-
 Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
-
Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest

-
 Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
-
Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win

-
 Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
-
A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
-
 US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
-
CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform

-
 Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
-
India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits

-
 McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
-
Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey

-
 'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
-
Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce

-
 As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
-
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
 Heirs Energies Agrees $750m Afreximbank Financing to Drive Long-Term Growth
Heirs Energies Agrees $750m Afreximbank Financing to Drive Long-Term Growth
-
Black Book Poll: "Governed AI" Emerges as the Deciding Factor in 2026 NHS Procurement

-
 Hemogenyx Pharmaceuticals PLC Announces Update on Admission of Shares
Hemogenyx Pharmaceuticals PLC Announces Update on Admission of Shares
-
Pantheon Resources PLC Announces Shareholder Letter and Corporate Update on Dubhe-1

-
 Tocvan Begins Trenching Material for the Pilot Mine and Pushes Ahead With Infrastructure Development
Tocvan Begins Trenching Material for the Pilot Mine and Pushes Ahead With Infrastructure Development
-
Steelers receiver Metcalf strikes Lions fan

-
 Morocco coach 'taking no risks' with Hakimi fitness
Morocco coach 'taking no risks' with Hakimi fitness
-
Gang members given hundreds-years-long sentences in El Salvador

-
 Chargers, Bills edge closer to playoff berths
Chargers, Bills edge closer to playoff berths
-
Gang members given hundred-years-long sentences in El Salvador

-
 Hosts Morocco off to winning start at Africa Cup of Nations
Hosts Morocco off to winning start at Africa Cup of Nations
-
No jacket required for Emery as Villa dream of title glory

-
 Amorim fears United captain Fernandes will be out 'a while'
Amorim fears United captain Fernandes will be out 'a while'
-
Nigerian government frees 130 kidnapped Catholic schoolchildren

-
 Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear in Bundesliga
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear in Bundesliga
-
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear

-
 Rogers stars as Villa beat Man Utd to boost title bid
Rogers stars as Villa beat Man Utd to boost title bid
-
Barca strengthen Liga lead at Villarreal, Atletico go third

-
 Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut
-
Third day of Ukraine settlement talks to begin in Miami

-
 Barcelona's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win
Barcelona's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win
-
Macron, on UAE visit, announces new French aircraft carrier

-
 Barca's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win
Barca's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win
-
Gunmen kill 9, wound 10 in South Africa bar attack

-
 Allegations of new cover-up over Epstein files
Allegations of new cover-up over Epstein files
-
Atletico go third with comfortable win at Girona

-
 Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
-
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach

-
 Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
-
Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third


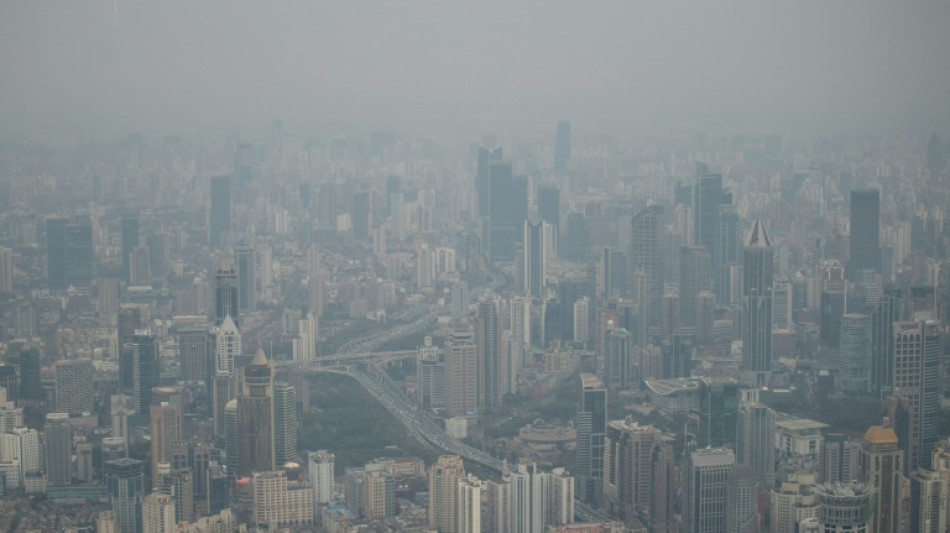
Ozone pollution linked to increased heart disease: study
Ozone air pollution is linked to a higher rate of hospitalisations for heart diseases, according to a large study released Friday, the latest warning of the health dangers posed by greenhouse gases.
While a layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere helps block harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from reaching Earth, at ground level it is a major component of the smog polluting most big cities.
Scientists have warned that a different kind of air pollution, fine particulate matter known as PM2.5, causes 8.8 million premature deaths a year, but ozone's full impact on health is still becoming clear.
Ozone is created in the atmosphere by a chemical reaction when two pollutants, often emitted by cars or industry, combine in the presence of sunlight, and has been shown to interfere with plant photosynthesis and growth.
The new study said it was the first to evaluate the risk of hospitalisation for heart disease when ozone levels rise above the World Health Organization's daily guideline of 100 microgrammes per cubic metre of air.
For the study, published in the European Heart Journal, a team of China-led researchers looked at data on hospital admissions from 2015 to 2017 in 70 Chinese cities collected for health insurance purposes.
The data covered 258 million people across 70 cities, representing roughly 18 percent of China's population.
The researchers compared the hospitalisations to air quality data tracked in real-time across the cities.
It found that -- independent of other pollutants -- ozone was associated with more than three percent of hospitalisations for coronary heart disease, heart failure and stroke.
Also, each increase of 10 microgrammes of ozone per cubic metre of air was linked to a 0.75 percent rise in hospitalisations for heart attacks, and to a 0.40 percent increase for stroke.
"Although these increments look modest," the impact would be "amplified by more than 20 times" when ozone levels soar above 200 microgrammes in the summer, study author Shaowei Wu of Xi'an Jiaotong University and his colleagues told AFP.
In this extreme example, ozone exposure would be linked to 15 percent of heart attacks and eight percent of strokes, the researchers said.
- Key for health, climate -
The researchers called for more aggressive action to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels, as well as a warning system so people could limit their exposure on high ozone days.
Because the study was observational, it was not able to directly show that ozone pollution causes heart disease.
But Chris Malley, an air pollution researcher at York University n Britain, who was not involved in the study, said it added to a growing "weight of evidence that there is a causal relationship".
In 2017, research led by Malley that estimated that ozone pollution was linked to more than one million deaths a year from respiratory disease.
"If cardiovascular disease were added to this total, then the health burden would be substantially higher than we estimated," Malley told AFP.
"Ozone is not just a threat to human health, it also has a large part to play in climate change," he added.
"Taking action to reduce ozone is therefore a key way to improve public health and combat climate change at the same time."
Th.Berger--AMWN