-
 Microsoft urges Pentagon pause blacklisting Anthropic
Microsoft urges Pentagon pause blacklisting Anthropic
-
Harvey Weinstein says prison is 'hell'

-
 'Put our faith in God': Tehran residents adapt to wartime
'Put our faith in God': Tehran residents adapt to wartime
-
Caviar, truffle and chicken pot pies: what Hollywood will eat at the Oscars

-
 US says wouldn't be 'happy' if Russia giving Iran intel
US says wouldn't be 'happy' if Russia giving Iran intel
-
US targets Iran mine-laying as war causes oil market havoc

-
 Yamal denies Newcastle, Liverpool lose and Atletico thrash Spurs in Champions League
Yamal denies Newcastle, Liverpool lose and Atletico thrash Spurs in Champions League
-
Olise could be world great, says Bayern coach Kompany

-
 Two more members of Iran women's football team claim asylum in Australia
Two more members of Iran women's football team claim asylum in Australia
-
'Incredible situation': Spurs coach Tudor on subbing Kinsky after errors

-
 Police say deadly Swiss bus fire could be deliberate
Police say deadly Swiss bus fire could be deliberate
-
Bayern on verge of Champions League quarters after hitting Atalanta for six

-
 Griezmann dreaming big at Atletico after Spurs rout
Griezmann dreaming big at Atletico after Spurs rout
-
Howe sees 'hope' for Newcastle despite blow of Barcelona equaliser

-
 Dassault pitches latest private jet against US, Canadian rivals
Dassault pitches latest private jet against US, Canadian rivals
-
Fresh Israeli strikes hit Lebanon after evacuation warnings

-
 Yamal penalty rescues Barca from defeat at Newcastle
Yamal penalty rescues Barca from defeat at Newcastle
-
Bayern on verge of Champions League quarters after smashing six past Atalanta

-
 Louis Vuitton takes Paris fashion week on mountain ride
Louis Vuitton takes Paris fashion week on mountain ride
-
Slot frustrated by sloppy Liverpool in Galatasaray defeat

-
 Atletico capitalise on Tottenham's Champions League nightmare
Atletico capitalise on Tottenham's Champions League nightmare
-
Fils surprises Auger-Aliassime to set Zverev quarter-final clash

-
 Will Trump blink on Iran as pressure mounts?
Will Trump blink on Iran as pressure mounts?
-
Mideast tanker escort: high-risk mission for US Navy

-
 Oil prices dive as IEA eyes emergency release with Hormuz Strait in focus
Oil prices dive as IEA eyes emergency release with Hormuz Strait in focus
-
Iran not seeking ceasefire as Trump steps up threats

-
 US satellite firm extends Middle East image delay
US satellite firm extends Middle East image delay
-
Spurs sub goalkeeper Kinsky after two huge errors in 17 minutes

-
 Oil plunges, stocks mostly rise as Trump says Iran war over 'very soon'
Oil plunges, stocks mostly rise as Trump says Iran war over 'very soon'
-
Sabalenka powers past Osaka into Indian Wells quarter-finals

-
 Trump team's Iran war rhetoric fuels backlash
Trump team's Iran war rhetoric fuels backlash
-
French Paralympian Bauchet's golden end to a 'tough' day

-
 Liverpool rocked by Galatasaray defeat in Champions League last 16 first leg
Liverpool rocked by Galatasaray defeat in Champions League last 16 first leg
-
Liverpool rocked by Galatasaray defeat in last 16 first leg

-
 White House says US Navy has not escorted tanker through Strait of Hormuz
White House says US Navy has not escorted tanker through Strait of Hormuz
-
Rosenior says Club World Cup victory irrelevant as Chelsea and PSG clash again

-
 'Don't use that phrase': Arteta shuts down Arsenal quadruple talk
'Don't use that phrase': Arteta shuts down Arsenal quadruple talk
-
Shifting sands? Trump and his elastic timeline for Iran war

-
 Ukraine says hit 'key' Russian military factory in missile strike
Ukraine says hit 'key' Russian military factory in missile strike
-
Will Trump 'TACO' on Iran?

