
-
 'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory
'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory
-
Indonesia landfill collapse kills four

-
 Equities plunge as energy prices soar on Mideast crisis
Equities plunge as energy prices soar on Mideast crisis
-
Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history

-
 Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring
-
Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis

-
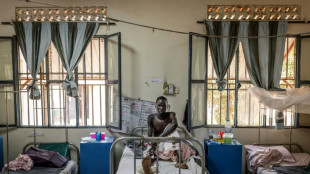 Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
-
Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival

-
 Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports
-
Iran launches missiles as Khamenei's son takes charge

-
 Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions
-
Gauff retires with 'scary' injury to send Eala through at Indian Wells

-
 Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader
-
Sabalenka, Osaka set Indian Wells clash as Gauff retires injured

-
 Wemby shines as Spurs thrash Rockets, Lakers down Knicks
Wemby shines as Spurs thrash Rockets, Lakers down Knicks
-
Troubled Spurs haunted by European ghosts in Atletico clash

-
 Double super-over drama to Allen's record ton: T20 World Cup moments
Double super-over drama to Allen's record ton: T20 World Cup moments
-
Liverpool go back to Galatasaray cauldron in Champions League last 16

-
 Pressure builds for Australia to offer Iran women's football team asylum
Pressure builds for Australia to offer Iran women's football team asylum
-
Hezbollah says fighting Israeli forces who landed in east Lebanon

-
 France to host G7 finance meeting on Mideast
France to host G7 finance meeting on Mideast
-
One year after arrest, Turkey opposition champion Imamoglu goes on trial

-
 Newcastle eye history in Champions League clash with Barcelona
Newcastle eye history in Champions League clash with Barcelona
-
Mercedes set gold standard at Australian GP but new F1 rules 'suck'

-
 Iran fires new missiles as Khamenei's son takes charge
Iran fires new missiles as Khamenei's son takes charge
-
Fake AI satellite imagery spurs US-Iran war disinformation

-
 Oscar nominee Benicio del Toro says 'One Battle' has 'heart'
Oscar nominee Benicio del Toro says 'One Battle' has 'heart'
-
Shelter rankings and shower-timing apps: Israelis, Palestinians adjust to Iranian rockets

-
 Sinner eases past Shapovalov, Zverev advances at Indian Wells
Sinner eases past Shapovalov, Zverev advances at Indian Wells
-
Trump defends Iran war decision as oil soars above $100

-
 InterContinental Hotels Group PLC Announces Transaction in Own Shares - March 09
InterContinental Hotels Group PLC Announces Transaction in Own Shares - March 09
-
Lobe Sciences Announces Appointment of Mr. Mirza Rahimani, CPA, CA as Chief Financial Officer
-
 Doncic, Reaves lead Lakers over Knicks
Doncic, Reaves lead Lakers over Knicks
-
Osaka tops Osorio to set Indian Wells Sabalenka clash

-
 Brilliant Bhatia snatches Arnold Palmer victory in playoff
Brilliant Bhatia snatches Arnold Palmer victory in playoff
-
Villarreal stay on Atletico's tail, Valencia snatch vital victory

-
 Genesis GV60 Magma before launch
Genesis GV60 Magma before launch
-
Macron to visit Cyprus as French warships deploy to counter Iran threat

-
 Milan edge derby to trim Inter's Serie A lead
Milan edge derby to trim Inter's Serie A lead
-
Speed cameras: Brazen rip-off or necessary?

-
 10 vessels attacked in Hormuz Strait: analysts
10 vessels attacked in Hormuz Strait: analysts
-
Germany: Electric car boom remains fragile

-
 Iran names Khamenei's son as new supreme leader
Iran names Khamenei's son as new supreme leader
-
Gambhir lauds India's 'courage' after T20 World Cup triumph

-
 Zverev holds off Nakashima to reach Indian Wells fourth round
Zverev holds off Nakashima to reach Indian Wells fourth round
-
Germany: Fuel rage and the 2026 election year

-
 In Istanbul, despite ban, thousands march for Women's Day
In Istanbul, despite ban, thousands march for Women's Day
-
Sabalenka sails into Indian Wells last 16

-
 Aaja Chemnitz, Greenland politician standing up to Trump
Aaja Chemnitz, Greenland politician standing up to Trump
-
NY police say device thrown near anti-Islam protest was IED


