
-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
-
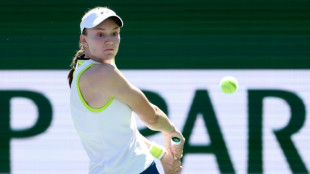
Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
-
 USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
-
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise

-
 Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
-
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record

-
 Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
-
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje

-
 Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
-
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up

-
 US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
-
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries

-
 India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
-
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz

-
 Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through

-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
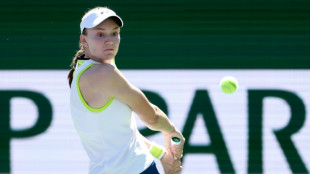
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'

-
 Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
-
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot

-
 'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
-
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall

-
 Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
-
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time

-
 Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
-
Griezmann 'will continue' with Atletico despite MLS option: sporting director

-
 Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
-
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France

-
 Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
-
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels

-
 Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
-
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes


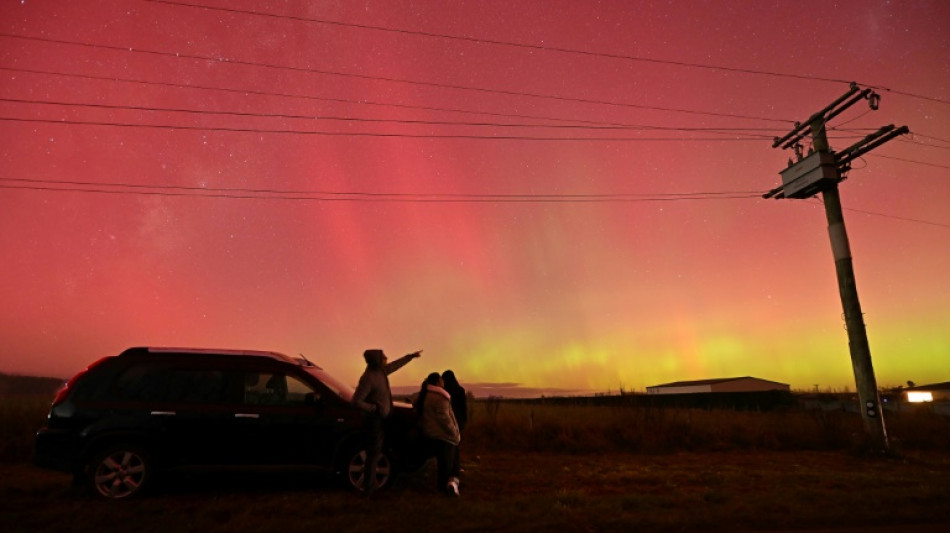
Solar storms could cause more auroras on Tuesday night
Massive explosions on the Sun have triggered warnings of geomagnetic storms that could create dazzling auroras in the northern United States, Europe and southern Australia on Tuesday night.
In May, the most powerful geomagnetic storm to strike Earth in more than two decades lit up night skies with colourful light displays in Hawaii, Spain, South Africa and other places far from the extreme latitudes where they are normally seen.
These storms are caused by coronal mass ejections (CMEs) -- expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun which take days to reach Earth.
At least four CMEs that erupted in recent days are headed towards Earth, the US-based National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said late Monday.
They will arrive from Tuesday to Thursday, with "geomagnetic storm watches" declared by the NOAA on those days.
But "the brunt of the activity is most likely" to come on Tuesday, when there is a "strong" geomagnetic storm warning of G3, the NOAA said.
May's record storms were classified as the most extreme level of G5. This means any potential auroras this week are unlikely to stray as far, or as be as powerful, as those seen earlier this year.
But if the current forecast is correct, during the late evening hours in the US on Tuesday, an "aurora could become visible as far south as the northeast US through the upper Midwest and across the rest of the northern states to include northern Oregon", the NOAA said.
"With a bit of luck," aurora borealis -- also known as the northern lights -- could also be seen in areas such as England, northern Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium, according to the website SpaceWeatherLive.
Australia's Bureau of Meteorology said that a sequence of CMEs arriving in the next few days mean that aurora australis might be visible in some areas.
- 'Cannibal CME' -
When CMEs erupt, they shoot around a billion tons of plasma -- with an accompanying magnetic field -- from the Sun towards our home planet.
One of the CMEs coming towards Earth this week merged with another, forming what is called a "Cannibal CME", according to spaceweather.com.
The NOAA warned that more CMEs are continuing to erupt, so more could be coming our way.
When the CMEs slam into Earth's magnetosphere, they can create geomagnetic storms.
These storms can mess with satellites orbiting Earth and affect things like radio signals and GPS positioning systems.
They can also knock out electricity grids -- the "Halloween Storms" of October 2003 sparked blackouts in Sweden and damaged power infrastructure in South Africa.
Astronauts on the International Space Station often shelter during extreme solar activity to avoid being exposed to radiation.
Numerous strong solar flares -- huge explosions on the Sun's surface which can cause CMEs -- have also been emitted in recent days.
Most CMEs and flares come from sunspots, which are massive, darker areas of intense activity on the solar surface. The sunspot cluster that caused May's storms was 17 times the size of Earth.
More geomagnetic storms could be yet to come, because solar activity is only just approaching the peak of its roughly 11-year cycle.
The peak -- called "solar maximum" -- is expected between late 2024 and early 2026.
X.Karnes--AMWN



