-
 Man set himself alight in fatal Swiss bus fire: prosecutor
Man set himself alight in fatal Swiss bus fire: prosecutor
-
'This is me, very pretty': inside a Cambodian cyberscam site

-
 Spain to deploy tool to track social media hate speech
Spain to deploy tool to track social media hate speech
-
Death toll from Ukrainian attack on Russia's Bryansk rises to 7: governor

-
 'Legendary' Barbra Streisand to receive Honorary Palme d'Or at Cannes
'Legendary' Barbra Streisand to receive Honorary Palme d'Or at Cannes
-
Devine, Mooney top women's Hundred auction

-
 British fintech Revolut gets full UK banking licence
British fintech Revolut gets full UK banking licence
-
US consumer inflation unchanged but price shocks from Iran war loom

-
 Kneecap rapper scores new court victory as UK prosecutors lose appeal
Kneecap rapper scores new court victory as UK prosecutors lose appeal
-
IEA says members to release 400 mn barrels from oil reserves

-
 Trump's 'racist hate speech' fuelling rights abuses: UN watchdog
Trump's 'racist hate speech' fuelling rights abuses: UN watchdog
-
Four killed in Ukraine as Moscow and Kyiv exchange drone strikes

-
 India T20 hero dons disguise for unexpected train home
India T20 hero dons disguise for unexpected train home
-
Russia says internet outages to last as long as 'necessary'

-
 US consumer inflation unchanged at 2.4% year-on-year in February
US consumer inflation unchanged at 2.4% year-on-year in February
-
Rana takes five wickets as Bangladesh crush Pakistan in ODI opener

-
 Barca blunder: Fan ends up at wrong St James Park
Barca blunder: Fan ends up at wrong St James Park
-
Malaysia's JDT reach Asian Champions League quarter-finals

-
 Oil jumps, stocks drop as Mideast war prolongs market volatility
Oil jumps, stocks drop as Mideast war prolongs market volatility
-
French aid worker killed in DR Congo air strike

-
 Germany, Japan to unblock oil reserves as G7 stands 'ready' to act
Germany, Japan to unblock oil reserves as G7 stands 'ready' to act
-
German defence giant Rheinmetall sees business boost from Mideast war

-
 Malawi court dismisses 15-year lawsuit against Madonna charity
Malawi court dismisses 15-year lawsuit against Madonna charity
-
Trade ships hit as Iran threatens Gulf oil chokepoint

-
 Airlines grapple with impact of Mideast war
Airlines grapple with impact of Mideast war
-
Iran's new supreme leader injured but 'safe', says president's son

-
 Thai navy says cargo ship attacked in Strait of Hormuz
Thai navy says cargo ship attacked in Strait of Hormuz
-
Poland starts human trafficking probe into Epstein ring

-
 Airlines in Asia hike fares as Mideast war raises fuel costs
Airlines in Asia hike fares as Mideast war raises fuel costs
-
UK govt to release first batch of Mandelson files

-
 European football clubs score with stadium rebuilds
European football clubs score with stadium rebuilds
-
Trump said Iran 'welcome to compete' in World Cup, says Infantino

-
 'No good choice': the Afghans forced to return from Iran
'No good choice': the Afghans forced to return from Iran
-
Asia stocks rise but oil resumes gains amid IEA supply report

-
 Cathay says surcharge to rise as fuel prices jump during Mideast war
Cathay says surcharge to rise as fuel prices jump during Mideast war
-
Cargo vessels hit as Iran threatens to close Gulf oil chokepoint

-
 G7 energy ministers 'ready' to take 'necessary measures' on oil reserves
G7 energy ministers 'ready' to take 'necessary measures' on oil reserves
-
Punch the baby monkey isn't being bullied: Japan zoo

-
 German defence giant Rheinmetall sees faster growth as Europe rearms
German defence giant Rheinmetall sees faster growth as Europe rearms
-
Fears of fuel shortage in Pakistan as tankers wait to fill up

-
 Cathay Pacific expects to carry more passengers in 2026
Cathay Pacific expects to carry more passengers in 2026
-
Yak hack: Kyrgyz want the world to love their blonde bovine beauties

-
 Iran women footballers evacuate from safe house in Australia
Iran women footballers evacuate from safe house in Australia
-
Shabby beauty: Inside Japan's oldest, defiant student dorm

-
 Seoul says can deter threats from North if US weapons shifted to Mideast
Seoul says can deter threats from North if US weapons shifted to Mideast
-
Italy stun United States 8-6 in World Baseball Classic

