
-
 Lossiemouth in 'league of her own' as she wins Champion Hurdle
Lossiemouth in 'league of her own' as she wins Champion Hurdle
-
UN warns Hormuz standstill will hit world's most vulnerable
-
 Israelis dance on at Tel Aviv 'bunker party' as missiles fly
Israelis dance on at Tel Aviv 'bunker party' as missiles fly
-
Oil crisis: Is world better placed than in 1973?

-
 Trump administration does about face on autism treatment
Trump administration does about face on autism treatment
-
Expats cling to Dubai's allure despite Iran's missiles

-
 Global energy body discusses releasing strategic oil reserves
Global energy body discusses releasing strategic oil reserves
-
UAE closes biggest oil refinery as Iran vows to choke off crude exports

-
 Gunfire at US consulate in Toronto a 'national security incident': police
Gunfire at US consulate in Toronto a 'national security incident': police
-
Spain's Ayuso takes Paris-Nice race lead after team time-trial

-
 Oscar nominee Chalamet woos Chinese fans days before Best Actor bid
Oscar nominee Chalamet woos Chinese fans days before Best Actor bid
-
'Heated Rivalry' stars condemn 'hateful' fan engagement

-
 How is Trump's 'freedom' war seen by those it aimed to help?
How is Trump's 'freedom' war seen by those it aimed to help?
-
Egyptians feel Iran war shockwaves as fuel prices jump

-
 Walker retires from international duty after 96 England caps
Walker retires from international duty after 96 England caps
-
Borthwick makes one change as England seek to avoid worst Six Nations

-
 Machida, Buriram advance in Asian Champions League
Machida, Buriram advance in Asian Champions League
-
Vietnam to tap emergency fund to cool surging fuel prices

-
 Chukwuemeka switches eligibility to Austria from England before World Cup
Chukwuemeka switches eligibility to Austria from England before World Cup
-
First group of Indonesians evacuated from Iran arrive home

-
 UK trial opens against Sony over PlayStation video game prices
UK trial opens against Sony over PlayStation video game prices
-
Leverkusen coach questions legality of Arsenal's set-piece tactics

-
 Russia committed 'crimes against humanity' in deporting Ukrainian children: UN inquiry
Russia committed 'crimes against humanity' in deporting Ukrainian children: UN inquiry
-
Oil plunges, stocks steady as Trump says Iran war over 'very soon'

-
 Citing 'strategic mistake' EU pivots back to nuclear energy
Citing 'strategic mistake' EU pivots back to nuclear energy
-
Journalists face restrictions, detention covering Mideast war

-
 Defiant Iran vows to block Gulf oil until US-Israel bombing stops
Defiant Iran vows to block Gulf oil until US-Israel bombing stops
-
Ex-footballer Barton charged with assault near golf club

-
 Real Madrid not inferior to Man City even without Mbappe: Arbeloa
Real Madrid not inferior to Man City even without Mbappe: Arbeloa
-
Finland warns end of Ukraine war could bring more Russian spying

-
 Japan survive Czech scare to stay unbeaten at World Baseball Classic
Japan survive Czech scare to stay unbeaten at World Baseball Classic
-
Italy buys rare Caravaggio portrait for 30 million euros

-
 Luis Enrique confident PSG can raise game ahead of Chelsea showdown
Luis Enrique confident PSG can raise game ahead of Chelsea showdown
-
Iran war sends prices in next door Turkmenistan soaring

-
 'Home' at last: Ghana grants citizenship to 150 members of African diaspora
'Home' at last: Ghana grants citizenship to 150 members of African diaspora
-
Japan upstarts Machida advance in Asian Champions League

-
 EU chief, Macron say Mideast war exposes Europe energy vulnerability
EU chief, Macron say Mideast war exposes Europe energy vulnerability
-
In which Pooh turns 100: Hunny-loving bear marks a milestone

-
 Volkswagen says to cut 50,000 jobs as profit slides
Volkswagen says to cut 50,000 jobs as profit slides
-
Ig Nobel prizes moving to Europe because US 'unsafe' to visit

-
 Greece hopes eco moorings will protect vital seagrass colonies
Greece hopes eco moorings will protect vital seagrass colonies
-
Iranian Kurds hunted by drones in Iraqi Kurdistan

-
 In southeast Pakistan, Ramadan brings Hindus and Muslims closer
In southeast Pakistan, Ramadan brings Hindus and Muslims closer
-
Red Cross launches Iran emergency appeal as needs soar

-
 German exports drop in setback to fragile recovery
German exports drop in setback to fragile recovery
-
French AI startup AMI announces $1 bn raised in funding

-
 Nicaragua ramping up repression of exiles: UN experts
Nicaragua ramping up repression of exiles: UN experts
-
Iran vows to fight on and block all Gulf oil

