-
 Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw
Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw
-
Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round

-
 How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not
How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not
-
Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family

-
 Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought
-
Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania

-
 Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea
Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea
-
Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine

-
 Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit
Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit
-
Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota

-
 Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo
Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo
-
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck

-
 Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
-
Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role

-
 UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles
UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles
-
Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects

-
 'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year
'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year
-
Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes

-
 Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday
Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday
-
US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says

-
 Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest
Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest
-
Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth

-
 Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit
Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit
-
Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years

-
 Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power
Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power
-
Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage

-
 Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win
Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win
-
What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction

-
 Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'
Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'
-
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire
-
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall

-
 England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland

-
 England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage

-
 Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan
-
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test

-
 New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television
New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television
-
Dental Implant Financing and Insurance Options in Georgetown, TX

-
 Man Utd made to 'suffer' for Newcastle win, says Amorim
Man Utd made to 'suffer' for Newcastle win, says Amorim
-
Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance

-
 Key NFL week has playoff spots, byes and seeds at stake
Key NFL week has playoff spots, byes and seeds at stake
-
Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw

-
 Dorgu delivers winner for depleted Man Utd against Newcastle
Dorgu delivers winner for depleted Man Utd against Newcastle
-
US stocks edge lower from records as precious metals surge

-
 Somalia denounces Israeli recognition of Somaliland
Somalia denounces Israeli recognition of Somaliland
-
The Cure guitarist and keyboard player Perry Bamonte dies aged 65

-
 Draper to miss Australian Open
Draper to miss Australian Open
-
Police arrest suspect after man stabs 3 women in Paris metro


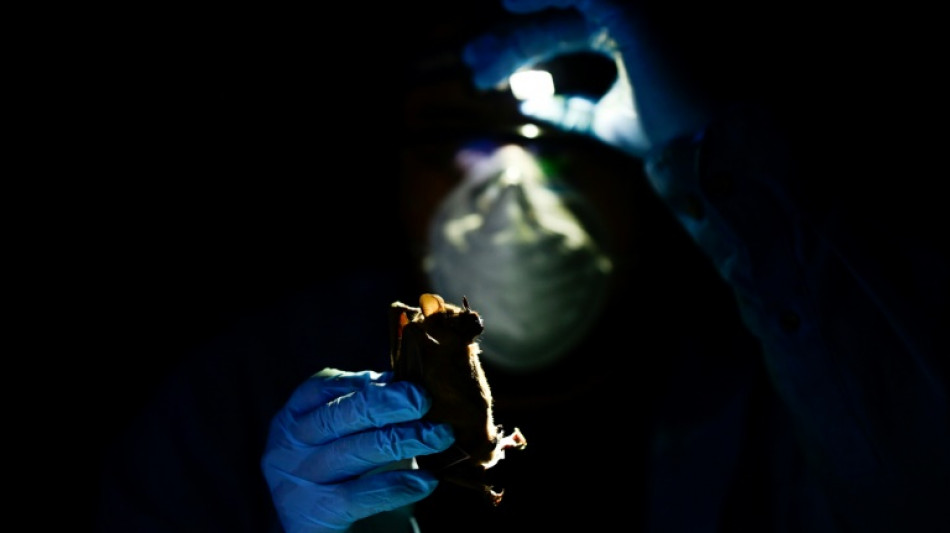
In Mexican jungle, scientists prepare for future pandemics
As night fell in Mexico's Yucatan jungle, veterinarian Omar Garcia extracted blood and fluids from a bat as part of an investigation aimed at preventing the next potential pandemic.
The goal of the Franco-Mexican project is to detect diseases -- known as zoonoses -- transmitted from animals to humans in tropical climates.
Bats are under scrutiny from the international scientific community as a possible source of coronavirus transmission.
The winged mammal remained immobile while bearing its fangs, before being released by Garcia, a vector-borne disease expert.
Scientists from France's Research Institute for Development (IRD) and the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) have been collaborating in the study since 2017, using a modern laboratory in Merida, the Yucatan state capital.
The aim is to discover how different viruses that circulate between animals such as mammals, birds and rodents, can potentially pass to humans, said Audrey Arnal, an infectious diseases expert at the IRD.
"This is zoonosis... understanding what the consequences of human contact with wildlife could be and then understanding what could be the next epidemic that can come out of nature," she told AFP.
Scientists take samples of all kinds of animals from the rich ecosystem of the tropical rainforest, where they have identified 61 species of mosquitoes.
"We have many questions" to try to "complete the history of the transmission cycle" of viruses, said UNAM biologist Maria Jose Tolsa, who after a decade of research finally feels that the importance of her work is recognized.
"A pandemic has serious consequences for health and the economy," she said.
- High-risk zone -
The area was chosen for the research because rapid deforestation has made it "a highly emblematic region in terms of zoonosis emergency risks," said Benjamin Roche, a specialist in ecology and evolutionary biology at the IRD.
It is estimated that between 500,000 and 800,000 viruses could affect humans, he added.
The risks grow with the expansion of agriculture and tourism, which increase contact between animals and humans, according to researchers.
Thousands of trees have been felled in the Yucatan Peninsula to build President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador's flagship tourist rail project, the Mayan Train, scheduled to start operating in December.
The government says that it is offsetting the loss with a tree-planting program and the creation of the second-largest tropical rainforest reserve in the world after the Amazon.
The key is to achieve a balance between humans and nature, Arnal said.
"The population have to live, eat and develop their economy," she added.
The research is being carried out in 12 communities across the three states that make up the Yucatan Peninsula.
"In birds we've found species that have been identified as reservoirs for the West Nile virus or influenza," said Rosa Elena Sarmiento, from the virology laboratory of the UNAM Veterinary School.
- 'Great revealer' -
Field work begins at dawn by placing a dozen fine nets to trap birds. At dusk it is the turn of bats and even owls.
Once caught, blood, fluid and ectoparasite samples -- if they carry them -- are taken.
Scientists identify the animal, measure it, record the data and check its condition before releasing it.
Later the material is analyzed in the laboratory.
"DNA is a great revealer," Arnal said.
"With the blood of the mosquito we can determine which species or which animal was bitten," she added.
Blood samples will also be taken from local residents to determine if they carry any virus that came from an animal.
The project also includes consultations with communities to learn about their environmental and social problems, and encourage forms of coexistence with nature.
"There has to be a knowledge dialogue with the communities," said Erika Marce Santos, a member of the Mexican Association of Conservation Medicine who liaises with residents.
The Merida laboratory is connected with others in Africa, South Asia and other Latin American countries within the framework of an initiative called Preventing Zoonotic Disease Emergence.
Launched by France in 2022, it brings together 22 countries and 200 organizations.
"What we're looking for in the Yucatan is to devise a prevention strategy against zoonoses that can serve as an example to the whole world," Roche said.
P.Martin--AMWN



