-
 Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
-
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach

-
 Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
-
Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third

-
 Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million
Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million
-
Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation

-
 Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future
Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future
-
Taiwan police rule out 'terrorism' in metro stabbing

-
 Australia falls silent, lights candles for Bondi Beach shooting victims
Australia falls silent, lights candles for Bondi Beach shooting victims
-
DR Congo's amputees bear scars of years of conflict

-
 Venison butts beef off menus at UK venues
Venison butts beef off menus at UK venues
-
Cummins, Lyon doubts for Melbourne after 'hugely satsfying' Ashes

-
 'It sucks': Stokes vows England will bounce back after losing Ashes
'It sucks': Stokes vows England will bounce back after losing Ashes
-
Australia probes security services after Bondi Beach attack

-
 West Indies need 462 to win after Conway's historic century
West Indies need 462 to win after Conway's historic century
-
Thai border clashes displace over half a million in Cambodia

-
 Australia beat England by 82 runs to win third Test and retain Ashes
Australia beat England by 82 runs to win third Test and retain Ashes
-
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge

-
 Japan footballer 'King Kazu' to play on at the age of 58
Japan footballer 'King Kazu' to play on at the age of 58
-
New Zealand's Conway joins elite club with century, double ton in same Test

-
 Australian PM orders police, intelligence review after Bondi attack
Australian PM orders police, intelligence review after Bondi attack
-
Durant shines as Rockets avenge Nuggets loss

-
 Pressure on Morocco to deliver as Africa Cup of Nations kicks off
Pressure on Morocco to deliver as Africa Cup of Nations kicks off
-
Australia remove Smith as England still need 126 to keep Ashes alive

-
 Myanmar mystics divine future after ill-augured election
Myanmar mystics divine future after ill-augured election
-
From the Andes to Darfur: Colombians lured to Sudan's killing fields

-
 Eagles win division as Commanders clash descends into brawl
Eagles win division as Commanders clash descends into brawl
-
US again seizes oil tanker off coast of Venezuela

-
 New Zealand 35-0, lead by 190, after racing through West Indies tail
New Zealand 35-0, lead by 190, after racing through West Indies tail
-
West Indies 420 all out to trail New Zealand by 155

-
 Arteta tells leaders Arsenal to 'learn' while winning
Arteta tells leaders Arsenal to 'learn' while winning
-
Honour to match idol Ronaldo's Real Madrid calendar year goal record: Mbappe

-
 Dupont helps Toulouse bounce back in Top 14 after turbulent week
Dupont helps Toulouse bounce back in Top 14 after turbulent week
-
Mbappe matches Ronaldo record as Real Madrid beat Sevilla

-
 Gyokeres ends drought to gift Arsenal top spot for Christmas
Gyokeres ends drought to gift Arsenal top spot for Christmas
-
Arsenal stay top despite Man City win, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs

-
 US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
-
PSG cruise past fifth-tier Fontenay in French Cup

-
 Isak injury leaves Slot counting cost of Liverpool win at Spurs
Isak injury leaves Slot counting cost of Liverpool win at Spurs
-
Juve beat Roma to close in on Serie A leaders Inter

-
 US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela: US media
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela: US media
-
Haaland sends Man City top, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs

-
 Epstein victims, lawmakers criticize partial release and redactions
Epstein victims, lawmakers criticize partial release and redactions
-
Leverkusen beat Leipzig to move third in Bundesliga

-
 Lakers guard Smart fined $35,000 for swearing at refs
Lakers guard Smart fined $35,000 for swearing at refs
-
Liverpool sink nine-man Spurs but Isak limps off after rare goal

-
 Guardiola urges Man City to 'improve' after dispatching West Ham
Guardiola urges Man City to 'improve' after dispatching West Ham
-
Syria monitor says US strikes killed at least five IS members

-
 Australia stops in silence for Bondi Beach shooting victims
Australia stops in silence for Bondi Beach shooting victims
-
Olympic champion Joseph helps Perpignan to first Top 14 win despite red card


