
-
 Trump threatens air traffic controllers over shutdown absences
Trump threatens air traffic controllers over shutdown absences
-
US to remove warnings from menopause hormone therapy

-
 UK water firm says 'highly likely' behind plastic pellet pollution incident
UK water firm says 'highly likely' behind plastic pellet pollution incident
-
Syria's ex-jihadist president holds historic Trump talks

-
 End to record-long US government shutdown in sight
End to record-long US government shutdown in sight
-
France's ex-leader Sarkozy says after jail release 'truth will prevail'

-
 Atalanta sack coach Juric after poor start to season
Atalanta sack coach Juric after poor start to season
-
Trump threatens $1 billion action as BBC apologises for speech edit

-
 Gattuso wants 'maximum commitment' as Italy's World Cup bid on the line
Gattuso wants 'maximum commitment' as Italy's World Cup bid on the line
-
Indian capital car blast kills at least eight

-
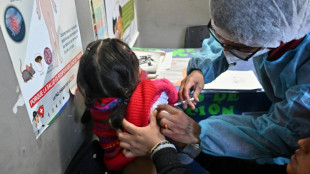 Deadly measles surge sees Canada lose eradicated status
Deadly measles surge sees Canada lose eradicated status
-
Brazil's Lula urges 'defeat' of climate deniers as COP30 opens

-
 Strangled by jihadist blockade, Malians flee their desert town
Strangled by jihadist blockade, Malians flee their desert town
-
US Supreme Court declines to hear case challenging same-sex marriage

-
 'Fired-up' Fritz sees off Musetti in ATP Finals
'Fired-up' Fritz sees off Musetti in ATP Finals
-
Injured Courtois set to miss Belgium World Cup qualifiers

-
 Bulatov, pillar of Russian contemporary art scene, dies at 92
Bulatov, pillar of Russian contemporary art scene, dies at 92
-
Fritz sees off Musetti in ATP Finals

-
 US strikes on alleged drug boats kill six more people
US strikes on alleged drug boats kill six more people
-
Sarkozy released from jail 'nightmare' pending appeal trial

-
 COP30 has a mascot: the fiery-haired guardian of Brazil's forest
COP30 has a mascot: the fiery-haired guardian of Brazil's forest
-
The Sudanese who told the world what happened in El-Fasher

-
 Three things we learned from the Sao Paulo Grand Prix
Three things we learned from the Sao Paulo Grand Prix
-
ASC acquire majority share in Atletico Madrid

-
 Ferrari boss tells Hamilton, Leclerc to drive, not talk
Ferrari boss tells Hamilton, Leclerc to drive, not talk
-
Bank of England seeks to 'build trust' in stablecoins

-
 China suspends 'special port fees' on US vessels for one year
China suspends 'special port fees' on US vessels for one year
-
French court frees ex-president Sarkozy from jail pending appeal

-
 No link between paracetamol and autism, major review finds
No link between paracetamol and autism, major review finds
-
Typhoon Fung-wong floods Philippine towns, leaves 5 dead in its wake

-
 France's Sarkozy says prison a 'nightmare' as prosecutors seek his release
France's Sarkozy says prison a 'nightmare' as prosecutors seek his release
-
Guinness maker Diageo picks new CEO after US tariffs cloud

-
 China suspends 'special port fees' on US vessels
China suspends 'special port fees' on US vessels
-
US senators take major step toward ending record shutdown

-
 Typhoon Fung-wong leaves flooded Philippine towns in its wake
Typhoon Fung-wong leaves flooded Philippine towns in its wake
-
From Club Med to Beverly Hills: Assinie, the Ivorian Riviera

-
 The 'ordinary' Arnie? Glen Powell reboots 'The Running Man'
The 'ordinary' Arnie? Glen Powell reboots 'The Running Man'
-
Typhoon exposes centuries-old shipwreck off Vietnam port

-
 French court to decide if ex-president Sarkozy can leave jail
French court to decide if ex-president Sarkozy can leave jail
-
China lifts sanctions on US units of South Korea ship giant Hanwha

-
 Japan death row inmate's sister still fighting, even after release
Japan death row inmate's sister still fighting, even after release
-
Taylor sparks Colts to Berlin win as Pats streak hits seven

-
 Dreyer, Pellegrino lift San Diego to 4-0 MLS Cup playoff win over Portland
Dreyer, Pellegrino lift San Diego to 4-0 MLS Cup playoff win over Portland
-
Indonesia names late dictator Suharto a national hero

-
 Fourth New Zealand-West Indies T20 washed out
Fourth New Zealand-West Indies T20 washed out
-
Tanzania Maasai fear VW 'greenwashing' carbon credit scheme

-
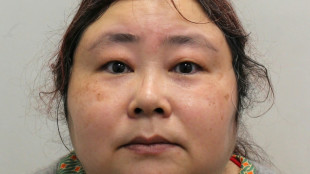 Chinese businesswoman faces jail after huge UK crypto seizure
Chinese businesswoman faces jail after huge UK crypto seizure
-
Markets boosted by hopes for deal to end US shutdown

-
 Amazon poised to host toughest climate talks in years
Amazon poised to host toughest climate talks in years
-
Ex-jihadist Syrian president due at White House for landmark talks


Heat waves cost poor countries the most, exacerbating inequality
Heat waves, intensified by climate change, have cost the global economy trillions of dollars in the last 30 years, a study published Friday found, with poor countries paying the steepest price.
And those lopsided economic effects contribute to widening inequalities around the world, according to the research.
"The cost of extreme heat from climate change so far has been disproportionately borne by the countries and regions least culpable for global warming," Dartmouth College professor Justin Mankin, one of the authors of the study published in the journal Science Advances, told AFP. "And that's an insane tragedy."
"Climate change is playing out on a landscape of economic inequality, and it is acting to amplify that inequality," he said.
Periods of extreme heat cost the global economy about $16 trillion dollars between 1992 and 2013, the study calculated.
But while the richest countries have lost about 1.5 percent of their annual per capita GDPs dealing with heat waves, poorer countries have lost about 6.7 percent of their annual per capita GDPs.
The reason for that disparity is simple: poor countries are often situated closer to the tropics, where temperatures are warmer anyway. During heat waves, they become even hotter.
The study comes just days ahead of the start of the COP27 climate summit in Egypt, where the question of compensation for countries which are disproportionately vulnerable to but least responsible for climate change is expected to be one of the key topics.
The costs of heat waves come from several factors: effects on agriculture, strains on health systems, less productive workforces and physical damage to infrastructure, such as melting roads.
- 'Cost of inaction' -
Study researchers examined five days of weather considered extreme for a specific region each year.
"The general idea is to use variation in extreme heat, which is effectively randomly assigned to all these economic regions, and see the extent to which that accounts for variation in economic growth" in a given region, Mankin explained.
"Then the second part is to say, 'ok, how has human-caused warming influenced extreme heat?'" he added.
Despite these calculations, the study results almost certainly underestimate the true cost of extreme heat, according to the paper -- only studying five days per year does not reflect the increased frequency of such heat events, and not all potential costs were included.
Previous studies on the subject had focused on the costs of heat to specific sectors, though scientists say it is important to look at the price tag of climate change wholistically.
"You want to know what those costs are, so that you have a frame of reference against which to compare the cost of action," Mankin said, such as establishing cooling centers or installing air conditioners, versus "the cost of inaction."
"The dividends economically of responding to the five hottest days of the year could be quite great," he said.
But according to Mankin, the most important response is to reduce carbon emissions to slow down global warming at the source.
"We need to adapt to the climate we have now, and we also need to deeply invest in mitigation," he said.
B.Finley--AMWN