-
 Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
-
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third

-
 Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third
Goggia wins World Cup super-G as Vonn takes third
-
Cambodia says Thai border clashes displace over half a million

-
 Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation
Kremlin denies three-way US-Ukraine-Russia talks in preparation
-
Williamson says 'series by series' call on New Zealand Test future

-
 Taiwan police rule out 'terrorism' in metro stabbing
Taiwan police rule out 'terrorism' in metro stabbing
-
Australia falls silent, lights candles for Bondi Beach shooting victims

-
 DR Congo's amputees bear scars of years of conflict
DR Congo's amputees bear scars of years of conflict
-
Venison butts beef off menus at UK venues

-
 Cummins, Lyon doubts for Melbourne after 'hugely satsfying' Ashes
Cummins, Lyon doubts for Melbourne after 'hugely satsfying' Ashes
-
'It sucks': Stokes vows England will bounce back after losing Ashes

-
 Australia probes security services after Bondi Beach attack
Australia probes security services after Bondi Beach attack
-
West Indies need 462 to win after Conway's historic century

-
 Thai border clashes displace over half a million in Cambodia
Thai border clashes displace over half a million in Cambodia
-
Australia beat England by 82 runs to win third Test and retain Ashes

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Japan footballer 'King Kazu' to play on at the age of 58

-
 New Zealand's Conway joins elite club with century, double ton in same Test
New Zealand's Conway joins elite club with century, double ton in same Test
-
Australian PM orders police, intelligence review after Bondi attack

-
 Durant shines as Rockets avenge Nuggets loss
Durant shines as Rockets avenge Nuggets loss
-
Pressure on Morocco to deliver as Africa Cup of Nations kicks off

-
 Australia remove Smith as England still need 126 to keep Ashes alive
Australia remove Smith as England still need 126 to keep Ashes alive
-
Myanmar mystics divine future after ill-augured election

-
 From the Andes to Darfur: Colombians lured to Sudan's killing fields
From the Andes to Darfur: Colombians lured to Sudan's killing fields
-
Eagles win division as Commanders clash descends into brawl

-
 US again seizes oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
US again seizes oil tanker off coast of Venezuela
-
New Zealand 35-0, lead by 190, after racing through West Indies tail

-
 West Indies 420 all out to trail New Zealand by 155
West Indies 420 all out to trail New Zealand by 155
-
Arteta tells leaders Arsenal to 'learn' while winning

-
 Honour to match idol Ronaldo's Real Madrid calendar year goal record: Mbappe
Honour to match idol Ronaldo's Real Madrid calendar year goal record: Mbappe
-
Dupont helps Toulouse bounce back in Top 14 after turbulent week

-
 Mbappe matches Ronaldo record as Real Madrid beat Sevilla
Mbappe matches Ronaldo record as Real Madrid beat Sevilla
-
Gyokeres ends drought to gift Arsenal top spot for Christmas

-
 Arsenal stay top despite Man City win, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs
Arsenal stay top despite Man City win, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs
-
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela

-
 PSG cruise past fifth-tier Fontenay in French Cup
PSG cruise past fifth-tier Fontenay in French Cup
-
Isak injury leaves Slot counting cost of Liverpool win at Spurs

-
 Juve beat Roma to close in on Serie A leaders Inter
Juve beat Roma to close in on Serie A leaders Inter
-
US intercepts oil tanker off coast of Venezuela: US media

-
 Haaland sends Man City top, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs
Haaland sends Man City top, Liverpool beat nine-man Spurs
-
Epstein victims, lawmakers criticize partial release and redactions

-
 Leverkusen beat Leipzig to move third in Bundesliga
Leverkusen beat Leipzig to move third in Bundesliga
-
Lakers guard Smart fined $35,000 for swearing at refs

-
 Liverpool sink nine-man Spurs but Isak limps off after rare goal
Liverpool sink nine-man Spurs but Isak limps off after rare goal
-
Guardiola urges Man City to 'improve' after dispatching West Ham

-
 Syria monitor says US strikes killed at least five IS members
Syria monitor says US strikes killed at least five IS members
-
Australia stops in silence for Bondi Beach shooting victims

-
 Olympic champion Joseph helps Perpignan to first Top 14 win despite red card
Olympic champion Joseph helps Perpignan to first Top 14 win despite red card
-
Zelensky says US mooted direct Ukraine-Russia talks on ending war


