-
 Benfica investigate video of fans' monkey gestures
Benfica investigate video of fans' monkey gestures
-
French minister pledges tight security at rally for killed activist

-
 Guardiola 'couldn't care less' about Arsenal stumble in title race
Guardiola 'couldn't care less' about Arsenal stumble in title race
-
UK police search property as royals reel from Andrew's arrest

-
 Germany's Merz to visit China next week
Germany's Merz to visit China next week
-
Kompany says Mourinho made 'huge mistake' in Vinicius racism row

-
 X appeals EU's 120-mn-euro fine over digital content violations
X appeals EU's 120-mn-euro fine over digital content violations
-
Galthie recalls hulking locks Flament, Meafou for Italy

-
 Turkey, Saudi sign major solar power deal
Turkey, Saudi sign major solar power deal
-
US Olympic freeskier Hess embraces 'loser' tag after Trump blast

-
 European stocks rebound, oil prices ease after US-Iran volatility
European stocks rebound, oil prices ease after US-Iran volatility
-
'Alpha male' AI world shuts out women: computing prof Hall

-
 New Zealand freestyle skier Ives in hard Olympic crash
New Zealand freestyle skier Ives in hard Olympic crash
-
New Zealand must adapt quickly to Sri Lanka wickets: Chapman

-
 Thai activist's jail term for royal insult extended to 30 years
Thai activist's jail term for royal insult extended to 30 years
-
Families of Duterte's drug war victims eye Hague hearing with hope

-
 India chases 'DeepSeek moment' with homegrown AI
India chases 'DeepSeek moment' with homegrown AI
-
UN touts panel for 'human control' of AI at global summit

-
 Ukraine Paralympics team to boycott Opening Ceremony over Russian flag decision: statement
Ukraine Paralympics team to boycott Opening Ceremony over Russian flag decision: statement
-
UK monarchy reels from Andrew's stunning arrest

-
 Somaliland, where Muslims love Israel
Somaliland, where Muslims love Israel
-
Florida airport to be renamed after US President Donald Trump

-
 Fans flock to Japan zoo to see viral baby monkey Punch
Fans flock to Japan zoo to see viral baby monkey Punch
-
Stocks mixed, oil rises after Trump Iran threat

-
 Outspoken Laos lawmaker's election exit sparks rare dissent
Outspoken Laos lawmaker's election exit sparks rare dissent
-
Kim Jong Un vows to boost living standards as he opens rare congress

-
 Shepherd hat-trick to Samra ton: Five top T20 World Cup performances so far
Shepherd hat-trick to Samra ton: Five top T20 World Cup performances so far
-
Zimbabwe surprise as T20 World Cup Super Eights begin without Australia

-
 Victorious Takaichi promises 'strong and prosperous' Japan
Victorious Takaichi promises 'strong and prosperous' Japan
-
Ex-South Korea leader apologises for martial law crisis

-
 Ex-S. Korea leader apologises for martial law crisis
Ex-S. Korea leader apologises for martial law crisis
-
Messi kicks off MLS season in key World Cup year

-
 Teen burnout to Olympic gold: Alysa Liu 'looking to inspire others'
Teen burnout to Olympic gold: Alysa Liu 'looking to inspire others'
-
Cunningham stars as NBA-leading Pistons ease past Knicks

-
 Andre Gomes joins MLS side Columbus Crew
Andre Gomes joins MLS side Columbus Crew
-
Scottish inconsistency 'bugs everyone' says former international Beattie

-
 England turn to Pollock for Six Nations boost against Ireland
England turn to Pollock for Six Nations boost against Ireland
-
Arsenal aim to banish title jitters in Spurs showdown

-
 Scrutiny on Flick rises as Barca seek recovery
Scrutiny on Flick rises as Barca seek recovery
-
Leipzig host red-hot Dortmund with Champions League hopes slipping away

-
 Nvidia nears deal for scaled-down investment in OpenAI: report
Nvidia nears deal for scaled-down investment in OpenAI: report
-
Japan inflation eases in welcome news for PM Takaichi

-
 McIlroy shares Riviera clubhouse lead as Rai charges, Scheffler fades
McIlroy shares Riviera clubhouse lead as Rai charges, Scheffler fades
-
Philippines' Duterte earned global infamy, praise at home

-
 Stocks drop, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
Stocks drop, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
-
As European heads roll from Epstein links, US fallout muted

-
 Families of Duterte's drug war victims eye Hague hearing hopefully
Families of Duterte's drug war victims eye Hague hearing hopefully
-
Russian decision is a betrayal: Ukrainian Paralympics chief

-
 Venezuela parliament unanimously approves amnesty law
Venezuela parliament unanimously approves amnesty law
-
Martinez missing as Inter limp to Lecce after Bodo/Glimt humbling


