
-
 Giannis triumphant in NBA return as Spurs win streak ends
Giannis triumphant in NBA return as Spurs win streak ends
-
How company bets on bitcoin can backfire

-
 Touadera on path to third presidential term as Central African Republic votes
Touadera on path to third presidential term as Central African Republic votes
-
'Acoustic hazard': Noise complaints spark Vietnam pickleball wars

-
 Iraqis cover soil with clay to curb sandstorms
Iraqis cover soil with clay to curb sandstorms
-
Australia's Head backs struggling opening partner Weatherald

-
 'Make emitters responsible': Thailand's clean air activists
'Make emitters responsible': Thailand's clean air activists
-
Zelensky looks to close out Ukraine peace deal at Trump meet

-
 MCG curator in 'state of shock' after Ashes Test carnage
MCG curator in 'state of shock' after Ashes Test carnage
-
Texans edge Chargers to reach NFL playoffs

-
 Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw
Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw
-
Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round

-
 How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not
How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not
-
Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family

-
 Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought
-
Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania

-
 Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea
Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea
-
Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine

-
 Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit
Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit
-
Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota

-
 Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo
Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo
-
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck

-
 Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
-
Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role

-
 UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles
UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles
-
Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects

-
 'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year
'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year
-
Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes

-
 Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday
Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday
-
US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says

-
 Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest
Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest
-
Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth

-
 Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit
Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit
-
Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years

-
 Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power
Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power
-
Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage

-
 Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win
Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win
-
What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction

-
 Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'
Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'
-
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire
-
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall

-
 England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland

-
 England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage

-
 Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan
-
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test

-
 New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television
New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television
-
Dental Implant Financing and Insurance Options in Georgetown, TX


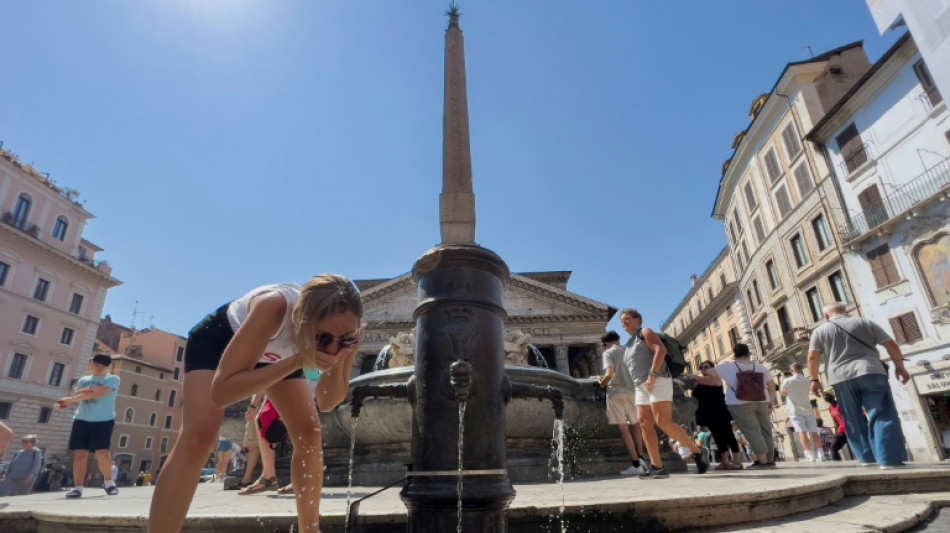
Trees could cut urban heatwave mortality by a third: study
Planting more trees in urban areas to lower summertime temperatures could decrease deaths directly linked to hot weather and heatwaves by a third, researchers said Wednesday.
Modelling found that increasing tree cover to 30 percent would shave off 0.4 degrees Celsius (0.7 degrees Fahrenheit) locally, on average, during hot summer months, they reported in The Lancet.
Of the 6,700 premature deaths attributed to higher temperatures in 93 European cities during 2015, one third could have been prevented, according to the findings.
Currently, just under 15 percent of urban environments in Europe, on average, are covered by some kind of foliage.
The study is the first to project the number of premature deaths due to higher temperatures in cities that could be prevented by additional tree cover, said lead author Tamar Iungman, a researcher at the Barcelona Institute for Global Health.
"We already know that high temperatures in urban environments are associated with negative health outcomes, such as cardiorespiratory failure, hospital admission, and premature death," he said in a statement.
"Our goal is to inform local policy and decision-makers about the benefits of strategically integrating green infrastructure into urban planning in order to promote more sustainable, resilient and healthy urban environments."
Cities record higher temperatures than surrounding suburbs or countryside due to the so-called urban heat island effect.
This extra heat is caused primarily by a lack of vegetation, exhaust from air conditioning systems, along with dark-hued asphalt and building materials that absorb and trap warmth.
Climate change has already amplified the problem. Last year, Europe saw its hottest summer on record, and second warmest year.
- Health benefits -
Heatwaves around the world are seeing record-breaking peaks, and have increased in duration in recent decades.
Today, cold conditions still cause more deaths in Europe than hot weather. But climate models project that heat-related illness and death will present a bigger burden to health services within a decade.
"This is becoming increasingly urgent as Europe experiences more extreme temperature fluctuations caused by climate change," said Iungman.
The researchers estimated mortality rates for people over 20 years old between June and August 2015, accounting for 57 million inhabitants in total.
This data was analysed in relation to daily average city temperatures in two modelling scenarios.
The first compared the city temperature with and without urban heat islands. The second simulating temperature reduction if tree cover was increased to 30 percent.
On average, the temperature in cities was 1.5C warmer during summer 2015 than in the surrounding countryside. The city with the highest difference -- 4.1C -- was Cluj-Napoca, Romania.
Across all cities, 75 percent of the total population lived in areas at least one degree warmer, while 20 percent experienced temperatures at least two degrees higher.
Overall, cities with highest temperature-elated mortality rates were in southern and eastern Europe.
"This is an important piece of research," commented Laurence Wainwright, a lecturer at the University of Oxford's Smith School of Enterprise and the Environment.
"Urban tree planting -– on the right scale, in the right places, and under certain other conditions -– likely leads to a modest-yet-real reduction in heat-related deaths in many urban areas."
Earlier studies have shown that green spaces can have additional health benefits such as reducing cardiovascular disease, dementia and poor mental health, as well as improving cognitive functioning of children and the elderly.
F.Dubois--AMWN



