industry is particularly concerned about unauthorized use of its content to train generative AI models like Suno, Udio or Mubert.
Several major labels filed a lawsuit last year at a federal court in New York against the parent company of Udio, accusing it of developing its technology with "copyrighted sound recordings for the ultimate purpose of poaching the listeners, fans and potential licensees of the sound recordings it copied."
More than nine months later, proceedings have yet to begin in earnest. The same is true for a similar case against Suno, filed in Massachusetts.
At the center of the litigation is the principle of fair use, allowing limited use of some copyrighted material without advance permission. It could limit the application of intellectual property rights.
"It's an area of genuine uncertainty," said Joseph Fishman, a law professor at Vanderbilt University.
Any initial rulings won't necessarily prove decisive, as varying opinions from different courts could punt the issue to the Supreme Court.
In the meantime, the major players involved in AI-generated music continue to train their models on copyrighted work -- raising the question of whether the battle isn't already lost.
Fishman said it may be too soon to say that: although many models are already training on protected material, new versions of those models are released continuously, and it's unclear whether any court decisions would create licensing issues for those models going forward.
- Deregulation -
When it comes to the legislative arena, labels, artists and producers have found little success.
Several bills have been introduced in the US Congress, but nothing concrete has resulted.
A few states -- notably Tennessee, home to much of the powerful country music industry -- have adopted protective legislation, notably when it comes to deepfakes.
Donald Trump poses another potential roadblock: the Republican president has postured himself as a champion of deregulation, particularly of AI.
Several giants in AI have jumped into the ring, notably Meta, which has urged the administration to "clarify that the use of publicly available data to train models is unequivocally fair use."
If Trump's White House takes that advice, it could push the balance against music professionals, even if the courts theoretically have the last word.
The landscape is hardly better in Britain, where the Labor government is considering overhauling the law to allow AI companies to use creators' content on the internet to help develop their models, unless rights holders opt out.
More than a thousand musicians, including Kate Bush and Annie Lennox, released an album in February entitled "Is This What We Want?" -- featuring the sound of silence recorded in several studios -- to protest those efforts.
For analyst Goldman, AI is likely to continue plaguing the music industry -- as long as it remains unorganized.
"The music industry is so fragmented," he said. "I think that that winds up doing it a disservice in terms of solving this thing."
J.Williams--AMWN

