-
 Real Madrid keep pressure on Barca with tight win at Valencia
Real Madrid keep pressure on Barca with tight win at Valencia
-
PSG trounce Marseille to move back top of Ligue 1

-
 Hong Kong to sentence media mogul Jimmy Lai in national security trial
Hong Kong to sentence media mogul Jimmy Lai in national security trial
-
Lillard will try to match record with third NBA 3-Point title

-
 Vonn breaks leg as crashes out in brutal end to Olympic dream
Vonn breaks leg as crashes out in brutal end to Olympic dream
-
Malinin enters the fray as Japan lead USA in Olympics team skating

-
 Thailand's Anutin readies for coalition talks after election win
Thailand's Anutin readies for coalition talks after election win
-
Fans arrive for Patriots-Seahawks Super Bowl as politics swirl

-
 'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ
'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ
-
Japan close gap on USA in Winter Olympics team skating event

-
 Liverpool improvement not reflected in results, says Slot
Liverpool improvement not reflected in results, says Slot
-
Japan PM Takaichi basks in election triumph

-
 Machado's close ally released in Venezuela
Machado's close ally released in Venezuela
-
Dimarco helps Inter to eight-point lead in Serie A

-
 Man City 'needed' to beat Liverpool to keep title race alive: Silva
Man City 'needed' to beat Liverpool to keep title race alive: Silva
-
Czech snowboarder Maderova lands shock Olympic parallel giant slalom win

-
 Man City fight back to end Anfield hoodoo and reel in Arsenal
Man City fight back to end Anfield hoodoo and reel in Arsenal
-
Diaz treble helps Bayern crush Hoffenheim and go six clear

-
 US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
-
Israeli president to honour Bondi Beach attack victims on Australia visit

-
 Apologetic Turkish center Sengun replaces Shai as NBA All-Star
Apologetic Turkish center Sengun replaces Shai as NBA All-Star
-
Romania, Argentina leaders invited to Trump 'Board of Peace' meeting

-
 Kamindu heroics steer Sri Lanka past Ireland in T20 World Cup
Kamindu heroics steer Sri Lanka past Ireland in T20 World Cup
-
Age just a number for veteran Olympic snowboard champion Karl

-
 England's Feyi-Waboso out of Scotland Six Nations clash
England's Feyi-Waboso out of Scotland Six Nations clash
-
Thailand's pilot PM lands runaway election win

-
 Sarr strikes as Palace end winless run at Brighton
Sarr strikes as Palace end winless run at Brighton
-
Olympic star Ledecka says athletes ignored in debate over future of snowboard event

-
 Auger-Aliassime retains Montpellier Open crown
Auger-Aliassime retains Montpellier Open crown
-
Lindsey Vonn, skiing's iron lady whose Olympic dream ended in tears

-
 Conservative Thai PM claims election victory
Conservative Thai PM claims election victory
-
Kamindu fireworks rescue Sri Lanka to 163-6 against Ireland

-
 UK PM's top aide quits in scandal over Mandelson links to Epstein
UK PM's top aide quits in scandal over Mandelson links to Epstein
-
Reed continues Gulf romp with victory in Qatar

-
 Conservative Thai PM heading for election victory: projections
Conservative Thai PM heading for election victory: projections
-
Heartache for Olympic downhill champion Johnson after Vonn's crash

-
 Takaichi on course for landslide win in Japan election
Takaichi on course for landslide win in Japan election
-
Wales coach Tandy will avoid 'knee-jerk' reaction to crushing England loss

-
 Sanae Takaichi, Japan's triumphant first woman PM
Sanae Takaichi, Japan's triumphant first woman PM
-
England avoid seismic shock by beating Nepal in last-ball thriller

-
 Karl defends Olympic men's parallel giant slalom crown
Karl defends Olympic men's parallel giant slalom crown
-
Colour and caution as banned kite-flying festival returns to Pakistan

-
 England cling on to beat Nepal in last-ball thriller
England cling on to beat Nepal in last-ball thriller
-
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy

-
 England's Arundell eager to learn from Springbok star Kolbe
England's Arundell eager to learn from Springbok star Kolbe
-
Czech snowboard great Ledecka fails in bid for third straight Olympic gold

-
 Expectation, then stunned silence as Vonn crashes out of Olympics
Expectation, then stunned silence as Vonn crashes out of Olympics
-
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off

-
 Breezy Johnson wins Olympic downhill gold, Vonn crashes out
Breezy Johnson wins Olympic downhill gold, Vonn crashes out
-
Vonn's Olympic dream cut short by downhill crash