-
 Family of Canada mass shooting victim sues OpenAI
Family of Canada mass shooting victim sues OpenAI
-
Blasts rock Tehran as US says strikes to intensify

-
 Real Madrid as good as Man City even without Mbappe: Arbeloa
Real Madrid as good as Man City even without Mbappe: Arbeloa
-
Musk, already world's richest person, eyes $1 trillion fortune

-
 US energy secretary's post saying US escorted tanker in Hormuz deleted
US energy secretary's post saying US escorted tanker in Hormuz deleted
-
Peruvian literary great Alfredo Bryce Echenique dead at 87

-
 After women players defect, Iran hints men will skip World Cup
After women players defect, Iran hints men will skip World Cup
-
Lossiemouth in 'league of her own' as she wins Champion Hurdle

-
 UN warns Hormuz standstill will hit world's most vulnerable
UN warns Hormuz standstill will hit world's most vulnerable
-
Israelis dance on at Tel Aviv 'bunker party' as missiles fly


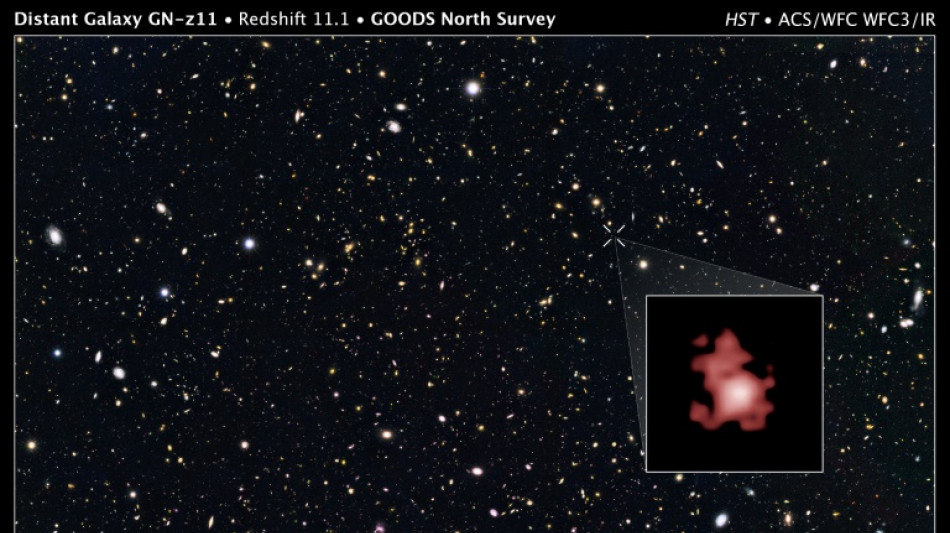
Webb telescope discovers oldest black hole yet
The James Webb space telescope has discovered the oldest black hole ever detected, which was thriving so soon after the Big Bang that it challenges our understanding of how these celestial behemoths form, astronomers said Wednesday.
The black hole was vigorously gobbling up its host galaxy just 430 million years after the birth of the universe during a period called the cosmic dawn, according to a study in the journal Nature.
That makes it 200 million years older than any other massive black hole ever observed, study co-author and Cambridge University astronomer Jan Scholtz told AFP.
Yet it has a mass 1.6 million times greater than our Sun.
Exactly how it had time to grow that big so quickly after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago will provide new information "for the next generation of theoretical models" aiming to explain what creates black holes, Scholtz said.
Like all black holes, it is invisible and can only be detected by the vast explosions of light created when it gobbles up whatever matter is unlucky enough to be nearby.
It was this light that allowed the Hubble space telescope in 2016 to spot its host galaxy GN-z11, which is in the direction of the Ursa Major constellation.
At the time GN-z11 was the oldest -- and therefore most distant -- galaxy ever observed. However Hubble did not spot the black hole lurking at its centre.
In 2022, Webb usurped Hubble as the most powerful space telescope, unleashing a torrent of discoveries that have scientists rushing to keep up.
Not only has it spotted the black hole at the heart of GN-z11, but it has also discovered galaxies even further back in time and space, which are also bigger than had been thought possible.
- Growing up fast -
The black hole was energetically eating up GN-z11 during the cosmic dawn, a period which came right after the universe's "dark ages," when stars and galaxies were first born.
It normally takes the supermassive black holes squatting at the centre of galaxies hundreds of millions -- if not billions -- of years to form.
So how could this one have grown so quickly?
Study co-author Stephane Charlot, an astrophysicist at France's Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, suggested that black holes in the early universe could have been formed in a different way than those closer by.
One theory is that they were born huge due to the explosion of especially massive stars that only existed in the early universe, he told AFP.
Or they could have been created by the "direct collapse of a dense gas cloud, without going through the star formation phase," he added.
Once born, the black hole would have been able to gorge itself on the plentiful gas nearby, prompting an almighty growth spurt.
Scholtz emphasised that what has been discovered so far about the black hole of GN-z11 "doesn't rule out any of these scenarios".
And it could be just the beginning.
Scholtz hopes that Webb -- and other telescopes on the way, such as the European Space Agency's Euclid -- will discover more of these black holes in the earliest glimmers of the universe.
Y.Aukaiv--AMWN