-
 Lego posts record profit despite geopolitical turmoil: CEO to AFP
Lego posts record profit despite geopolitical turmoil: CEO to AFP
-
India team to pocket $14 million for T20 World Cup win


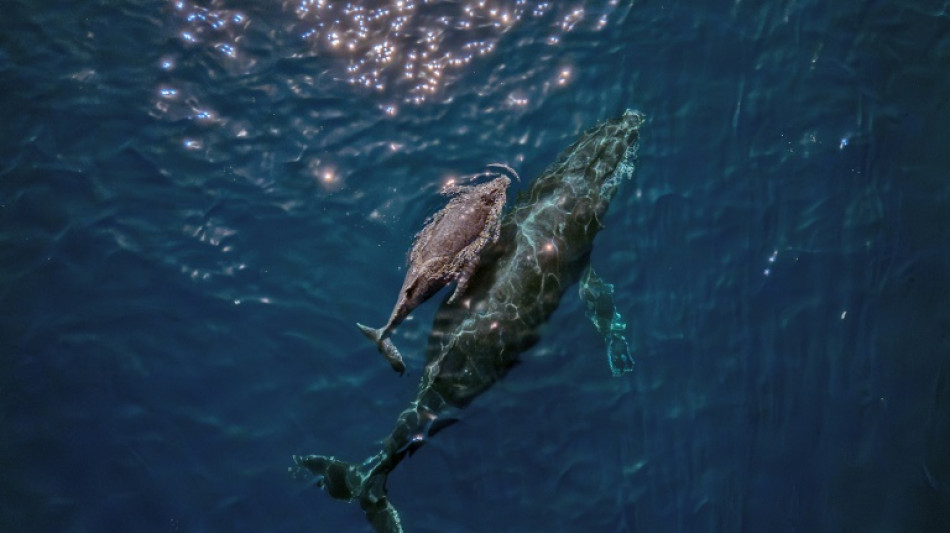
Whales 'cannot out-sing' human noise pollution
Baleen whales have evolved a special voice box to help them to sing underwater -- but this could also make them uniquely vulnerable to being drowned out by human noise pollution, according to new research published Wednesday.
Complex whale melodies, first recorded some 50 years ago, are known to play a key role in the social and reproductive communication of these massive marine mammals.
While toothed whales have a nasal vocal organ, filter-feeding baleen whales use a larynx, although scientists had not figured out exactly how it created the vocalisations.
In a new study published in the journal Nature, a team of scientists in Denmark, Austria, and the United States examined the larynxes of three stranded baleen whales -- the sei, minke, and humpback species -- using scanning and modelling techniques to reconstruct how they produce sound.
They found several differences from land mammals, including a U-shaped structure instead of vocal cords, that allows them to generate their low-frequency songs.
"We've never seen this in any other animal," lead author Coen Elemans, professor of bioacoustics at the University of Southern Denmark, told AFP.
"This is a completely novel adaptation, and we think this allowed these large whales to make sound in the water while basically holding their breath."
But the scientists also found a potentially serious challenge for the whales: the struggle to make themselves heard over noise pollution from ships.
- No escape -
Computer models showed that baleen whale songs can travel long distances through water, but at a maximum depth of 100 metres (330 feet) and at a frequency of up to 300 Hz -- within the range noise made by shipping vessels.
This means that whales in a noisy ocean soundscape are essentially trying to talk across a busy motorway or at a loud party: the further away you are, the less you'll be able to hear, Elemans said.
"It's really sad that baleen whale vocalisations exactly overlap with the sounds we make, predominantly with shipping noise, and there is no way for the whales to sing louder, at a higher frequency, or deeper in the water," Elemans said.
"These animals really can't escape this, and we really need to mitigate the noise we make."
They cannot even dive down to escape the din.
The deeper they go, the greater the pressure which reduces the volume of air available for vocalising, said Joy Reidenberg, a professor at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who was not involved in the study.
Noise pollution can force whales to change their behaviour, such as remaining silent until quiet returns, moving to another location, or trying to communicate over the noise –- the latter two requiring whales to exert extra energy, potentially weakening their body condition and affecting long-term survival, Reidenberg said.
She said that understanding whale vocalisations could aid conservation efforts by helping understand which depths are "critical habitats".
This is particularly important at mating sites where, depending on the season, noise pollution can disrupt reproduction.
"We must be smarter about when and where we put sound into the water," Reidenberg said.
Researchers say there is an urgent need to regulate underwater noise.
The harm goes beyond whales -- there is evidence that scores of marine species are negatively affected by underwater noise pollution, Melanie Lancaster, senior Arctic species specialist at the World Wildlife Fund, who was not involved in the study, told AFP.
"We know the most about marine mammals, which is why they feature so prominently, yet the impacts are much farther reaching, essentially impacting entire marine ecosystems," she said.
D.Cunningha--AMWN

