
-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued from torpedoed Iranian vessel
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued from torpedoed Iranian vessel
-
Piastri takes blame for crashing out before home Australian Grand Prix

-
 Turkey's jailed mayor says demand for change cannot be stopped
Turkey's jailed mayor says demand for change cannot be stopped
-
Venezuela frees more political prisoners under amnesty law

-
 Dominant Russell wins Australian Grand Prix in Mercedes 1-2
Dominant Russell wins Australian Grand Prix in Mercedes 1-2
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round, Djokovic fights through

-
 Iran says can fight for months as Israel strikes Beirut hotel
Iran says can fight for months as Israel strikes Beirut hotel
-
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors

-
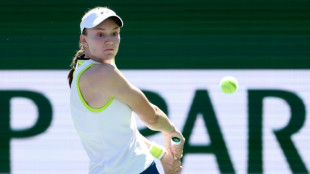 Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
-
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic

-
 Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise
-
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users

-
 Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record
-
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide

-
 White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje
-
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs

-
 Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up
-
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent

-
 Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries
-
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent

-
 German state election a test for Chancellor Merz
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz
-
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon

-
 Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through
-
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase

-
 Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?
-
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener

-
 Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup
-
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer

-
 Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops
-
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United

-
 Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran
-
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad

-
 Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1
-
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more

-
 Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao
-
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare

-
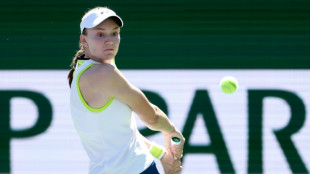 Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways

-
 As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'
-
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war

-
 US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations
-
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller

-
 Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'
-
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad

-
 Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot
-
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France

-
 Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall
-
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'

-
 Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time
-
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction


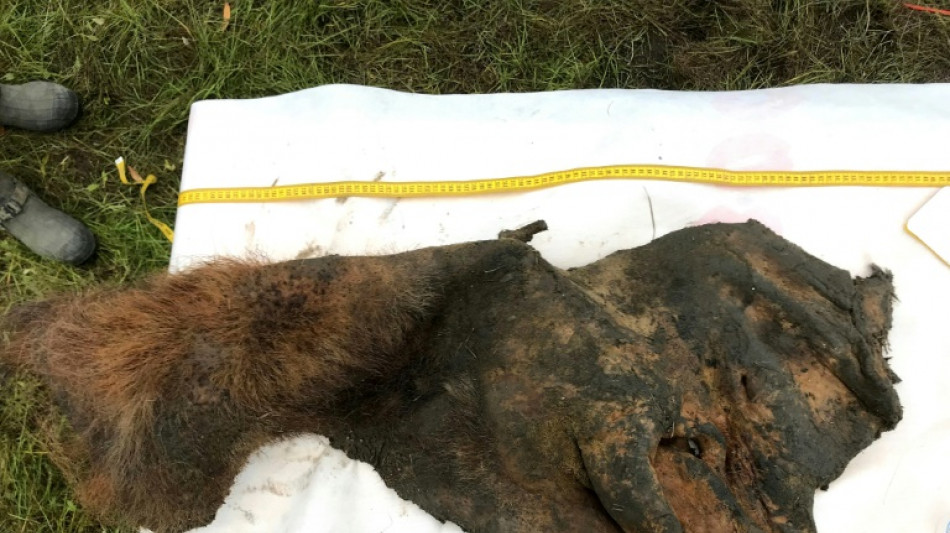
3D genome extracted from 'freeze-dried' woolly mammoth
About 52,000 years ago, the skinned hide of a Siberian woolly mammoth was exposed to conditions so frigid that it spontaneously freeze-dried, locking its DNA fragments into place.
In a study published Thursday in the journal Cell, scientists reported using this remarkable sample to reconstruct the animal's genome in three dimensions -- a breakthrough that could yield important new insights about extinct species and even boost efforts to bring them back to life.
Until now, ancient DNA specimens have only been found in short, scrambled fragments, severely limiting the amount of information researchers could extract.
"Now we show that, at least under some circumstances, it's not just those snippets of that DNA that survive, but they survive in such a way that preserves the original arrangement," co-author Olga Dudchenko, a geneticist at Baylor College of Medicine, told AFP.
Understanding the 3D architecture of an organism's genome —- the complete set of its DNA -- is crucial for identifying which genes are active in specific tissues, revealing why brain cells think, heart cells beat, and immune cells fight disease.
It was long assumed that due to the rapid degradation of very small particles, such information would inevitably be lost to history.
But around a decade ago, an international team of scientists set out to find an ancient sample where the 3D organization of the DNA remained intact such that it could be fully reconstructed with a new analytical technique.
Their quest led them to an exceptionally well-preserved woolly mammoth sample, excavated in northeastern Siberia in 2018.
Whether the hirsute pachyderm -— a female with a distinctive mullet-style hairdo -- died naturally or was killed by humans is unknown. However, it does appear that early humans skinned her, leaving tissue around the head, neck, and left ear intact, according to Dudchenko.
- Woolly mammoth jerky -
The team hypothesizes that the skin cooled and dehydrated, transitioning into a glasslike state that trapped its molecules in place and preserved the shape of its chromosomes, or the threadlike structures that hold DNA strands.
Essentially, they had discovered a piece of freeze-dried woolly mammoth jerky.
To test the resilience of jerky, they subjected lab-made and store-bought beef jerky pieces to a series of tests simulating the kind of damage ancient samples might encounter over millennia.
"We fired a shotgun at it. We ran over it with a car. We had a former starting pitcher for the Houston Astros throw a fastball at it," said Cynthia Perez Estrada, co-author of the study and a researcher at Baylor College of Medicine and Rice University.
The jerky would break into tiny bits, shattering as dramatically as window glass at times. "But at the nano-scale, the chromosomes were intact, unchanged," said Perez Estrada in a statement.
One significant discovery from their research established that mammoths had 28 pairs of chromosomes. The finding aligns with the 28 chromosomal pairs found in elephants, the closest living relatives of mammoths, "but before this study, it was anybody's guess," said Dudchenko.
- 'Fossil chromosomes' -
The team's analysis also identified several "candidate" genes which might be responsible for what made woolly mammoths woolly -- including a gene responsible for long, thick eyelashes, and another associated with sparse sweat glands.
Erez Lieberman Aiden of Baylor College of Medicine, who co-led the team, told AFP that while the researchers' goal was not to bring mammoths back, the information they gleaned could be used for such efforts.
A Japanese team is looking at cloning woolly mammoths, while a group in the United States is aiming to create genetically "mammothized" elephants.
Within the skin, "96 percent of genes are basically in the same activity state as an elephant," said Aiden, meaning that scientists working on de-extinction could now focus on the remaining four percent.
The team now hopes that the benefit of their study will extend far beyond their special sample and open a new chapter in paleogenetics if other such "fossil chromosomes" can be found.
The Arctic permafrost remains a promising place to look, and it is also possible that mummification from ancient civilizations in warmer climates could preserve genomic structures too, according to Dudchenko.
Th.Berger--AMWN