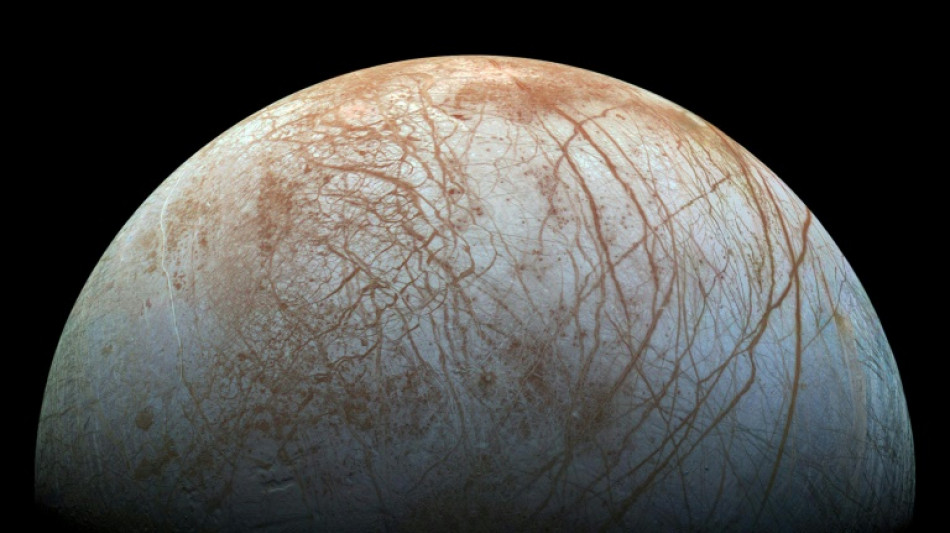
Hidden ocean the source of CO2 on Jupiter moon: research
Carbon dioxide detected on Jupiter's moon Europa comes from the vast ocean beneath its icy shell, research using James Webb Space Telescope data indicated on Thursday, potentially bolstering hopes the hidden water could harbour life.
Scientists are confident there is a huge ocean of saltwater kilometres below Europa's ice-covered surface, making the moon a prime candidate for hosting extra-terrestrial life in our Solar System.
But determining whether this concealed ocean has the right chemical elements to support life has been difficult.
Carbon dioxide -- one of the key building blocks of life -- has been detected on Europa's surface, but whether it rose up from the ocean below remained an open question.
Aiming to find an answer, two US-led teams of researchers used data from the Webb telescope's near-infrared spectrometer to map CO2 on the surface of Europa, publishing their results in separate studies in the journal Science.
The most CO2 was in a 1,800 kilometre-wide (1,120 mile) area called Tara Regio, where there is a lot of "chaos terrain" with jagged ridges and cracks.
Exactly what creates chaos terrain is not well understood, but one theory is that warm water from the ocean rises up to melt the surface ice, which then re-freezes over time into new uneven crags.
The first study used the Webb data to look at whether the CO2 could have come from somewhere other than the ocean below -- hitching a ride on a meteorite, for example.
Samantha Trumbo, a planetary scientist at Cornell University and the study's lead author, told AFP they concluded that the carbon was "ultimately derived from the interior, likely the internal ocean".
But the researchers could not rule out that the carbon came up from the planet's interior as rock-like carbonate minerals, which irradiation could then have broken apart to become CO2.
- 'Very exciting' -
Table salt has also been detected in Tara Regio -- making the area significantly more yellow than the rest of Europa's scarred white plains -- and scientists think it may also have come up from the ocean.
"So now we've got salt, we've got CO2: we're starting to learn a little bit more what that internal chemistry might look like," Trumbo said.
Looking at the same Webb data, the second study also indicated that "carbon is sourced from within Europa".
The NASA-led researchers had also hoped to find plumes of water or volatile gases shooting out of the moon's surface, but failed to spot any.
Two major space missions plan to get a closer look at Europa and its mysterious ocean.
The European Space Agency's Jupiter moon probe Juice launched in April, while NASA's Europa Clipper mission is scheduled to blast off in October 2024.
Juice project scientist Olivier Witasse welcomed the two new studies, saying they were "very exciting".
When Juice flies past Europa twice in 2032, it will collect "a wealth of new information," including about surface chemistry, he told AFP.
Juice will also look at two of Jupiter's other moons -- Ganymede and Callisto -- where carbon has been detected.
Witasse emphasised that the goal of the Juice mission, like the Europa Clipper, is to find out whether these icy moons have the right conditions to support life -- they will not be able to confirm if aliens exist.
And even if some future mission does discover life, anything able to live in such extreme conditions under more than 10 kilometres of ice is expected to be tiny, such as primitive microbes.
M.Thompson--AMWN