
-
 Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
Sinner rolls into Indian Wells semi-final clash with Zverev
-
Iran says will make US regret war as oil prices soar

-
 Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
Trump says Iran war moving 'very rapidly'
-
NASA says 'on track' for Artemis 2 launch as soon as April 1

-
 Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
Valentino mixes 80s and Baroque splendour on Rome return
-
Italian prosecutors seek trial for Amazon over tax evasion

-
 Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
Polish president vetoes 40-bn-euro EU defence funding plan
-
Duplantis clears 6.31m to set 15th pole vault world record

-
 Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
Dating app Tinder dabbles with AI matchmaking
-
Sabalenka out-guns Mboko to reach Indian Wells semi-finals

-
 Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
Watkins ends drought as Villa snatch Europa last 16 advantage over Lille
-
'Say a prayer and send it': Paralympic alpine skiers tackle fear

-
 Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel renews Beirut strikes after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Assailant dead after ramming vehicle into Michigan synagogue

-
 The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
The Chinese cable that could trip up Chile's new leader
-
Assailant dead after ramming car into Michigan synagogue

-
 World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
World in 'new dark age' of abuse: UN rights expert
-
Morikawa pulls out of Players Championship with back trouble

-
 Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
Scavenging ravens memorize vast tracts of wolf hunting grounds: study
-
In Iran, shut shops, joblessness and a dash for cash

-
 Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
Polish bishops announce 'independent' probe of child sexual abuse
-
Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris

-
 Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations
-
Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise

-
 Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage
-
Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia

-
 Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow
-
Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military

-
 Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead
-
Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub

-
 Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize
-
Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'

-
 Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots
-
Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy

-
 Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan
-
IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred

-
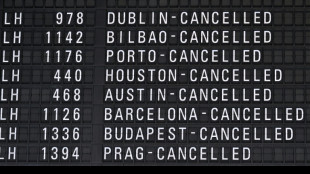 Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
-
Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister

-
 Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release
-
Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages

-
 US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary
-
'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel

-
 Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland
-
Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack

-
 WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes
-
EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US

-
 The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years
-
'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform

-
 Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute
-
More than goals: Valverde draws Real Madrid map to glory


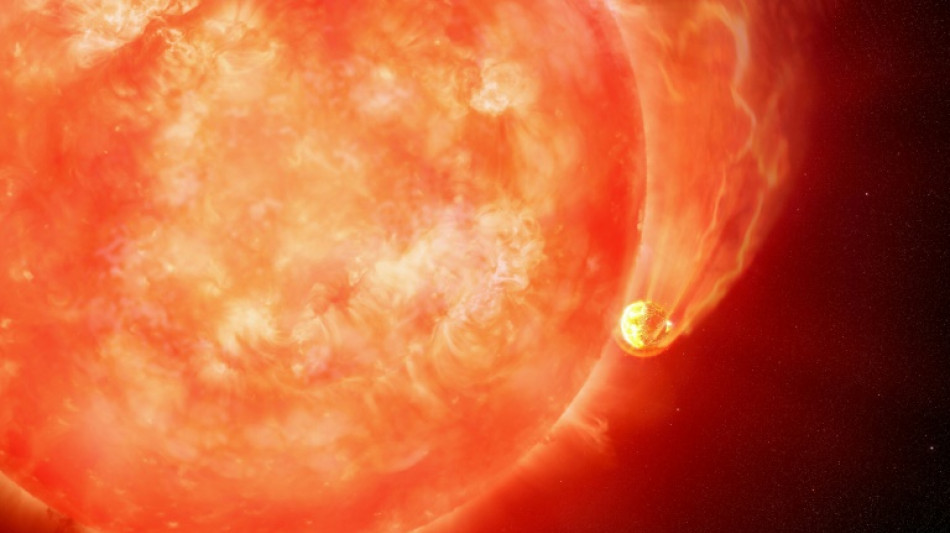
Star swallows planet in first glimpse of Earth's likely end
Scientists said Wednesday that they have observed a dying star swallowing a planet for the first time, offering a preview of Earth's expected fate in around five billion years.
But when the Sun finally does engulf Earth, it will cause only a "tiny perturbation" compared to this cosmic explosion, the US astronomers said.
Most planets are believed to meet their end when their host star runs out of energy, turning into a red giant that massively expands, devouring anything unlucky enough to be in its path.
Astronomers had previously seen the before-and-after effects of this process, but had never before caught a planet in the act of being consumed.
Kishalay De, a postdoc researcher at MIT in the United States and the lead author of the new study, said the accidental discovery unfolded like a "detective story".
"It all started about three years ago when I was looking at data from the Zwicky Transient Facility survey, which takes images of the sky every night," De told an online press conference.
He stumbled across a star that had suddenly increased in brightness by more than 100 times over a 10-day period.
The star is in the Milky Way galaxy, around 12,000 light years from Earth near the Aquila constellation, which resembles an eagle.
- Ice in boiling water -
De had been searching for binary star systems, in which the larger star takes bites out of its companion, creating incredibly bright explosions called outbursts.
But data showed that this outburst was surrounded by cold gas, suggesting it was not a binary star system.
And NASA's infrared space telescope NEOWISE showed that dust had started to shoot out of the area months before the outburst.
More puzzling still was that the outburst produced around 1,000 times less energy than previously observed mergers between stars.
"You ask yourself: what is 1,000 less massive than a star?" De said.
The answer was close to home: Jupiter.
The team of researchers from MIT, Harvard and Caltech established that the swallowed planet was a gas giant with a similar mass to Jupiter, but was so close to its star that it completed an orbit in just one day.
The star, which is quite similar to the Sun, engulfed the planet over a period of around 100 days, starting off by nibbling at its edges, which ejected dust.
The bright explosion occurred in the final 10 days as the planet was totally destroyed when it plunged inside the star.
Miguel Montarges, an astronomer at the Paris Observatory who was not involved in the research, noted that the star was thousands of degrees hotter than the planet.
"It's like putting an ice cube into a boiling pot," he told AFP.
- Watching Earth's fate -
Morgan MacLeod, a postdoc at Harvard University and co-author of the study, published in the journal Nature, said that most of the thousands of planets discovered outside the Solar System so far "will eventually suffer this fate".
And in comparison, Earth will most likely end not with a bang but a whimper.
When the Sun expands past Mercury, Venus and Earth in an estimated five billion years, they will make "less dramatic disturbances" because rocky planets are so much smaller than gas giants, MacLeod said.
"In fact, they will be really minor perturbations to the power output of the Sun," he said.
But even before it gets swallowed, Earth will already be "quite inhospitable," because the dying Sun will have already evaporated all the planet's water, MacLeod added.
Ryan Lau, an astronomer and study co-author, said the discovery "speaks to the transience of our existence".
"After the billions of years that span the lifetime of our Solar System, our own end stages will likely conclude in a final flash that lasts only a few months," he said in a statement.
Now that astronomers know what to look for, they hope that soon they will be able to watch many more planets be consumed by their stars.
In the Milky Way alone, a planet could be engulfed once a year, De said.
A.Malone--AMWN

