
-
 Forest stunned by Midtjylland, Villa beat Lille in Europa League
Forest stunned by Midtjylland, Villa beat Lille in Europa League
-
Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev

-
 Iran says will make US regret war as oil prices soar
Iran says will make US regret war as oil prices soar
-
Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'

-
 NASA says 'on track' for Artemis 2 launch as soon as April 1
NASA says 'on track' for Artemis 2 launch as soon as April 1
-
Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return

-
 Italian prosecutors seek trial for Amazon over tax evasion
Italian prosecutors seek trial for Amazon over tax evasion
-
Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan

-
 Duplantis clears 6.31m to set 15th pole vault world record
Duplantis clears 6.31m to set 15th pole vault world record
-
Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking

-
 Sabalenka out-guns Mboko to reach Indian Wells semi-finals
Sabalenka out-guns Mboko to reach Indian Wells semi-finals
-
Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille

-
 'Say a prayer and send it': Paralympic alpine skiers tackle fear
'Say a prayer and send it': Paralympic alpine skiers tackle fear
-
Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations

-
 Assailant dead after ramming vehicle into Michigan synagogue
Assailant dead after ramming vehicle into Michigan synagogue
-
The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader

-
 Assailant dead after ramming car into Michigan synagogue
Assailant dead after ramming car into Michigan synagogue
-
World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert

-
 Morikawa pulls out of Players Championship with back trouble
Morikawa pulls out of Players Championship with back trouble
-
Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study

-
 In Iran, shut shops, joblessness and a dash for cash
In Iran, shut shops, joblessness and a dash for cash
-
Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse

-
 Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris
Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris
-
Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations

-
 Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise
Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise
-
Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage

-
 Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia
Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia
-
Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow

-
 Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military
Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military
-
Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead

-
 Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub
Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub
-
Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize

-
 Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'
Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'
-
Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots

-
 Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy
Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy
-
Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan

-
 IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred
IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred
-
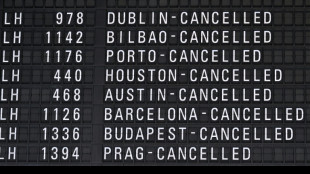
Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
-
 Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister
Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister
-
Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release

-
 Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages
Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages
-
US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary

-
 'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel
'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel
-
Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland

-
 Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack
Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack
-
WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes

-
 EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US
EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US
-
The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years

-
 'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform
'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform
-
Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute


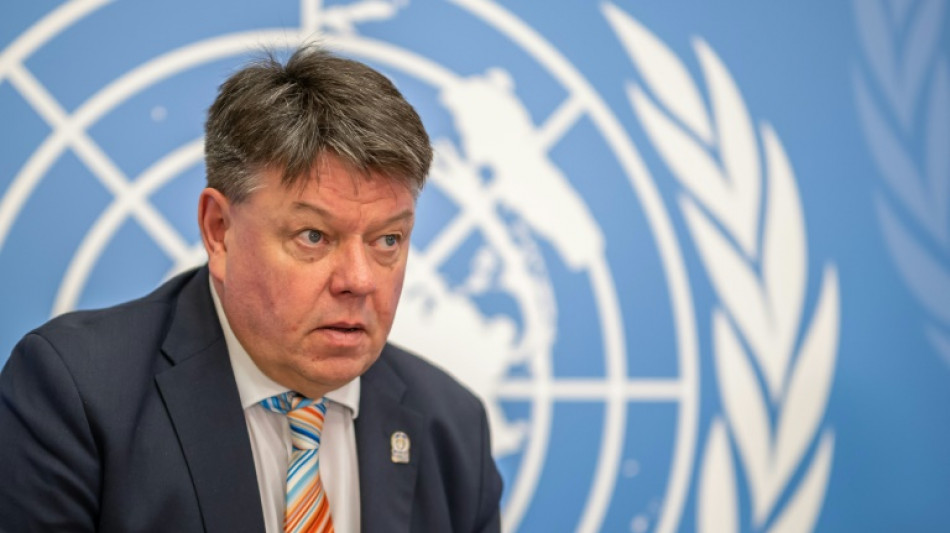
UN reports 'off the charts' melting of glaciers
The world's glaciers melted at dramatic speed last year and saving them is effectively a lost cause, the United Nations reported Friday, as climate change indicators once again hit record highs.
The last eight years have been the warmest ever recorded, while concentrations of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide hit new peaks, the UN's World Meteorological Organization said.
"Antarctic sea ice fell to its lowest extent on record and the melting of some European glaciers was, literally, off the charts," the WMO said as it launched its annual climate overview.
Sea levels are also at a record high, having risen by an average of 4.62 millimetres per year between 2013 and 2022 -- double the annual rate between 1993 and 2002.
Record high temperatures were also recorded in the oceans -- where around 90 percent of the heat trapped on Earth by greenhouse gases ends up.
The 2015 Paris Agreement saw countries agree to cap global warming at "well below" two degrees Celsius above average levels measured between 1850 and 1900 -- and 1.5C if possible.
The global mean temperature in 2022 was 1.15C above the 1850-1900 average, the WMO report said.
Record global mean temperatures over the past eight years came despite the cooling impact of a drawn-out La Nina weather phenomenon that stretched over nearly half that period.
The report said greenhouse gas concentrations reached new highs in 2021.
The concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) reached 415.7 parts per million globally, or 149 percent of the pre-industrial (1750) level, while methane reached 262 percent and nitrous oxide hit 124 percent.
Data indicate they continued to increase in 2022.
- Glacier game lost -
WMO chief Petteri Taalas told a press conference that extreme weather caused by greenhouse gas emissions "may continue until the 2060s, independent of our success in in climate mitigation"
"We have already emitted so much, especially CO2 in the atmosphere that this kind of phasing out of the negative trend takes several decades."
The world's 40-odd reference glaciers -- those for which long-term observations exist -- saw an average thickness loss of more than 1.3 metres between October 2021 and October 2022 -- a loss much larger than the average over the last decade.
The cumulative thickness loss since 1970 amounts to almost 30 metres.
In Europe, the Alps smashed records for glacier melt due to a combination of little winter snow, an intrusion of Saharan dust in March 2022 and heatwaves between May and early September.
"We have already lost the melting of the glaciers game, because we already have such a high concentration of CO2," Taalas told AFP.
In the Swiss Alps, "last summer we lost 6.2 percent of the glacier mass, which is the highest amount since records started".
"This is serious," he said, explaining that the disappearance of the glaciers would limit freshwater supplies for humans and for agriculture, and also harm transport links if rivers become less navigable, calling it "a big risk for the future".
"Many of these mountain glaciers will disappear, and also the shrinking of the Antarctic and Greenland glaciers will continue for a long-term basis -- unless we create a means to remove CO2 from the atmosphere," he said.
- Glimmers of hope -
Despite the report's bad news, Taalas said there was cause for some optimism.
The means to battle climate change were becoming more affordable, he said, with green energy becoming cheaper than fossil fuels, while the world is developing better mitigation methods.
The planet is no longer heading towards 3-5 C warming, as forecast in 2014, but was now on track for 2.5-3 C warming, he said.
"In the best case, we would still be able to reach 1.5 C warming, which would be best for the welfare of mankind, the biosphere and the global economy," the WMO secretary-general told AFP.
Taalas said 32 countries had reduced their emissions and their economies still grew.
"There is no more automatic link between economic growth and emissions growth," he said.
In stark contrast to the world leaders of 10 years ago, now "practically all of them are talking about climate change as a serious problem and countries have started acting", he said.
Ch.Havering--AMWN

