-
 The Jukebox Man on song as Redknapp records 'dream' King George win
The Jukebox Man on song as Redknapp records 'dream' King George win
-
Liverpool boss Slot says Ekitike reaping rewards for greater physicality

-
 Judge jails ex-Malaysian PM Najib for 15 more years after new graft conviction
Judge jails ex-Malaysian PM Najib for 15 more years after new graft conviction
-
Musona rescues Zimbabwe in AFCON draw with Angola

-
 Zelensky to meet Trump in Florida on Sunday
Zelensky to meet Trump in Florida on Sunday
-
'Personality' the key for Celtic boss Nancy when it comes to new signings

-
 Arteta eager to avoid repeat of Rice red card against Brighton
Arteta eager to avoid repeat of Rice red card against Brighton
-
Nigeria signals more strikes likely in 'joint' US operations

-
 Malaysia's former PM Najib convicted in 1MDB graft trial
Malaysia's former PM Najib convicted in 1MDB graft trial
-
Elusive wild cat feared extinct rediscovered in Thailand

-
 Japan govt approves record budget, including for defence
Japan govt approves record budget, including for defence
-
Seoul to ease access to North Korean newspaper

-
 History-maker Tongue wants more of the same from England attack
History-maker Tongue wants more of the same from England attack
-
Australia lead England by 46 after 20 wickets fall on crazy day at MCG

-
 Asia markets edge up as precious metals surge
Asia markets edge up as precious metals surge
-
Twenty wickets fall on day one as Australia gain edge in 4th Ashes Test

-
 'No winner': Kosovo snap poll unlikely to end damaging deadlock
'No winner': Kosovo snap poll unlikely to end damaging deadlock
-
Culture being strangled by Kosovo's political crisis

-
 Main contenders in Kosovo's snap election
Main contenders in Kosovo's snap election
-
Australia all out for 152 as England take charge of 4th Ashes Test

-
 Boys recount 'torment' at hands of armed rebels in DR Congo
Boys recount 'torment' at hands of armed rebels in DR Congo
-
Inside Chernobyl, Ukraine scrambles to repair radiation shield

-
 Bondi victims honoured as Sydney-Hobart race sets sail
Bondi victims honoured as Sydney-Hobart race sets sail
-
North Korea's Kim orders factories to make more missiles in 2026

-
 Palladino's Atalanta on the up as Serie A leaders Inter visit
Palladino's Atalanta on the up as Serie A leaders Inter visit
-
Hooked on the claw: how crane games conquered Japan's arcades

-
 Shanghai's elderly waltz back to the past at lunchtime dance halls
Shanghai's elderly waltz back to the past at lunchtime dance halls
-
Japan govt approves record 122 trillion yen budget

-
 US launches Christmas Day strikes on IS targets in Nigeria
US launches Christmas Day strikes on IS targets in Nigeria
-
Australia reeling on 72-4 at lunch as England strike in 4th Ashes Test

-
 Too hot to handle? Searing heat looming over 2026 World Cup
Too hot to handle? Searing heat looming over 2026 World Cup
-
Packers clinch NFL playoff spot as Lions lose to Vikings

-
 Guinea's presidential candidates hold final rallies before Sunday's vote
Guinea's presidential candidates hold final rallies before Sunday's vote
-
Calvin B. Taylor Bankshares, Inc. Reports Third Quarter Financial Results and Announces New Stock Repurchase Program

-
 Processa Pharmaceuticals and 60 Degrees Pharmaceuticals Interviews to Air on the RedChip Small Stocks, Big Money(TM) Show on Bloomberg TV
Processa Pharmaceuticals and 60 Degrees Pharmaceuticals Interviews to Air on the RedChip Small Stocks, Big Money(TM) Show on Bloomberg TV
-
Aptevo Therapeutics Announces 1-for-18 Reverse Stock Split

-
 Loar Holdings Inc. Announced The Completion of its Acquisition of LMB Fans & Motors
Loar Holdings Inc. Announced The Completion of its Acquisition of LMB Fans & Motors
-
IRS Can Freeze Installment Agreements After Missed Filings - Clear Start Tax Explains Why Compliance Comes First

-
 How the Terms of SMX's $111 Million Capital Facility Shape the Valuation Discussion
How the Terms of SMX's $111 Million Capital Facility Shape the Valuation Discussion
-
A Christmas Message to the DEA's Diversion Anti Marijuana Cabal

-
 QAT Community Sets QuantumTrade 5.0 for Public Beta Testing in March 2026
QAT Community Sets QuantumTrade 5.0 for Public Beta Testing in March 2026
-
BondwithPet Expands B2B Offering with Custom Pet Memorial Product

-
 Best Crypto IRA Companies (Rankings Released)
Best Crypto IRA Companies (Rankings Released)
-
Eon Prime Intelligent Alliance Office Unveils New Brand Identity and Completes Website Upgrade

-
 Villa face Chelsea test as Premier League title race heats up
Villa face Chelsea test as Premier League title race heats up
-
Spurs extend domination of NBA-best Thunder

