-
 Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory
-
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach

-
 Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third
-
Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third

-
 Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million
Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million
-
Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation

-
 Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future
Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future
-
Taiwan police rule out 'terrorism' in metro stabbing

-
 Australia falls silent, lights candles for Bondi Beach shooting victims
Australia falls silent, lights candles for Bondi Beach shooting victims
-
DR Congo's amputees bear scars of years of conflict

-
 Venison butts beef off menus at UK venues
Venison butts beef off menus at UK venues
-
Cummins, Lyon doubts for Melbourne after 'hugely satsfying' Ashes

-
 'It sucks': Stokes vows England will bounce back after losing Ashes
'It sucks': Stokes vows England will bounce back after losing Ashes
-
Australia probes security services after Bondi Beach attack

-
 West Indies need 462 to win after Conway's historic century
West Indies need 462 to win after Conway's historic century
-
Thai border clashes displace over half a million in Cambodia

-
 Australia beat England by 82 runs to win third Test and retain Ashes
Australia beat England by 82 runs to win third Test and retain Ashes
-
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge

-
 Japan footballer 'King Kazu' to play on at the age of 58
Japan footballer 'King Kazu' to play on at the age of 58
-
New Zealand's Conway joins elite club with century, double ton in same Test

-
 Australian PM orders police, intelligence review after Bondi attack
Australian PM orders police, intelligence review after Bondi attack
-
Durant shines as Rockets avenge Nuggets loss

-
 Pressure on Morocco to deliver as Africa Cup of Nations kicks off
Pressure on Morocco to deliver as Africa Cup of Nations kicks off
-
Australia remove Smith as England still need 126 to keep Ashes alive

-
 Myanmar mystics divine future after ill-augured election
Myanmar mystics divine future after ill-augured election
-
From the Andes to Darfur: Colombians lured to Sudan's killing fields

-
 Eagles win division as Commanders clash descends into brawl
Eagles win division as Commanders clash descends into brawl
-
US again seizes oil tanker off coast of Venezuela

-
 New Zealand 35-0, lead by 190, after racing through West Indies tail
New Zealand 35-0, lead by 190, after racing through West Indies tail
-
West Indies 420 all out to trail New Zealand by 155

-
 Arteta tells leaders Arsenal to 'learn' while winning
Arteta tells leaders Arsenal to 'learn' while winning
-
Honour to match idol Ronaldo's Real Madrid calendar year goal record: Mbappe

-
 Dupont helps Toulouse bounce back in Top 14 after turbulent week
Dupont helps Toulouse bounce back in Top 14 after turbulent week
-
Mbappe matches Ronaldo record as Real Madrid beat Sevilla

-
 Gyokeres ends drought to gift Arsenal top spot for Christmas
Gyokeres ends drought to gift Arsenal top spot for Christmas
-
Arsenal stay top despite Man City win, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs

-
 US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
-
PSG cruise past fifth-tier Fontenay in French Cup

-
 Isak injury leaves Slot counting cost of Liverpool win at Spurs
Isak injury leaves Slot counting cost of Liverpool win at Spurs
-
Juve beat Roma to close in on Serie A leaders Inter

-
 US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela: US media
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela: US media
-
Haaland sends Man City top, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs

-
 Epstein victims, lawmakers criticize partial release and redactions
Epstein victims, lawmakers criticize partial release and redactions
-
Leverkusen beat Leipzig to move third in Bundesliga

-
 Lakers guard Smart fined $35,000 for swearing at refs
Lakers guard Smart fined $35,000 for swearing at refs
-
Liverpool sink nine-man Spurs but Isak limps off after rare goal

-
 Guardiola urges Man City to 'improve' after dispatching West Ham
Guardiola urges Man City to 'improve' after dispatching West Ham
-
Syria monitor says US strikes killed at least five IS members

-
 Australia stops in silence for Bondi Beach shooting victims
Australia stops in silence for Bondi Beach shooting victims
-
Olympic champion Joseph helps Perpignan to first Top 14 win despite red card