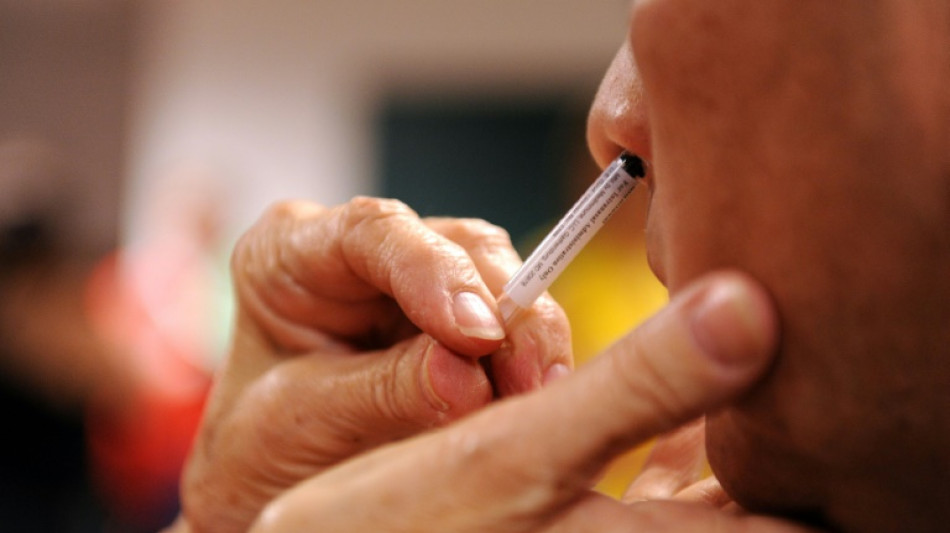
High hopes for nasal Covid vaccines despite 'disappointing' trial
Nasal vaccines could still be a powerful future weapon in the fight against Covid-19 despite "disappointing" recent trial results for an AstraZeneca spray, experts say.
By entering the body the same way as the virus, nasal vaccines aim to build immunity in the mucous membrane that lines the nose and mouth.
This could block people from getting infected in the first place -- and also potentially hamper those who have Covid from spreading it further.
That would represent a huge boost compared to traditional shots in the arm, which have proved very effective at preventing severe Covid but perform far less well when it comes to stopping transmission.
Last month China became the first country to approve a needle-free Covid vaccine, an aerosolised mist inhaled through the nose and mouth using a nebuliser device, while India greenlit a homegrown nasal drop vaccine days later.
With some wondering when Western nations would catch up, last week Oxford researchers revealed the results of a phase 1 trial for a simple nasal spray using the AstraZeneca vaccine.
However, the vaccine promoted mucosal antibodies only in a minority of the participants, and the immune responses were weaker compared to those from traditional vaccines, according to a study published in the journal eBioMedicine.
- Don't be 'too downhearted' -
"The nasal spray did not perform as well in this study as we had hoped," said the trial's chief investigator, Sandy Douglas of Oxford University.
"This was quite different from recent data from China, which has suggested good results can be achieved by delivery of a similar vaccine deep into the lungs with a more complex nebuliser device," Douglas said in a statement.
"One possibility is simply that the majority of the nasal spray vaccine ends up being swallowed and destroyed in the stomach -- delivery to the lungs could avoid that."
Connor Bamford, a virologist at Queen's University Belfast, told AFP that it was important to "not be too downhearted" about the AstraZeneca results.
He said that working out exactly why the nasal spray fell short could help researchers discover how to make a future version more effective.
Unlike AstraZeneca, successful nasal vaccines used for other diseases such as polio, rotavirus and influenza are all live vaccines, which means they replicate inside the nose, Bamford said, potentially pointing a way forwards for researchers.
Eric Tartour, an immunologist at the European Hospital Georges Pompidou in Paris, said that while the AstraZeneca results "are indeed disappointing", he did not think the news "dampens hope for nasal vaccines".
It was "reassuring" that the AstraZeneca, Chinese and Indian nasal vaccines have not shown any serious side effects, he added.
Around 100 different intranasal Covid vaccines are under development worldwide, according to analysis by health data firm Airfinity and Nature last month, with some 20 being tested on humans.
Russia and Iran have also approved nasal vaccines. However, like China and India, they have not published trial data showing that their vaccines stop transmission in a peer-reviewed journal.
And with falling inoculation rates worldwide leading some countries to destroy millions of expired doses, the demand for a new Covid vaccine remains unclear.
- 'Wake up and lead' -
For example, in 2020 France's Pasteur Institute and biotech firm TheraVectys developed a nasal vaccine candidate that was found to block transmission and produce antibodies for different variants in tests on animals, according to chief scientific officer Pierre Charneau.
However, the vaccine has not "aroused enough interest from funding agencies or 'Big Pharma' to hold trials on humans," so the firm has turned its focus back towards cancer vaccines, Charneau said.
US biotech firm Meissa Vaccines has developed a nasal vaccine shown to produce an immune response in phase 1 trials on humans, said its chief scientific officer Martin Moore.
So how long could it take for such a nasal vaccine to be made available to the public? It depends, Moore said.
He called for the world to put similar resources into creating a nasal vaccine as it did into the first round of Covid jabs, which were developed and deployed en masse in less than a year -- the fastest rate in history.
"If there was a Warp Speed 2.0, and there should be, our vaccine could be available to the public with a similar timeline," Moore said.
"Reducing transmission is the best way to gain control over the virus," Moore said. "The challenge is proving that a nasal vaccine can actually do this," he added.
"The upside to our health and economies is enormous. Western countries need to wake up and lead."
P.Martin--AMWN


