
-
 Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
-
Iran says will make US regret war as oil prices soar

-
 Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
-
NASA says 'on track' for Artemis 2 launch as soon as April 1

-
 Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
-
Italian prosecutors seek trial for Amazon over tax evasion

-
 Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
-
Duplantis clears 6.31m to set 15th pole vault world record

-
 Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
-
Sabalenka out-guns Mboko to reach Indian Wells semi-finals

-
 Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
-
'Say a prayer and send it': Paralympic alpine skiers tackle fear

-
 Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Assailant dead after ramming vehicle into Michigan synagogue

-
 The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
-
Assailant dead after ramming car into Michigan synagogue

-
 World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
-
Morikawa pulls out of Players Championship with back trouble

-
 Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
-
In Iran, shut shops, joblessness and a dash for cash

-
 Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
-
Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris

-
 Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise

-
 Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
-
Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia

-
 Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
-
Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military

-
 Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
-
Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub

-
 Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
-
Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'

-
 Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
-
Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy

-
 Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
-
IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred

-
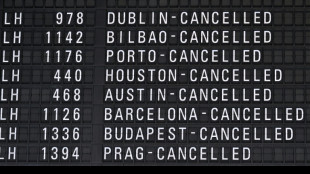 Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
-
Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister

-
 Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
-
Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages

-
 US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
-
'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel

-
 Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
-
Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack

-
 WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
-
EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US

-
 The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
-
'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform

-
 Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
-
More than goals: Valverde draws Real Madrid map to glory


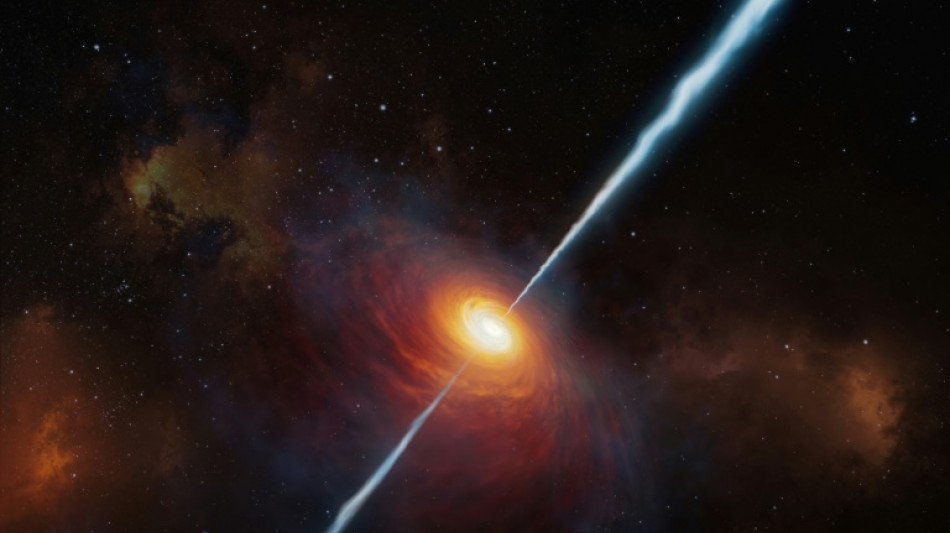
Milky Way's fate? Astronomers reveal what ignites quasars
Astronomers said Wednesday that for the first time they have confirmed what ignites quasars, the brightest and most powerful objects in the universe, which put galaxies in their "death throes".
These celestial behemoths form when two galaxies smash into each other, the astronomers said, warning that this could be the Milky Way's fate in a few billion years.
Quasars are one of the most extreme objects in the universe, some shining with the brightness of a trillion stars despite being packed into the space of our Solar System.
They sit in the heart of galaxies, powered by supermassive black holes, requiring a huge amount of gas to be so staggeringly bright.
But exactly what creates quasars has been a matter of debate since their discovery in the 1950s.
In a new study, an international team of researchers said they have "clear evidence" that quasars are triggered by two galaxies colliding, which releases the vast amounts of energy needed.
Clive Tadhunter, an astrophysicist at the University of Sheffield in the UK and one of the study's authors, told AFP that this could be the fate of the Milky Way one day.
The nearby Andromeda Galaxy is "coming directly towards us at about 200 kilometres (125 miles) a second," he said.
It will collide with the Milky War in roughly five billion years, and "we could get a quasar" as a result, he said.
Quasars push out all the gas from a galaxy, preventing any new stars from forming, he added.
- 'Beacons to the distant universe' -
The researchers compared observations of 48 galaxies with quasars at their centre to 100 without them.
Galaxies hosting quasars were three times as likely to have had collisions with other galaxies, the study said.
While the theory that such collisions ignited quasars has been around for decades, it was difficult to prove.
Tadhunter said this was because observations had often been carried out with telescopes that were optimised to look at objects in the centre of galaxies, but were less effective at spotting the distorted features at their edges that indicate past collisions.
For example, these diffuse structures "get washed out" when observed by the Hubble Space Telescope, he said.
So the team used land-based observatories, such as the Isaac Newton Telescope on the Spanish island of La Palma.
The new study, published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, also reviewed previous research to show how it may have missed the tell-tale signs of collisions.
Tadhunter said that quasars "act like beacons to the distant universe" because of their incredible brightness.
The James Webb Space Telescope, which has a much bigger aperture than Hubble, could help reveal more about quasars in this distant universe, when the universe was in its infancy, he said.
O.Norris--AMWN

