
-
 France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
France, allies preparing bid to 'gradually' reopen Strait of Hormuz
-
Anthropic takes Trump administration to court over Pentagon row

-
 Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
Antarctic sea ice improves after four years of extreme lows: US scientists
-
Beating Barca would make us Newcastle legends: Howe

-
 Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
Iran war sends crude prices soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
-
Zelensky says 11 countries asking Ukraine for drone help against Iran

-
 France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz: Macron
-
Ships brandish China-links to weave through Strait of Hormuz

-
 Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
Trump says Australia will grant asylum to Iran women footballers
-
War in the Middle East: economic impact around the world

-
 Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF
Huge numbers at imminent risk from S.Sudan army offensive: MSF
-
G7 'not there yet' on release of oil reserves: French minister

-
 Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object
Live Nation settles antitrust case with US Justice Dept, states object
-
EU lawmakers set to greenlight 'return hubs' for migrants

-
 Macron says France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz
Macron says France, allies preparing 'defensive' mission to reopen Strait of Hormuz
-
Water emerges as a dangerous new war target

-
 Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
Scotland locks Cummings and Brown ruled out of Ireland Six Nations clash
-
Stocks slide as oil soars past $100 on Mideast war

-
 NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
NATO intercepts second Iran missile in Turkish airspace: Ankara
-
South Korea squeeze into World Baseball Classic quarter-finals

-
 Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
Premier League teams are faster: Atletico's Simeone on Spurs clash
-
North Korea cancels Pyongyang international marathon: tour agency

-
 Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
Ukrainian bank worker detained by Hungary was forcibly medicated: Kyiv
-
Macron discusses security in Cyprus, plans aircraft carrier visit

-
 UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war
UK PM Starmer says 'monitoring' economic impact of Iran war
-
Stranded Iran sailors put Sri Lanka, India in diplomatic dilemma

-
 Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch
Bangladesh scraps light displays as Mideast war worsens fuel crunch
-
Stocks tumble, oil soars past $100 on Mideast war

-
 Iran war sends oil price soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
Iran war sends oil price soaring as Khamenei son takes charge
-
Incensed North Korea briefly refuse to play in bitter Asian Cup loss

-
 Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu
Landmark trial opens for Turkish opposition champion Imamoglu
-
Indonesia landfill collapse kills five

-
 African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again
African players in Europe: Marmoush torments Newcastle again
-
Kenya flash floods death toll rises to 45

-
 Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home
Asian economies move to limit Mideast war's impact at home
-
Jail for up to 16 years for Australian hitmen who killed compatriot in Bali

-
 Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
Russia wins first Paralympic gold since 2014
-
'T20 kings': nation celebrates Indian romp to World Cup glory

-
 Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
Indonesia landfill collapse kills four
-
Equities plunge as energy prices soar on Mideast crisis

-
 Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history
Unstoppable India target Olympic gold after making World Cup history
-
Khamenei's son takes charge as Iran war sends oil price soaring

-
 Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis
Asian equities plunge as oil soars 30% on Mideast crisis
-
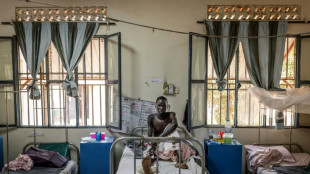
Dead on arrival: South Sudan's devastated health system
-
 Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival
Redknapp and The Jukebox Man the headline act at Cheltenham Festival
-
Singer Rihanna's LA mansion struck by gunfire: reports

-
 Iran launches missiles as Khamenei's son takes charge
Iran launches missiles as Khamenei's son takes charge
-
Sharp drop in Chinese military aircraft near Taiwan raises questions

-
 Gauff retires with 'scary' injury to send Eala through at Indian Wells
Gauff retires with 'scary' injury to send Eala through at Indian Wells
-
Mojtaba Khamenei: son and successor to Iran's supreme leader


