-
 England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire

-
 Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
-
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
-
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan

-
 Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
-
Man Utd made to 'suffer' for Newcastle win, says Amorim

-
 Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
-
Key NFL week has playoff spots, byes and seeds at stake

-
 Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
-
Dorgu delivers winner for depleted Man Utd against Newcastle

-
 US stocks edge lower from records as precious metals surge
US stocks edge lower from records as precious metals surge
-
Somalia denounces Israeli recognition of Somaliland

-
 The Cure guitarist and keyboard player Perry Bamonte dies aged 65
The Cure guitarist and keyboard player Perry Bamonte dies aged 65
-
Draper to miss Australian Open

-
 Police arrest suspect after man stabs 3 women in Paris metro
Police arrest suspect after man stabs 3 women in Paris metro
-
Former Montpellier coach Gasset dies at 72

-
 Trump's Christmas gospel: bombs, blessings and blame
Trump's Christmas gospel: bombs, blessings and blame
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump meeting on Ukraine plan

-
 Salah helps Egypt beat South Africa and book last-16 place
Salah helps Egypt beat South Africa and book last-16 place
-
Australia's Ikitau facing lengthy lay-off after shoulder injury

-
 Another 1,100 refugees cross into Mauritania from Mali: UN
Another 1,100 refugees cross into Mauritania from Mali: UN
-
Guardiola proud of Man City players' response to weighty issues

-
 Deadly blast hits mosque in Alawite area of Syria's Homs
Deadly blast hits mosque in Alawite area of Syria's Homs
-
The Jukebox Man on song as Redknapp records 'dream' King George win

-
 Liverpool boss Slot says Ekitike reaping rewards for greater physicality
Liverpool boss Slot says Ekitike reaping rewards for greater physicality
-
Judge jails ex-Malaysian PM Najib for 15 more years after new graft conviction

-
 Musona rescues Zimbabwe in AFCON draw with Angola
Musona rescues Zimbabwe in AFCON draw with Angola
-
Zelensky to meet Trump in Florida on Sunday

-
 'Personality' the key for Celtic boss Nancy when it comes to new signings
'Personality' the key for Celtic boss Nancy when it comes to new signings
-
Arteta eager to avoid repeat of Rice red card against Brighton

-
 Nigeria signals more strikes likely in 'joint' US operations
Nigeria signals more strikes likely in 'joint' US operations
-
Malaysia's former PM Najib convicted in 1MDB graft trial

-
 Elusive wild cat feared extinct rediscovered in Thailand
Elusive wild cat feared extinct rediscovered in Thailand
-
Japan govt approves record budget, including for defence

-
 Seoul to ease access to North Korean newspaper
Seoul to ease access to North Korean newspaper
-
History-maker Tongue wants more of the same from England attack

-
 Australia lead England by 46 after 20 wickets fall on crazy day at MCG
Australia lead England by 46 after 20 wickets fall on crazy day at MCG
-
Asia markets edge up as precious metals surge

-
 Twenty wickets fall on day one as Australia gain edge in 4th Ashes Test
Twenty wickets fall on day one as Australia gain edge in 4th Ashes Test
-
'No winner': Kosovo snap poll unlikely to end damaging deadlock

-
 Culture being strangled by Kosovo's political crisis
Culture being strangled by Kosovo's political crisis
-
Main contenders in Kosovo's snap election

-
 Australia all out for 152 as England take charge of 4th Ashes Test
Australia all out for 152 as England take charge of 4th Ashes Test
-
Boys recount 'torment' at hands of armed rebels in DR Congo

-
 Inside Chernobyl, Ukraine scrambles to repair radiation shield
Inside Chernobyl, Ukraine scrambles to repair radiation shield
-
Bondi victims honoured as Sydney-Hobart race sets sail


