
-
 Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
-
Iran says will make US regret war as oil prices soar

-
 Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
-
NASA says 'on track' for Artemis 2 launch as soon as April 1

-
 Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
-
Italian prosecutors seek trial for Amazon over tax evasion

-
 Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
-
Duplantis clears 6.31m to set 15th pole vault world record

-
 Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
-
Sabalenka out-guns Mboko to reach Indian Wells semi-finals

-
 Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
-
'Say a prayer and send it': Paralympic alpine skiers tackle fear

-
 Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Assailant dead after ramming vehicle into Michigan synagogue

-
 The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
-
Assailant dead after ramming car into Michigan synagogue

-
 World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
-
Morikawa pulls out of Players Championship with back trouble

-
 Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
-
In Iran, shut shops, joblessness and a dash for cash

-
 Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
-
Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris

-
 Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise

-
 Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
-
Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia

-
 Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
-
Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military

-
 Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
-
Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub

-
 Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
-
Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'

-
 Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
-
Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy

-
 Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
-
IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred

-
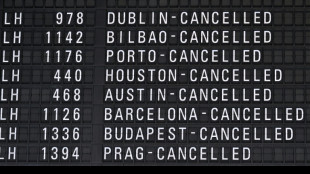 Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
-
Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister

-
 Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
-
Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages

-
 US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
-
'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel

-
 Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
-
Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack

-
 WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
-
EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US

-
 The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
-
'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform

-
 Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
-
More than goals: Valverde draws Real Madrid map to glory


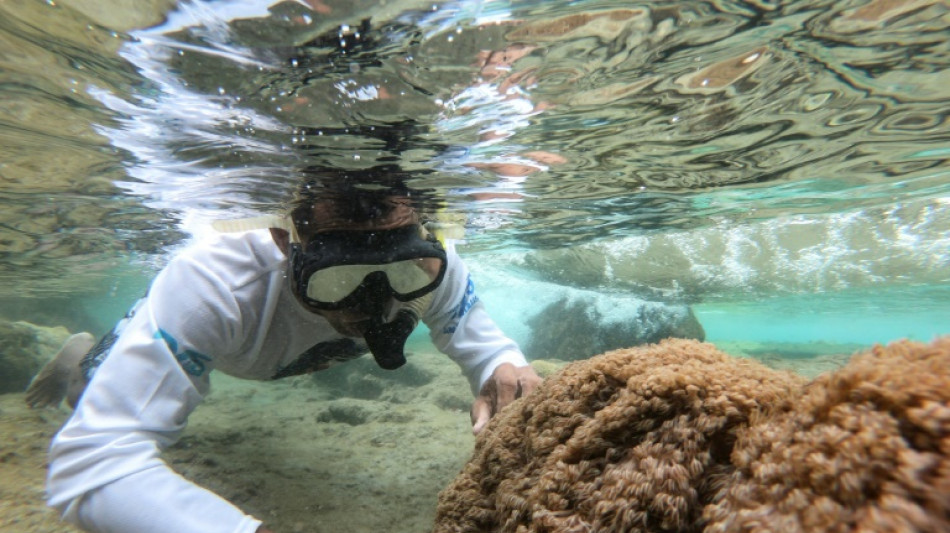
Deadly invader devastating Venezuelan coral reefs
An ominous shadow in the turquoise Caribbean waters off Venezuela comes from a deadly intruder -- a soft coral that experts say has caused one of the most destructive habitat invasions on record anywhere.
The Unomia stolonifera, native to Indonesia and the Indo-Pacific, is a pinkish type of pulse coral so called for its dance-like movements in the ocean currents.
It is a popular aquarium ornament -- pretty to look at and hardy -- with a single polyp fetching as much as $80 to $120.
But it is also a killer -- settling on native hard corals, rocks and even seagrass which it suffocates and replaces, ultimately destroying entire ecosystems.
Off Venezuela's north coast, Unomia dominates the ocean floor landscape after being introduced through the illegal aquarium trade around 20 years ago.
"This is an ecological catastrophe," said marine biologist Juan Pedro Ruiz-Allais, director of Project Unomia, named after the invader he has spent years investigating.
Fish stocks are drastically decreasing in the waters off Venezuela as native reefs, which serve as nurseries and feeding grounds, die off, he told AFP.
"When the reef dies, when it is covered by the Unomia stolonifera, a disruption of the food chain occurs," said the biologist.
"It is a social, food security, and economic problem because the livelihood of fishermen is compromised."
- 'Nobody knew' -
When Ruiz-Allais first came across the invader in 2007, it was an unknown species in the Caribbean and even the Atlantic, he recalled. "Nobody knew what it was."
It was first spotted in the Mochima National Park, a gorgeous archipelago covering more than 94,000 hectares, and has since been found to have colonized most of those islands.
The first scientific report was published in 2014, and the coral was initially classified as a member of the broad Xeniidae family before it was finally categorized in 2021 as Unomia stolonifera.
From Mochima, it has spread west and east in the Caribbean Sea.
Off the northern state of Anzoategui, it has taken over the equivalent of 300 football stadiums.
The coral is spread by fishing nets, anchors, and ship ballast water.
"It is a great colonizer," Gustavo Carrasquel, director of the Azul Ambientalistas, an environmental NGO, told AFP.
- 'Unprecedented' -
The threat extends beyond Venezuela's borders: officials say Unomia traces have been found near the islands of Aruba and Curacao, and in waters off Colombia and Brazil -- where it became attached to an oil rig but was controlled.
"It is a problem that will affect the rest of the Caribbean," said Ruiz-Allais.
But nowhere has it been more destructive than in Venezuela.
"It is an unprecedented case," said Project Unomia coordinator Mariano Onoro.
Fishermen and tour operators, concerned about the invasive coral's rapid propagation, have resorted to manual extraction.
But experts say this is not advised, because broken-off fragments are transported by the tides, settling to create yet more colonies.
The privately funded Project Unomia has developed an extraction machine with a group of engineers that is awaiting government approval for testing.
Venezuela's Institute for Scientific Research and the ministry of eco-socialism have launched an investigation into the coral's rapid spread but have yet to come up with a solution.
For now, the magnitude of the problem is such that the invader's elimination appears impossible.
"What we can do is recover some areas and control it," said Onoro.
O.Norris--AMWN