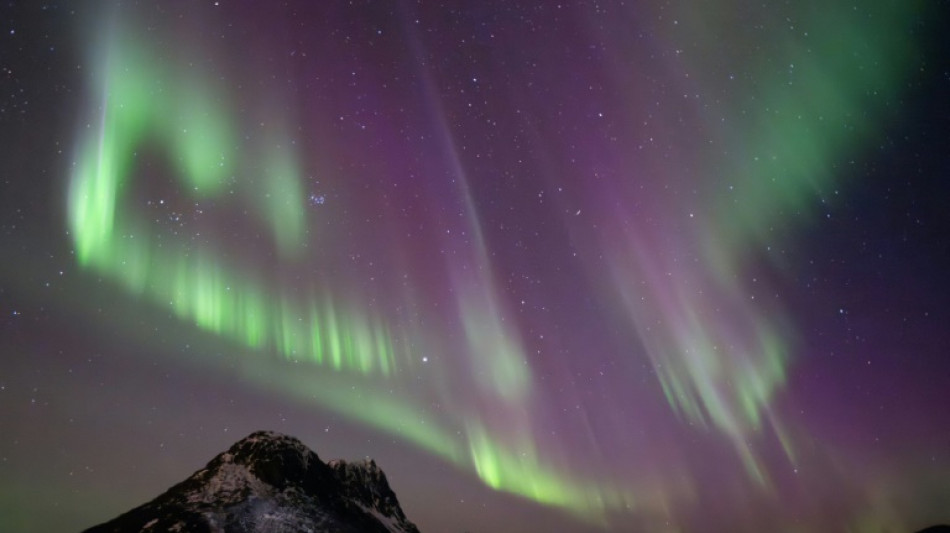
Powerful solar storm pummels Earth, threatening disruption
A huge solar storm begun pummeling Earth on Friday, bringing possible disruptions to satellites and power grids -- and stunning auroras -- as it intensifies.
The first of several coronal mass ejections (CMEs) -- expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun -- arrived in the early afternoon, US eastern time, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said.
Severe geomagnetic storm conditions are expected to persist over the weekend, and come as the Sun approaches the peak of an 11-year cycle that brings heightened activity.
"We have notified all of our infrastructure operators that we coordinate with, such as satellite operators, communication folks... and of course, the power grid here in North America," space weather forecaster Shawn Dahl told reporters.
The US Federal Aviation administration, however, said Friday in a social media post that "we do not anticipate any significant impacts to the national airspace system due to the potential geomagnetic storm."
Unlike solar flares, which travel at the speed of light and reach Earth in around eight minutes, CMEs travel at a more sedate pace, with officials putting the current average at 800 kilometers (500 miles) per second.
There were at one point up to seven CMEs in transit, emanating from a sunspot cluster that is 16 times wider than our planet, but it's not clear how they have merged together along the way.
- 'Go outside tonight and look' -
Mathew Owens, a professor of space physics at the University of Reading, told AFP the effects would be largely felt over the planet's northern and southern latitudes. How far they would extend would depend on the storm's final strength.
"Northern Canada, Scotland, those kinds of places are going to get some good auroras -- I think we can confidently say that, but it may build," he said, with the situation mirrored in the southern hemisphere.
"Go outside tonight and look would be my advice because if you see the aurora, it's quite a spectacular thing," he added. If people have eclipse glasses, they can also look for the sunspot cluster during the day.
In the United States, this could be as far south as Northern California and Alabama, officials said.
NOAA's Brent Gordon encouraged the public to try to capture the night sky with phone cameras even if they can't see auroras with their naked eyes.
"Just go out your back door and take a picture with the newer cell phones and you'd be amazed at what you see in that picture versus what you see with your eyes."
- Spacecraft and pigeons -
Fluctuating magnetic fields associated with geomagnetic storms induce currents in long wires, including power lines, which can potentially lead to blackouts. Long pipelines can also become electrified, leading to engineering problems.
Spacecraft are also at risk from high doses of radiation, though the atmosphere prevents this from reaching Earth.
NASA has a dedicated team looking into astronaut safety, and can ask astronauts on the International Space Station to move to places within the outpost that are better shielded.
Pigeons and other species that have internal biological compasses could also be affected. Pigeon handlers have noted a reduction in birds coming home during geomagnetic storms, according to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
In October 2003, geomagnetic storms rated as "extreme" led to blackouts in Sweden and damaged power transformers in South Africa. Impacts are also possible on high-frequency radio communication, GPS and satellites.
Officials said people should have the normal backup plans in place for power outages, such as having flashlights, batteries and radios at hand.
The most powerful geomagnetic storm in recorded history, known as the Carrington Event, occurred in September 1859, named after British astronomer Richard Carrington.
Excess currents on telegraph lines at that time caused electrical shocks to technicians and even set some telegraph equipment ablaze.
L.Durand--AMWN