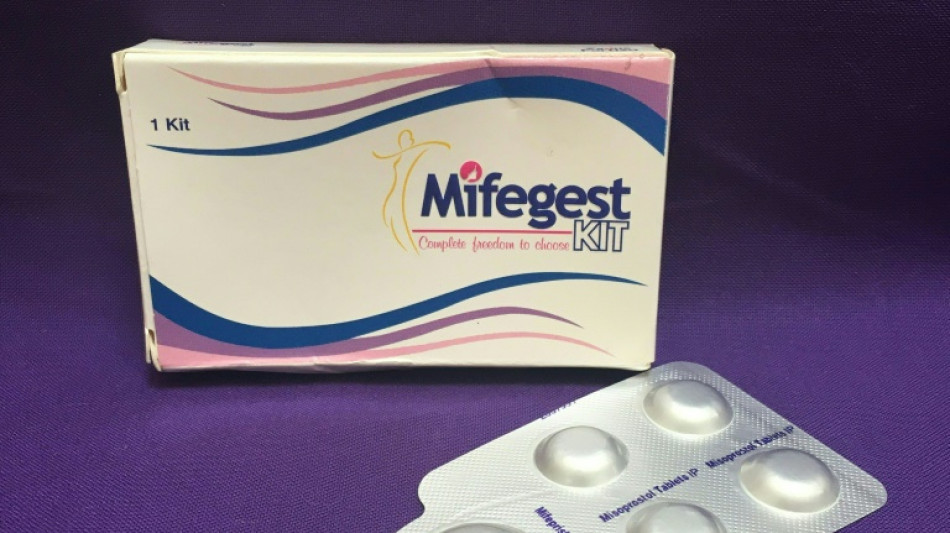
Abortion pill at the center of a US court battle
A widely used abortion pill is at the center of the latest legal battle in America's ongoing debate over abortion.
The US Supreme Court on Wednesday said that it would weigh in on restrictions imposed by a lower court on the drug mifepristone.
Here is the background on the drug and its use:
- How widespread is abortion pill use? -
According to the Guttmacher Institute, the pill accounted for more than half -- 53 percent -- of the 930,160 abortions documented by the reproductive health research and policy organization in the United States in 2020.
While the number of so-called medication abortions has gone up dramatically in the United States in recent years, it is still not as prevalent as in several European nations.
In France, for example, medication abortions represented 70 percent of the total number of abortions in 2020.
- How does it work? -
The abortion pill is different from the "morning after" pill, which is taken by a woman after sexual intercourse to prevent becoming pregnant.
The abortion pill is taken to induce an abortion once a woman confirms that she is pregnant.
The process in fact involves more than one pill. The first, mifepristone, also known as RU 486, stops a pregnancy from proceeding normally by blocking production of the hormone progesterone.
Another drug, misoprostol, is taken up to 48 hours later and causes cramps, bleeding and the emptying of the uterus.
Abortion pills can be used at home and a medical setting is not required.
- When was the abortion pill approved? -
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave the green light to mifepristone and misoprostol in 2000 for use up to seven weeks of pregnancy.
It was later approved for use up to 10 weeks of pregnancy, after which a woman would need to undergo an abortion through other means, such as vacuum aspiration.
The average cost of a medication abortion at Planned Parenthood is $580 but it can cost up to $800.
- Is it safe and effective? -
Use of the abortion pill during the specified time period is considered to be safe and effective by medical experts.
Pregnancies are successfully terminated in more than 95 percent of cases where the pill is used, according to studies.
Serious complications -- excessive bleeding, fever, infection or allergic reaction -- which require a medical consult, are rare.
The abortion pill does not work for ectopic pregnancies, which account for around two percent of all pregnancies and occur when a fertilized egg grows outside the uterus.
- Where is the pill available? -
Around 20 US states have banned or severely restricted access to abortions, including medication abortions, since the Supreme Court's ruling in June 2022 overturning the constitutional right to the procedure.
But anti-abortion groups are seeking to restrict access to mifepristone nationwide, including in states where abortion has remained legal.
The case before the Supreme Court concerns limiting the use of mifepristone to the first seven weeks of pregnancy, instead of 10, and blocking it from being distributed by mail.
O.Johnson--AMWN