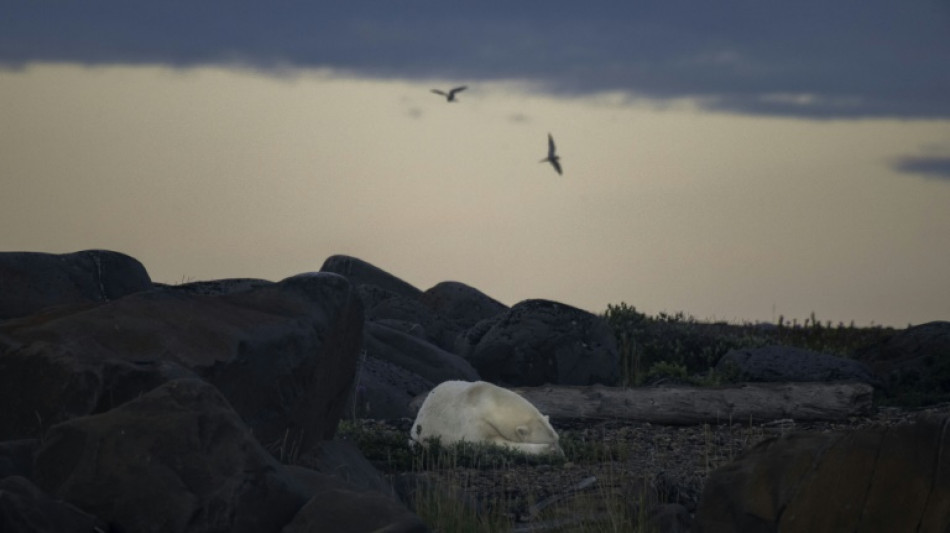
Study quantifies link between greenhouse gases, polar bear survival
Polar bears have long symbolized the dangers posed by climate change, as rising temperatures melt away the Arctic sea ice which they depend upon for survival.
But quantifying the impact of a single oil well or coal power plant on the tundra predators had eluded scientists, until now.
A new report published in the journal Science on Thursday shows it is possible to calculate how much new greenhouse gas emissions will increase the number of ice-free days in the bears' habitats, and how that in turn will affect the percentage of cubs that reach adulthood.
By achieving this level of granularity, the two authors hope to close a loophole in US law.
Although the apex carnivores have had endangered species protections since 2008, a long-standing legal opinion prevents climate considerations from affecting decisions on whether to grant permits to new fossil fuel projects.
"We have presented the information necessary to rescind the Bernhardt Memo," first co-author Steven Amstrup, a zoologist with Polar Bears International and the University of Wyoming, told AFP, referring to the legal caveat which was named after an attorney in former president George W. Bush's administration.
The memo stated it was beyond the scope of existing science to distinguish the impacts of a specific source of carbon emissions from the impacts of all greenhouse gasses since the beginning of the industrial age.
- Cub survival imperiled -
Polar bears rely heavily on the sea ice environment for hunting seals, traveling, mating and more.
When sea ice melts in summer, the apex carnivores retreat onto land or unproductive ice far from the shore, where they endure long stretches of fasting. These periods are growing longer as global temperatures rise.
A landmark paper published in Nature in 2020 was the first to calculate links between changes in the sea ice caused by climate and polar bear demographics.
Building on this work, Amstrup and Bitz established the mathematical relationships between greenhouse emissions and fasting days as well as cub survival, in 15 out of 19 of the polar bears' subpopulations, between 1979 and 2020.
For example, the world currently emits 50 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide or equivalent gasses into the atmosphere annually, and that is reducing the rate of cub survival by over three percentage points per year in the South Beaufort Sea subpopulation.
In healthy populations, cub survival during the first year of life is around 65 percent.
"You don't have to knock that down very far before you don't have enough cubs entering the next generation," said Amstrup.
In addition, the paper provides US policy makers the tools they need to quantify the impact of new fossil fuel projects slated to occur on public lands in the coming decades.
- Implications for other species -
Joel Berger, university chair of wildlife conservation at Colorado State University, praised the paper.
"Amstrup and Bitz render an incontrovertible quantitative link among (greenhouse gas) emissions, sea ice decline, fasting duration -- a physiological response to lost hunting opportunities for seals -- and subsequent polar bear demographics -- declining recruitment of young," said Berger, who was not involved in the research.
Beyond providing a potential policy solution to the legal loophole, the new research could have implications that reach far beyond polar bears, second co-author Cecilia Bitz, a climatologist at the University of Washington, told AFP.
Methods laid out in the paper can be adapted for other species and habitats, such as coral reefs, or Florida's Key deer.
"I really hope this stimulates a lot of research," Bitz said, adding she was already reaching out to new collaborators.
M.Thompson--AMWN