-
 New wave of Iran attacks as oil reserve release weighed
New wave of Iran attacks as oil reserve release weighed
-
Politics meets football as China, Taiwan face off at Asian Cup

-
 History offers Scots hope of ending losing run to Irish
History offers Scots hope of ending losing run to Irish
-
Trump-Infantino 'bromance' tested by Middle East war


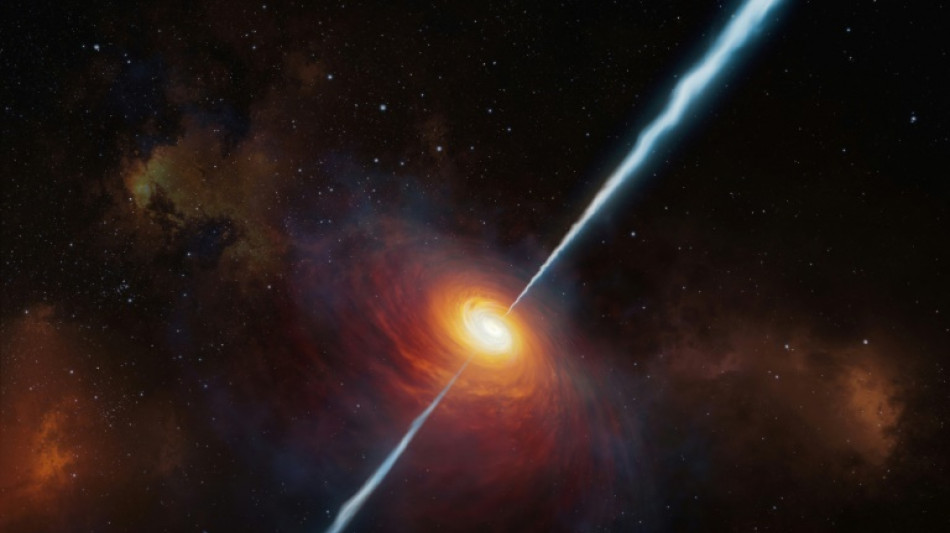
Time appears five times slower in early universe: study
Time appears to run five times slower in the early universe, scientists said on Monday, for the first time using extraordinarily bright cosmic objects called quasars as "clocks" to confirm this strange phenomenon.
Einstein's theory of relativity predicts that because space is expanding, "we should see the distant universe run in slow motion," said Geraint Lewis, an astrophysicist at the University of Sydney and the lead author of a new study.
Researchers had previously used observations of very bright exploding stars called supernovas as cosmic clocks to show that time ran twice as slowly back when the universe was half its current age.
The new study used even brighter quasars to peer further back into the history of the 13.8-billion-year-old universe.
Just over a billion years after the Big Bang, time appeared to flow five times slower, according to the study in the journal Nature Astronomy.
While "everything looks like it's slowed down" from here, Lewis emphasised that the experience of time in these distant places was not different.
"If I could magically transport you back 10 billion years and drop you next to one of these quasars, and you've got a stopwatch, time would just be normal," he told AFP.
"One second would be one second."
- Cosmic clocks -
Aiming to measure this phenomenon, which is called cosmological time dilation, Lewis and University of Auckland statistician Brendon Brewer analysed data from 190 quasars collected over two decades.
Quasars -- supermassive black holes at the centres of distant galaxies -- are thought to be the brightest and most powerful objects in the universe.
This makes them "useful beacons for charting the universe," Lewis said.
But they have proved more difficult to turn into cosmic clocks than supernovas, which provide a reliable single flash as a "tick".
Previous attempts to use quasars to measure time dilation had failed, leading to some "strange suggestions," Lewis said.
These included theories that perhaps quasars were not as distant as had been thought -- or even that "something fundamental was broken" in cosmology, he said.
But the new research "puts everything back in the right place," Lewis said.
It also confirmed that "Einstein is right again," he added.
The researchers were able to succeed where other attempts had fallen short because they had far more data on quasars, according to Lewis. Recent advances in the statistical understanding of randomness also helped.
To turn quasars into clocks with measurable ticks, the researchers had to make sense of the turbulent explosions that occurred as the black holes swallowed material.
Lewis compared it to watching a fireworks display, in which the great flashes seem random but different elements are "brightening and fading on their own kind of timescales".
"What we have done is unravel this firework display, showing that quasars, too, can be used as standard markers of time for the early universe."
F.Bennett--AMWN