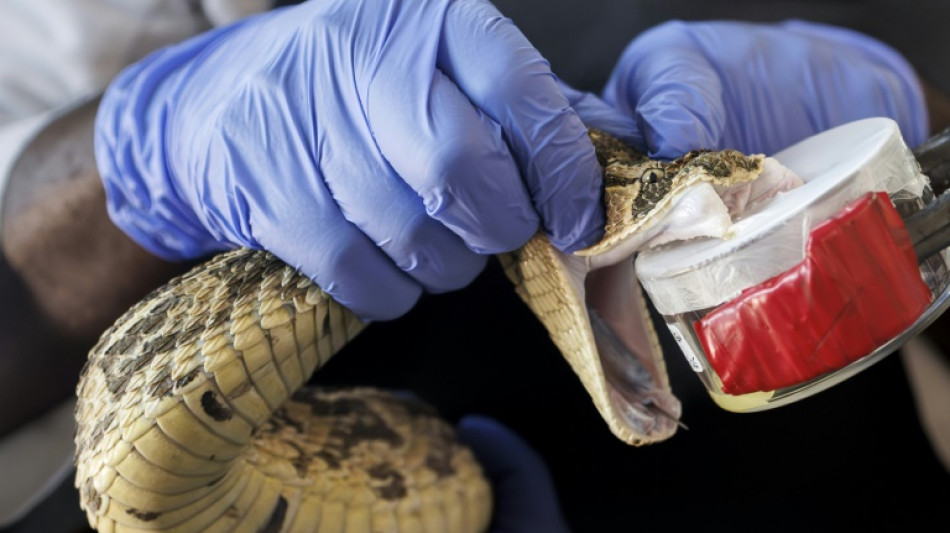
Kenya's desperate need for more snake antivenom
Writhing in pain on a hospital bed in a Kenyan coastal town, teenage snakebite victim Shukurani Konde Tuva faced the grim reality of his left leg from above the knee being amputated.
The 14-year-old was bitten by a puff adder -- a venomous snake and the most common snakebite in sub-Saharan Africa -- while eating outdoors in his village near the town of Malindi more than a month ago.
His family rushed him to hospital two hours away by motorbike, but the antivenom he received did not help.
"My son's leg is totally rotten and maggots are even emanating from it. They'll have to cut it," said his distraught mother, Mariamu Kenga Kalume.
Some 5.4 million people are bitten by snakes each year globally and roughly half are poisoned by venom, according to World Health Organization (WHO) data.
Up to 138,000 people die and 400,000 suffer permanent physical effects, though the WHO says the numbers are a "gross underestimation" since an estimated 70 percent of cases go unreported.
Traditional beliefs and myths skew the data as some victims turn to home-grown remedies or attribute bites to voodoo "sent by their enemies" instead of seeking medical care.
- 'Snake stone' -
A few kilometres (miles) from where Shukurani lay in pain, traditional healer Douglas Rama Bajila showed AFP the concoctions he uses to "suck out" venom.
One popular remedy is the "snake stone", made from a cow's bone and sold for about $1.
Bajila said it can be reused multiple times: it simply needs to be soaked in milk for a few hours to "recharge".
One was placed on Shukurani's leg as he was transported to hospital but unfortunately fell off along the way, his mother said.
Experts worry that by using traditional snakebite remedies, patients are losing precious time but they are popular because antivenom treatments are expensive.
Antivenoms cost up to 8,000 shillings (about $62) per vial, and some patients require as many as 20 doses.
Ruth Kintalel, 30, from a pastoralist community in Kajiado county near the capital Nairobi, said she spent over five months in hospital after a red spitting cobra bit her in her sleep.
"My husband sold our livestock to cover the rising hospital bill," said Kintalel, who is still paralysed in her right arm seven years later.
- 'Bad reactions' -
Experts say Kenya receives between 10,000 and 30,000 vials of antivenom per year and needs 100,000.
Antivenom is made by "milking" venom from the fangs of snakes, which is then diluted and injected in small doses into animals such as horses, which produce antibodies that can be extracted for use in humans.
Using snakes from different regions, even of the same species, can reduce the effectiveness of the antivenom and cause "really bad reactions", said Kyle Buster Ray, a curator at the Watamu Snake Farm on the Kenyan coast.
Kenya's stock of antivenom is not always effective because much comes from other countries like India, he said.
His farm houses over 400 venomous and non-venomous snakes and seeks to re-establish faith in antivenom that has been undermined by too many shoddy treatments.
It offers free antivenom to critical cases locally, but stocks are limited.
The farm also trains communities in life-saving snakebite responses.
During a session attended by AFP, about half the community said they had been bitten at least once, and nearly all had initially turned to traditional medicines.
Many showed signs of paralysis, with one suffering partial blindness.
- 'Trauma' -
In Nairobi, the Snakebite Research and Intervention Centre within the Kenya Institute of Primate Research is working on an antivenom specific to the country and applicable to multiple species.
Valentine Musabyimana, a research fellow at the institute, said they "are aiming for an antivenom where a patient will require only one vial with great potency".
Government subsidies should make it affordable, she hopes, though it is expected to take about two years before the antivenom is available.
That is too late for 14-year-old Shukurani.
At the snake farm, Ray warned that the boy faced psychological as well as physical consequences.
"Someone has watched their limb completely rot... there's a lot of mental trauma," Ray said.
O.Norris--AMWN

