
-
 Police, pro-Kurd protesters clash at Turkey border with Syria
Police, pro-Kurd protesters clash at Turkey border with Syria
-
Thai forces razed Cambodian homes on border: rights group

-
 Jellyfish-inspired Osaka battles into Australian Open round two
Jellyfish-inspired Osaka battles into Australian Open round two
-
Valentino taught us to respect women, says partner

-
 Mercedes chief designer Owen to leave F1 team
Mercedes chief designer Owen to leave F1 team
-
Trump unloads on allies as Davos showdown looms

-
 Moscow revels in Trump's Greenland plans but keeps concerns quiet
Moscow revels in Trump's Greenland plans but keeps concerns quiet
-
Global tourism hit new record level in 2025: UN

-
 Senegal poised to party with parade honouring AFCON champs
Senegal poised to party with parade honouring AFCON champs
-
Dogsled diplomacy in Greenland proves elusive for US

-
 Almost half of Kyiv without heat, power, after Russian attack
Almost half of Kyiv without heat, power, after Russian attack
-
European stocks sink, gold hits high on escalating tariff fears

-
 EU vows 'unflinching' response to Trump's Greenland gambit
EU vows 'unflinching' response to Trump's Greenland gambit
-
Osaka steals show at Australian Open as Sinner strolls through

-
 Brignone impresses in first run of Kronplatz giant slalom in World Cup comeback
Brignone impresses in first run of Kronplatz giant slalom in World Cup comeback
-
Osaka emerges for Melbourne opener under white hat and umbrella

-
 Malawi suffers as US aid cuts cripple healthcare
Malawi suffers as US aid cuts cripple healthcare
-
Bessent says Europe dumping US debt over Greenland would 'defy logic'

-
 Freeze, please! China's winter swimmers take the plunge
Freeze, please! China's winter swimmers take the plunge
-
Talks between Damascus, Kurdish-led forces 'collapse': Kurdish official to AFP

-
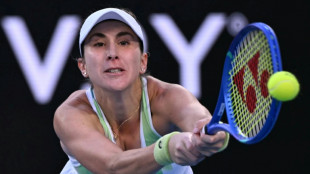 In-form Bencic makes light work of Boulter at Australian Open
In-form Bencic makes light work of Boulter at Australian Open
-
Sinner into Melbourne round two as opponent retires hurt

-
 Israel begins demolitions at UNRWA headquarters in east Jerusalem
Israel begins demolitions at UNRWA headquarters in east Jerusalem
-
Almost half of Kyiv without heat, power, after Russian attack: govt

-
 Veteran Monfils exits to standing ovation on Australian Open farewell
Veteran Monfils exits to standing ovation on Australian Open farewell
-
Precision-serving former finalist Rybakina powers on in Melbourne

-
 South Korea's women footballers threaten boycott over conditions
South Korea's women footballers threaten boycott over conditions
-
Australian lawmakers back stricter gun, hate crime laws

-
 EU wants to keep Chinese suppliers out of critical infrastructure
EU wants to keep Chinese suppliers out of critical infrastructure
-
AI reshaping the battle over the narrative of Maduro's US capture

-
 Penguins bring forward breeding season as Antarctica warms: study
Penguins bring forward breeding season as Antarctica warms: study
-
Ukrainian makes soldier dad's 'dream come true' at Australian Open

-
 'Timid' Keys makes shaky start to Australian Open title defence
'Timid' Keys makes shaky start to Australian Open title defence
-
Indiana crowned college champions to complete fairytale season

-
 South Koreans go cuckoo for 'Dubai-style' cookies
South Koreans go cuckoo for 'Dubai-style' cookies
-
Harris leads Pistons past Celtics in thriller; Thunder bounce back

-
 Tjen first Indonesian to win at Australian Open in 28 years
Tjen first Indonesian to win at Australian Open in 28 years
-
Long-delayed decision due on Chinese mega-embassy in London

-
 Djokovic jokes that he wants slice of Alcaraz's winnings
Djokovic jokes that he wants slice of Alcaraz's winnings
-
Trump tariff threat 'poison' for Germany's fragile recovery

-
 Tourists hit record in Japan, despite plunge from China
Tourists hit record in Japan, despite plunge from China
-
Jittery Keys opens Melbourne defence as Sinner begins hat-trick quest

-
 The impact of Trump's foreign aid cuts, one year on
The impact of Trump's foreign aid cuts, one year on
-
Belgian court weighs trial for ex-diplomat over Lumumba killing

-
 Inside China's buzzing AI scene year after DeepSeek shock
Inside China's buzzing AI scene year after DeepSeek shock
-
Asian markets sink, silver hits record as Greenland fears mount

-
 Shark bites surfer in Australian state's fourth attack in 48 hours
Shark bites surfer in Australian state's fourth attack in 48 hours
-
North Korea's Kim sacks vice premier, rails against 'incompetence'