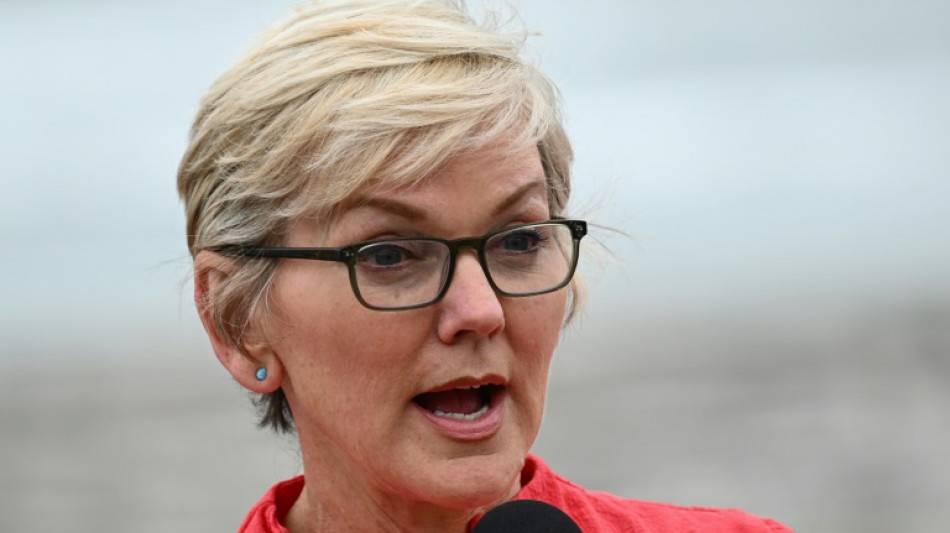
US to invest $1.2 bn on facilities to pull carbon from air
The US government said Friday it will spend up to $1.2 billion for two pioneering facilities to vacuum carbon out of the air, a historic gamble on a still developing technology to combat global warming that is criticized by some experts.
The two projects -- in Texas and Louisiana -- each aim to eliminate one million tons of carbon dioxide per year, equivalent in total to the annual emissions of 445,000 gas-powered cars.
It is "the world's largest investment in engineered carbon removal in history," the Energy Department said in a statement.
"Cutting back on our carbon emissions alone won't reverse the growing impacts of climate change," Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm said in the statement. "We also need to remove the CO2 that we've already put in the atmosphere."
Direct Air Capture (DAC) techniques -- also known as Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) -- focus on that CO2 emitted into the air, which is helping to fuel climate change and extreme weather.
Each of the projects will remove 250 times more CO2 from the air than the largest carbon capture site currently in operation, the Energy Department said.
The UN's International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) considers capturing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere one of the methods necessary to combat global warming.
But the sector is still marginal -- there are just 27 existing carbon capture sites commissioned worldwide, according to the International Energy Agency, though at least 130 projects are under development.
And some experts worry that use of the technology will be a pretext for continuing to emit greenhouse gases, rather than switching more quickly to clean energies.
Direct capture "requires a lot of electricity for extracting CO2 from the air and compressing it for pipes," Stanford University professor Mark Jacobson told AFP.
"Even in the best case, where the electricity is renewable, that renewable electricity is then prevented from replacing a fossil electricity source on the grid, such as coal or gas."
That means such technology is nothing more than a "gimmick," he said, adding: "It will only delay our solution to the climate problem."
- Storing CO2 underground -
US non-profit Battelle is the prime contractor on the Louisiana project, which will inject captured CO2 for storage deep underground.
It will partner with another American company, Heirloom, and the Swiss firm Climeworks, already a sector leader that operates a plant in Iceland with an annual capacity to capture 4,000 tons of CO2 from the air.
The Texas project will be led by the American company Occidental and other partners, including Carbon Engineering. It could be developed to eliminate up to 30 million tons of CO2 per year, according to a statement from Occidental.
"The rocks in the subsoil of Louisiana and Texas are sedimentary rocks, very different from Icelandic basalts, but they are perfectly viable for storing CO2," Helene Pilorge, an associate researcher at the University of Pennsylvania studying carbon capture, told AFP.
The two projects should create 4,800 jobs, according to the energy department. No start date is yet confirmed for either.
They will be funded by President Joe Biden's major infrastructure bill passed in 2021.
The Energy Department previously announced plans to invest in four projects to the tune of $3.5 billion.
Direct capture differs from carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems at source, such as factory chimneys, which prevent additional emissions from reaching the atmosphere.
In May, the Biden administration announced a plan to reduce CO2 emissions from gas-fired and coal-fired power plants, focusing in particular on this second technique.
O.Karlsson--AMWN