-
 Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
-
Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest

-
 Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
-
Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win

-
 Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
-
A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
-
 US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
-
CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform

-
 Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
-
India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits

-
 McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
-
Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey

-
 'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
-
Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce

-
 As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
-
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
 Pantheon Resources PLC Announces Shareholder Letter and Corporate Update on Dubhe-1
Pantheon Resources PLC Announces Shareholder Letter and Corporate Update on Dubhe-1
-
Tocvan Begins Trenching Material for the Pilot Mine and Pushes Ahead With Infrastructure Development

-
 Steelers receiver Metcalf strikes Lions fan
Steelers receiver Metcalf strikes Lions fan
-
Morocco coach 'taking no risks' with Hakimi fitness

-
 Gang members given hundreds-years-long sentences in El Salvador
Gang members given hundreds-years-long sentences in El Salvador
-
Chargers, Bills edge closer to playoff berths

-
 Gang members given hundred-years-long sentences in El Salvador
Gang members given hundred-years-long sentences in El Salvador
-
Hosts Morocco off to winning start at Africa Cup of Nations

-
 No jacket required for Emery as Villa dream of title glory
No jacket required for Emery as Villa dream of title glory
-
Amorim fears United captain Fernandes will be out 'a while'

-
 Nigerian government frees 130 kidnapped Catholic schoolchildren
Nigerian government frees 130 kidnapped Catholic schoolchildren
-
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear in Bundesliga

-
 Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear
-
Rogers stars as Villa beat Man Utd to boost title bid

-
 Barca strengthen Liga lead at Villarreal, Atletico go third
Barca strengthen Liga lead at Villarreal, Atletico go third
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 Third day of Ukraine settlement talks to begin in Miami
Third day of Ukraine settlement talks to begin in Miami
-
Barcelona's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win

-
 Macron, on UAE visit, announces new French aircraft carrier
Macron, on UAE visit, announces new French aircraft carrier
-
Barca's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win

-
 Gunmen kill 9, wound 10 in South Africa bar attack
Gunmen kill 9, wound 10 in South Africa bar attack
-
Allegations of new cover-up over Epstein files

-
 Atletico go third with comfortable win at Girona
Atletico go third with comfortable win at Girona
-
Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory

-
 Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
-
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third

-
 Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third
Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third
-
Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million

-
 Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation
Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation
-
Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future


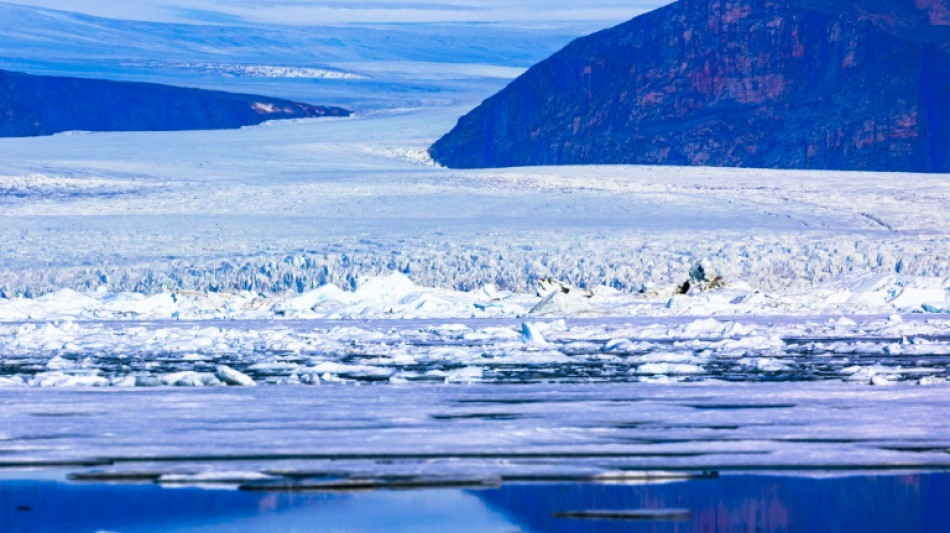
'Snowball Earth' might have been rather slushy: study
Millions of years ago, the Earth was so cold that most of its surface was covered in ice. But that hard freeze might have been slushier than once thought.
The longstanding "Snowball Earth" theory imagines our world as seen from space, a perfect sphere with ice covering land and sea alike.
It draws on clues including deposits made by glaciers near the Equator. For ice to have extended that far from the poles suggests much of our planet was once frozen.
But there has long been speculation about just how complete the cover was, with some convinced that areas of slush or open ocean remained, allowing oxygen to penetrate and creating incubators for life.
New research published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications adds weight to that theory, and suggests these oases in the tundra might have existed much further north than previously suspected.
The evidence comes from a thin layer of black shale that would have been under the sea during the Marinoan ice age, which began around 650 million years ago.
The shale in the Nantuo Formation in southern China acts as a sort of archive for the conditions in oceans at the time.
By analysing levels of elements such as iron, and the presence of nitrogen, scientists can infer whether oxygen was penetrating the ocean and nitrogen was being produced by lifeforms.
"We found evidence of ice-free conditions at mid-northern paleolatitudes (locations before continental drift)," Huyue Song, who helped lead the research, told AFP.
"Until now, ice-free areas had been identified only in peri-equatorial regions."
Instead of a "narrow ice-free belt" across the middle of the Earth, "patchy ice-free areas may have existed much more widely," added Song, a professor at the China University of Geosciences, Wuhan.
The findings build on other research at sites ranging from Australia to Brazil that suggest life was able to cling on in pockets while most of Earth was in deep freeze.
These incubators may even have helped spur "a rapid rebound of the biosphere" at the end of the ice age, the research published Tuesday argues.
The work took four years in total, and involved collecting samples at a remote site in the Shennongjia region of Hubei province, some 500 kilometres from Song's base in Wuhan.
Song believes the findings will help scientists better understand both how our planet's climate works, and how life evolved and survived on Earth through the ages.
And while Earth's ice ages might seem like ancient history, Song argues they could have useful lessons for a planet now experiencing new severe climate change.
"It provides insight into how life survived extreme climate events -- a topic that will become of increasing relevance as modern climate change intensifies," he said.
F.Pedersen--AMWN