-
 Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
-
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong

-
 Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
-
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz

-
 Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
-
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend

-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Best Gold Investment Companies in USA Announced (Augusta Precious Metals, Lear Capital, Robinhood IRA and More Ranked)
Best Gold Investment Companies in USA Announced (Augusta Precious Metals, Lear Capital, Robinhood IRA and More Ranked)
-
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup

-
 World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed

-
 Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
-
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice

-
 UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder

-
 Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
-
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
-
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest

-
 NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
-
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak

-
 Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
-
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos

-
 Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
-
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
 Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
-
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030

-
 Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes
-
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports

-
 Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'
-
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says

-
 Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce
-
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl

-
 World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time

-
 Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies
-
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP

-
 'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears
-
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists

-
 No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure
-
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa

-
 World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains
-
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82

-
 Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio
-
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood

-
 Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack
-
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch


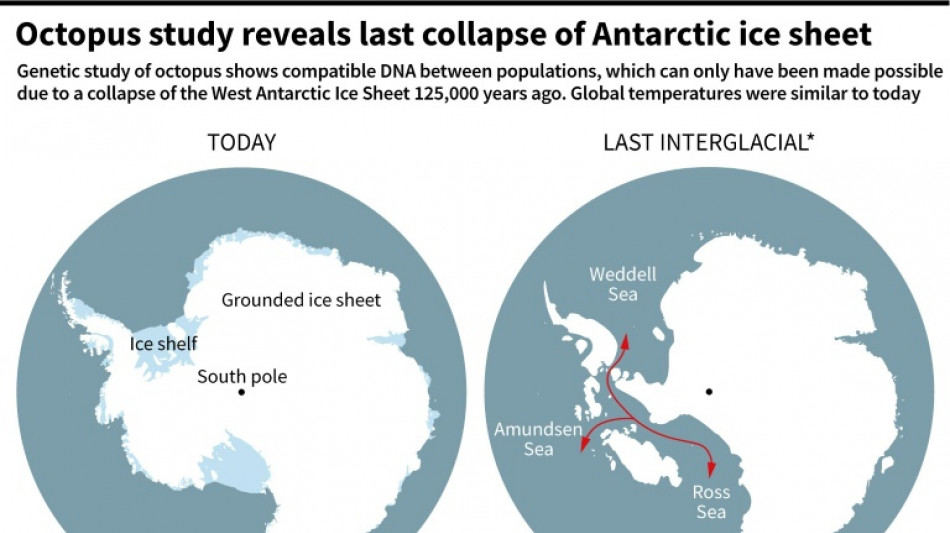
Antarctic octopus DNA reveals ice sheet collapse closer than thought
Scientists investigating how Antarctica's ice sheets retreated in the deep past have turned to an innovative approach: studying the genes of octopuses that live in its chilly waters.
A new analysis published Thursday in Science finds that geographically-isolated populations of the eight-limbed sea creatures mated freely around 125,000 years ago, signaling an ice-free corridor during a period when global temperatures were similar to today.
The findings suggest the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is closer to collapse than previously thought, threatening 3.3-5 meters of long term sea level rise if the world is unable to hold human-caused warming to the 1.5 degrees Celsius target of the Paris Agreement, said the authors.
Lead author Sally Lau of James Cook University in Australia told AFP that as an evolutionary biologist focused on marine invertebrates, "I understand and then apply DNA and biology as a proxy of changes to Antarctica in the past."
Turquet's octopus made an ideal candidate for studying WAIS, she said, because the species is found all around the continent and fundamental information about it has already been answered by science, such as its 12-year-lifespan, and the fact it emerged some four million years ago.
About half-a-foot (15 centimeters) long excluding the arms and weighing around 1.3 pounds (600 grams), they lay relatively few, but large eggs on the bottom of the seafloor. This means parents must put significant effort into ensuring their offspring hatch -- a lifestyle that prevents them traveling too far away.
They are also limited by circular sea currents, or gyres, in some of their modern habitats.
- 'Tipping point close' -
By sequencing the DNA across genomes of 96 samples that were generally collected inadvertently as fishing bycatch and then left in museum storage over the course of 33 years, Lau and colleagues found evidence of trans-West Antarctic seaways that once connected the Weddell, Amundsen and Ross seas.
The history of genetic mixing indicated WAIS collapsed at two separate points -- first in the mid-Pliocene, 3-3.5 million years ago, which scientists were already confident about, and the last time in a period called the Last Interglacial, a warm spell from 129,000 to 116,000 years ago.
"This was the last time the planet was around 1.5 degrees warmer than pre-industrial levels," said Lau. Human activity, primarily burning fossil fuels, has so far raised global temperatures by 1.2C compared to the late 1700s.
There were a handful of studies prior to the new Science paper that also suggested WAIS collapsed some time in the past, but they were far from conclusive because of the comparatively lower resolution genetic and geological data.
"This study provides empirical evidence indicating that the WAIS collapsed when the global mean temperature was similar to that of today, suggesting that the tipping point of future WAIS collapse is close," the authors wrote.
Sea level rise of 3.3 meters would drastically alter the world map as we know it, submerging low-lying coastal areas everywhere.
Writing in an accompanying commentary piece, Andrea Dutton of the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Robert DeConto of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst described the new research as "pioneering," adding it posed intriguing questions about whether ancient history will be repeated.
They flagged however that several key questions remained unanswered -- such as whether the past ice sheet collapse was caused by rising temperatures alone, or whether other variables like changing ocean currents and complex interactions between ice and solid Earth were also at play.
It's also not clear whether the sea level rise would be drawn out over millennia or occur in more rapid jumps.
But uncertainties such as these can't be an excuse for inaction against climate change "and this latest piece of evidence from octopus DNA stacks one more card on an already unstable house of cards," they wrote.
A.Rodriguezv--AMWN

