-
 Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
-
Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power

-
 Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
-
Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win

-
 What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
-
Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'

-
 England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire

-
 Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
-
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
-
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan

-
 Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
-
Man Utd made to 'suffer' for Newcastle win, says Amorim

-
 Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
-
Key NFL week has playoff spots, byes and seeds at stake

-
 Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
-
Dorgu delivers winner for depleted Man Utd against Newcastle

-
 US stocks edge lower from records as precious metals surge
US stocks edge lower from records as precious metals surge
-
Somalia denounces Israeli recognition of Somaliland

-
 The Cure guitarist and keyboard player Perry Bamonte dies aged 65
The Cure guitarist and keyboard player Perry Bamonte dies aged 65
-
Draper to miss Australian Open

-
 Police arrest suspect after man stabs 3 women in Paris metro
Police arrest suspect after man stabs 3 women in Paris metro
-
Former Montpellier coach Gasset dies at 72

-
 Trump's Christmas gospel: bombs, blessings and blame
Trump's Christmas gospel: bombs, blessings and blame
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump meeting on Ukraine plan

-
 Salah helps Egypt beat South Africa and book last-16 place
Salah helps Egypt beat South Africa and book last-16 place
-
Australia's Ikitau facing lengthy lay-off after shoulder injury

-
 Another 1,100 refugees cross into Mauritania from Mali: UN
Another 1,100 refugees cross into Mauritania from Mali: UN
-
Guardiola proud of Man City players' response to weighty issues

-
 Deadly blast hits mosque in Alawite area of Syria's Homs
Deadly blast hits mosque in Alawite area of Syria's Homs
-
The Jukebox Man on song as Redknapp records 'dream' King George win

-
 Liverpool boss Slot says Ekitike reaping rewards for greater physicality
Liverpool boss Slot says Ekitike reaping rewards for greater physicality
-
Judge jails ex-Malaysian PM Najib for 15 more years after new graft conviction

-
 Musona rescues Zimbabwe in AFCON draw with Angola
Musona rescues Zimbabwe in AFCON draw with Angola
-
Zelensky to meet Trump in Florida on Sunday

-
 'Personality' the key for Celtic boss Nancy when it comes to new signings
'Personality' the key for Celtic boss Nancy when it comes to new signings
-
Arteta eager to avoid repeat of Rice red card against Brighton

-
 Nigeria signals more strikes likely in 'joint' US operations
Nigeria signals more strikes likely in 'joint' US operations
-
Malaysia's former PM Najib convicted in 1MDB graft trial

-
 Elusive wild cat feared extinct rediscovered in Thailand
Elusive wild cat feared extinct rediscovered in Thailand
-
Japan govt approves record budget, including for defence

-
 Seoul to ease access to North Korean newspaper
Seoul to ease access to North Korean newspaper
-
History-maker Tongue wants more of the same from England attack

-
 Australia lead England by 46 after 20 wickets fall on crazy day at MCG
Australia lead England by 46 after 20 wickets fall on crazy day at MCG
-
Asia markets edge up as precious metals surge

-
 Twenty wickets fall on day one as Australia gain edge in 4th Ashes Test
Twenty wickets fall on day one as Australia gain edge in 4th Ashes Test
-
'No winner': Kosovo snap poll unlikely to end damaging deadlock


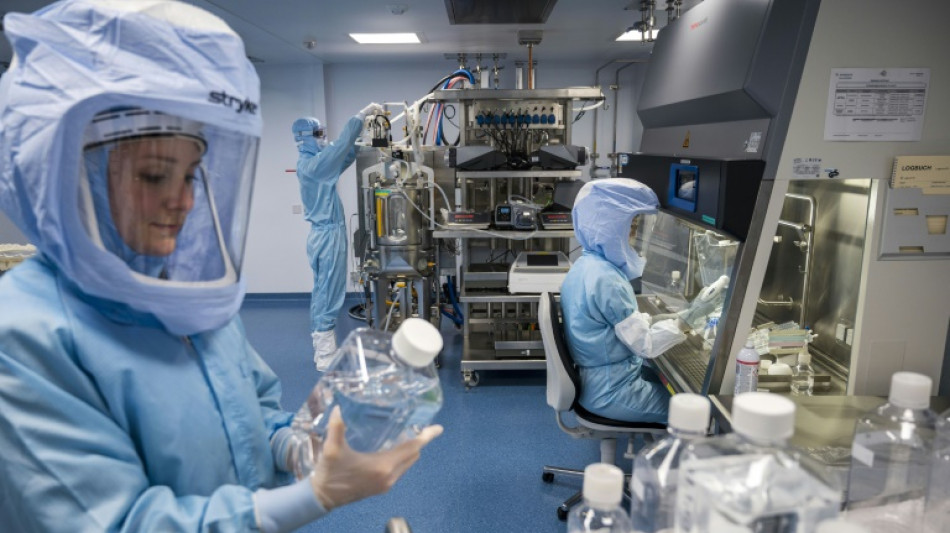
From Covid to cancer: High hopes for Nobel mRNA vaccines
The coronavirus pandemic brought global renown to the mRNA technology that underpins vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna, and on Monday earned a Nobel Prize for two scientists who have been key to its development.
Katalin Kariko of Hungary and Drew Weissman of the United States won the Nobel Medicine Prize for their work on "nucleoside base modifications that enabled the development of effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19".
These types of jabs are new but researchers have been working for decades to try to figure out how to use messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid) for other vaccinations and to treat illnesses from AIDS to cancer.
- How does it work? -
Messenger RNA's job in the body is to help deliver specific instructions from DNA to cells.
In the case of the Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna jabs, lab-generated mRNA tells human cells to create antigens -- proteins that are similar to ones found in the Covid-19 virus.
Thanks to those antigens, a person's immune system learns how to fight the virus and neutralise Covid if it enters the body.
After the cells create these proteins, the body breaks down the mRNA instructions and gets rid of them.
Such direct communication with cells is revolutionary -- classic vaccines aimed to provoke an immune response by injecting a neutralised form of a virus or antigens into the system.
- Where did this come from? -
The first big breakthrough, in the late 1970s, was in using mRNA to make test-tube cells produce proteins.
A decade later, scientists were able to get the same results in mice, but mRNA still had two major drawbacks as a medical tool.
For one thing, cells in live animals resisted synthetic mRNA, provoking a dangerous immune response.
On top of that, mRNA molecules are fragile, making them difficult to deliver to the system without altering them.
In 2005, Kariko and Weissman of Penn State University published a groundbreaking study showing that a lipid -- or fat molecule -- envelope could safely deliver mRNA without negative effects.
The research caused a buzz in the pharmaceutical community and start-ups dedicated to mRNA therapies began to pop up around the world.
- What else can mRNA do? -
Scientists have worked on developing mRNA jabs for illnesses like seasonal flu, rabies and Zika, as well as those that have remained vaccine-resistant until now, including malaria and AIDS.
Researchers have also started testing personalised treatments on cancer patients, using samples of the proteins in their tumours to create specialised mRNA.
This then triggers the immune system to target specific cancer cells.
"The mRNA platform is versatile," University of Pennsylvania biochemist Norbert Pardi told AFP. "Any protein can be encoded as mRNA so there are many potential applications."
G.Stevens--AMWN