-
 Spain mourns as train crash toll rises to 40
Spain mourns as train crash toll rises to 40
-
'Very nervous' Keys makes shaky start to Australian Open title defence


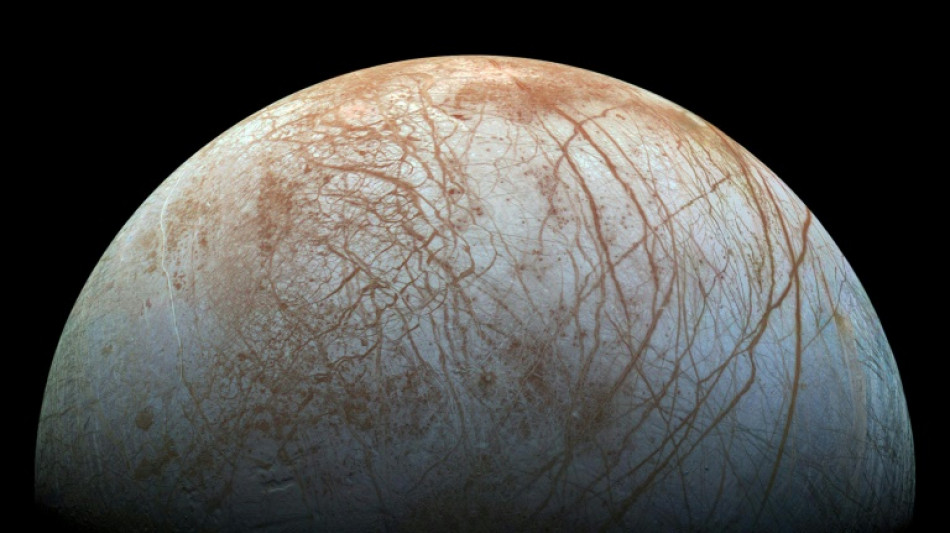
Water on Jupiter's moon closer to surface than thought: study
Ridges that criss-cross the icy surface of Jupiter's moon Europa indicate there are shallow pockets of water beneath, boosting hopes in the search for extra-terrestrial life, scientists said Tuesday.
Europa has long been a candidate for finding life in our solar system due to its vast ocean, which is widely thought to contain liquid water -- a key ingredient for life.
There is a problem: the ocean is predicted to be buried 25-30 kilometres (15-17 miles) beneath the moon's icy shell.
However water could be closer to the surface than previously thought, according to new research published in the journal Nature Communications.
The finding came partly by chance, when geophysicists studying an ice sheet in Greenland watched a presentation about Europa and spotted a feature they recognised.
"We were working on something totally different related to climate change and its impact on the surface of Greenland when we saw these tiny double ridges," said the study's senior author Dustin Schroeder, a geophysics professor at Stanford University.
They realised that the M-shaped icy crests on Greenland looked like smaller versions of double ridges on Europa, which are the most common feature on the moon.
Europa's double ridges were first photographed by NASA's Galileo spacecraft in the 1990s, but little was known about how they were formed.
The scientists used ice-penetrating radar to observe that Greenland's ridges were formed when water pockets around 30 metres (100 feet) below the ice sheet's surface refroze and fractured.
"This is particularly exciting, because scientists have been studying double ridges on Europa for more than 20 years and have not yet come to a definitive answer for how double ridges form," said lead study author Riley Culberg, an electrical engineering PhD student at Stanford.
"This was the first time that we were able to watch something similar happen on Earth and actually observe the subsurface processes that led to the formation of the ridges," he told AFP.
"If Europa's double ridges also form in this way, it suggests that shallow water pockets must have been (or maybe still are) extremely common."
- 'Life has a shot' -
Europa's water pockets could be buried five kilometres beneath the moon’s ice shell -- but that would still be much easier to access than the far deeper ocean.
"Particularly if such water pockets form because ocean water was forced up through fractures into the ice shell, then it's possible that they would preserve evidence of any life in the ocean itself," Culberg said.
Water closer to the surface would also contain "interesting chemicals" from space and other moons, increasing the "possibility that life has a shot," Schroeder said in a statement.
We may not have too long to wait to find out more.
NASA's Europa Clipper mission, scheduled to launch in 2024 and arrive in 2030, will have ice-penetrating radar equipment similar to that used by the scientists studying Greenland's double ridges.
The spacecraft is unlikely to find definitive proof of life because it will not land on Europa, instead flying by and analysing it.
But hopes remain high. The moon's ocean is predicted to have more water than all of Earth's seas combined, according to the Europa Clipper's website.
"If there is life in Europa, it almost certainly was completely independent from the origin of life on Earth... that would mean the origin of life must be pretty easy throughout the galaxy and beyond," project scientist Robert Pappalardo said on the website.
S.F.Warren--AMWN