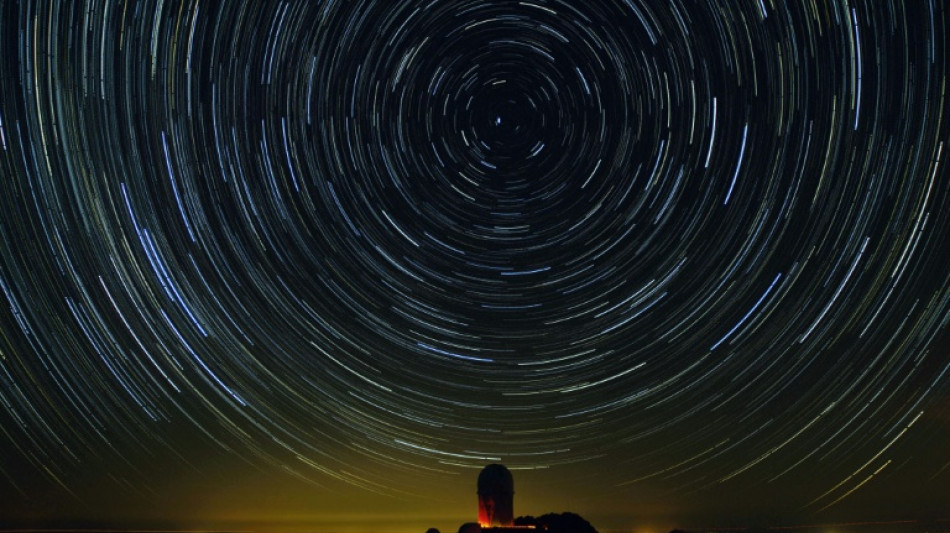
The universe's accelerated expansion might be slowing down
The universe is still expanding at an accelerating rate, but it may have slowed down recently compared to a few billion years ago, early results from the most precise measurement of its evolution yet suggested Thursday.
While the preliminary findings are far from confirmed, if they hold up it would further deepen the mystery of dark energy -- and likely mean there is something important missing in our understanding of the cosmos.
These signals of our universe's changing speeds were spotted by the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), which is perched atop a telescope at the Kitt Peak National Observatory in the US state of Arizona.
Each of the instrument's 5,000 fibre-optic robots can observe a galaxy for 20 minutes, allowing astronomers to chart what they have called the largest-ever 3D map of the universe.
"We measured the position of the galaxies in space but also in time, because the further away they are, the more we go back in time to a younger and younger universe," Arnaud de Mattia, a co-leader of the DESI data interpretation team, told AFP.
Just one year into its five-year survey, DESI has already drawn up a map which includes six million galaxies and quasars using light that stretches up to 11 billion years into the universe's past.
The results were announced at conferences in the United States and Switzerland on Thursday, ahead of a series of scientific papers being published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.
DESI is on a mission to shed light on the nature of dark energy -- a theoretical phenomenon thought to make up roughly 70 percent of the universe.
Another 25 percent of the universe is composed of the equally mysterious dark matter, leaving just five percent of normal matter -- such as everything you can see.
- An inconstant constant? -
For more than a century, scientists have known that the universe started expanding after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago.
But in the late 1990s, astronomers were shocked to discover it has been expanding at an ever-increasing rate.
This was a surprise because gravity from matter -- both normal and dark -- was thought to have been slowing the universe down.
But obviously something was making the universe expand at ever-faster speeds, and the name "dark energy" was given to this force.
More recently, it was discovered that the acceleration of the universe significantly sped up around six billion years after the Big Bang.
In the push-and-pull between matter and dark energy, the latter certainly seems to have the upper hand, according to the leading model of the universe called the Lambda CDM.
Under this model, the quickening expansion of the universe is called the "cosmological constant," which is closely linked to dark energy.
DESI director Michael Levi said that so far, the instrument's early results were showing "basic agreement with our best model of the universe".
"But we're also seeing some potentially interesting differences which could indicate that dark energy is evolving with time," Levi said in a statement.
In other words, the data "seems to show that the cosmological constant Lambda is not really a constant," because dark energy would be displaying "dynamic" and changing behaviour, De Mattia said.
- Slowing down in old age -
This could suggest that -- after switching into high gear six billion years after the Big Bang -- the speed at which the universe has been expanding has been "slowing down in recent times," DESI researcher Christophe Yeche said.
Whether dark energy does in fact change over time would need to be verified by more data from DESI and other instruments, such as the space telescope Euclid.
But if it was confirmed, our understanding of the universe will likely have to be changed to accommodate for this strange behaviour.
For example, the cosmological constant could be replaced by some kind of field linked to some as-yet-unknown particle.
It could even necessitate updating the equations of Einstein's theory of relativity "so that they behave slightly differently on the scale of large structures," De Mattia said.
But we are not there yet.
The history of science is full of examples in which "deviations of this type have been observed then resolved over time," De Mattia emphasised.
After all, Einstein's theory of relativity has withstood more than a century of scientific poking and prodding and still stands stronger than ever.
F.Schneider--AMWN