-
 Malaysia's Najib to face verdict in mega 1MDB graft trial
Malaysia's Najib to face verdict in mega 1MDB graft trial
-
King Charles calls for 'reconciliation' in Christmas speech

-
 Brazil's jailed ex-president Bolsonaro undergoes 'successful' surgery
Brazil's jailed ex-president Bolsonaro undergoes 'successful' surgery
-
UK tech campaigner sues Trump administration over US sanctions


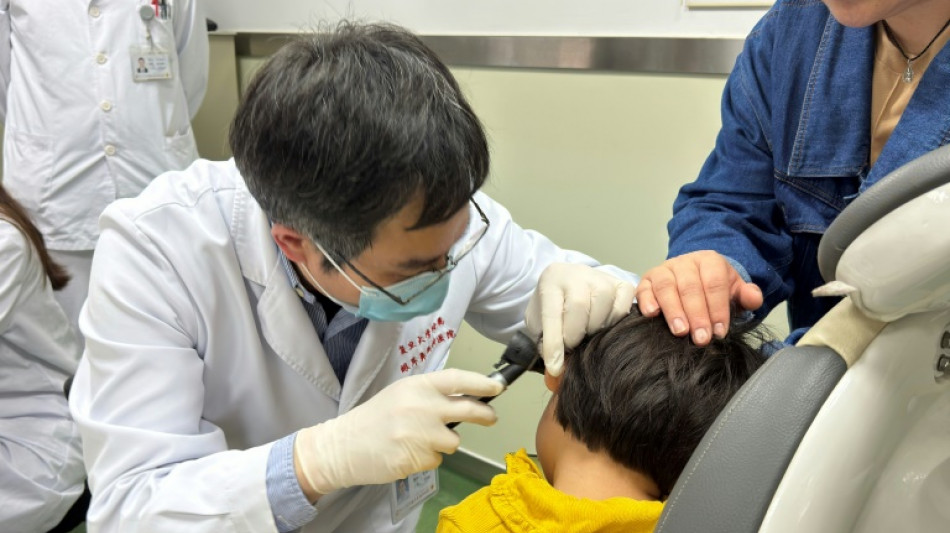
'Whole family cried': New gene therapy offers hope for deaf kids
Zhu Yangyang babbles away like a typical happy three-year-old, calling out for "mama" and "papa" and accurately naming colors -- a remarkable achievement considering he was completely deaf just months ago.
He is one of five children whose hearing was restored through a revolutionary new gene therapy in a clinical trial led by Chinese and American researchers, offering new hope for those born with a rare genetic mutation.
Yangyang's mother Chang Yiyi says she was moved to tears when she realized, around three weeks after the treatment last September, that Yangyang could hear her knocking on the door.
"I hid in a closet and called for him, and he still responded!" she told AFP in an interview from Shanghai.
The results of the study, published Wednesday in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine, mark the first time the procedure was performed on both ears. This led to significant improvements in speech perception and the ability to locate the source of sounds compared to treatment in just one ear.
"This is absolutely a turning point," Zheng-Yi Chen, the study's senior author at the Eaton-Peabody Laboratories at Mass Eye and Ear, told AFP, adding companies are now conducting clinical trials, including two in Boston, with the goal of moving towards regulatory approval.
"If the results hold, without any complications, I think in three to five years, it may be a medically approved product," he added.
- Rare mutation -
There are around 26 million people globally with genetic forms of deafness, with this particular therapy focusing on people born with a mutation of the OTOF gene -- roughly two to eight percent of inherited deafness cases.
This defect means they are unable to produce the protein otoferlin, which is needed for hair cells in the inner ear to convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be sent to the brain.
The treatment involves injecting a modified virus into the inner ear that smuggles in a working version of the OTOF gene, restoring hearing.
When they realized that Yangyang could hear for the first time, "the whole family cried" including Yangyang's mother and grandmother, said lead study author Yilai Shu of the Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University in Shanghai.
Chang, a 26-year-old homemaker, said that taking care of her son has become much easier since he began developing language skills, and the family soon hopes to move him from a speech rehabilitation school to traditional kindergarten.
- More genetic targets -
Shu led the research team that delivered the very first OTOF gene therapy in 2022, pioneering a treatment that has since been administered to more children around the world, including in the United States and the United Kingdom.
Treating both ears presented new challenges, he told AFP. Doubling the surgical procedures increased the risk of side effects.
However, careful dosing minimized the immune response, and only mild to moderate side effects -- like fever, vomiting and slightly elevated white cell counts -- were observed.
All five children, who ranged in age from one to 11, saw major improvements.
Two of them gained an ability to appreciate music -- a more complex acoustic signal -- and danced happily in videos recorded for the study.
Surprisingly, even the 11-year-old has gained some capacity to understand speech and talk, even though it was expected it would be too late for the brain to acquire this ability if it had never before perceived sound.
"That really shows our brain has a plasticity that maybe lasts much longer than we originally thought," said Chen. The clinical trial is ongoing, and the participants will be monitored for long-term follow up.
Meanwhile, Shu and Chen said they are working on further animal testing to develop treatments for other causes of genetic deafness, including those related to the GJB2 gene -- the most common cause of deafness present at birth.
F.Bennett--AMWN


