
-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
-
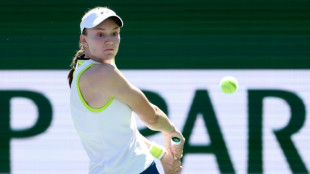
Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
-
 USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
-
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise

-
 Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
-
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record

-
 Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
-
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje

-
 Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
-
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up

-
 US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
-
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries

-
 India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
-
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz

-
 Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through

-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
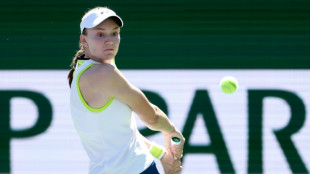
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'

-
 Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
-
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot

-
 'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
-
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall

-
 Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
-
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time

-
 Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
-
Griezmann 'will continue' with Atletico despite MLS option: sporting director

-
 Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
-
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France

-
 Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
-
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels

-
 Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
-
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes


Inbred, gibberish or just MAD? Warnings rise about AI models
When academic Jathan Sadowski reached for an analogy last year to describe how AI programs decay, he landed on the term "Habsburg AI".
The Habsburgs were one of Europe's most powerful royal houses, but entire sections of their family line collapsed after centuries of inbreeding.
Recent studies have shown how AI programs underpinning products like ChatGPT go through a similar collapse when they are repeatedly fed their own data.
"I think the term Habsburg AI has aged very well," Sadowski told AFP, saying his coinage had "only become more relevant for how we think about AI systems".
The ultimate concern is that AI-generated content could take over the web, which could in turn render chatbots and image generators useless and throw a trillion-dollar industry into a tailspin.
But other experts argue that the problem is overstated, or can be fixed.
And many companies are enthusiastic about using what they call synthetic data to train AI programs. This artificially generated data is used to augment or replace real-world data. It is cheaper than human-created content but more predictable.
"The open question for researchers and companies building AI systems is: how much synthetic data is too much," said Sadowski, lecturer in emerging technologies at Australia's Monash University.
- 'Mad cow disease' -
Training AI programs, known in the industry as large language models (LLMs), involves scraping vast quantities of text or images from the internet.
This information is broken into trillions of tiny machine-readable chunks, known as tokens.
When asked a question, a program like ChatGPT selects and assembles tokens in a way that its training data tells it is the most likely sequence to fit with the query.
But even the best AI tools generate falsehoods and nonsense, and critics have long expressed concern about what would happen if a model was fed on its own outputs.
In late July, a paper in the journal Nature titled "AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data" proved a lightning rod for discussion.
The authors described how models quickly discarded rarer elements in their original dataset and, as Nature reported, outputs degenerated into "gibberish".
A week later, researchers from Rice and Stanford universities published a paper titled "Self-consuming generative models go MAD" that reached a similar conclusion.
They tested image-generating AI programs and showed that outputs become more generic and strafed with undesirable elements as they added AI-generated data to the underlying model.
They labelled model collapse "Model Autophagy Disorder" (MAD) and compared it to mad cow disease, a fatal illness caused by feeding the remnants of dead cows to other cows.
- 'Doomsday scenario' -
These researchers worry that AI-generated text, images and video are clearing the web of usable human-made data.
"One doomsday scenario is that if left uncontrolled for many generations, MAD could poison the data quality and diversity of the entire internet," one of the Rice University authors, Richard Baraniuk, said in a statement.
However, industry figures are unfazed.
Anthropic and Hugging Face, two leaders in the field who pride themselves on taking an ethical approach to the technology, both told AFP they used AI-generated data to fine-tune or filter their datasets.
Anton Lozhkov, machine learning engineer at Hugging Face, said the Nature paper gave an interesting theoretical perspective but its disaster scenario was not realistic.
"Training on multiple rounds of synthetic data is simply not done in reality," he said.
However, he said researchers were just as frustrated as everyone else with the state of the internet.
"A large part of the internet is trash," he said, adding that Hugging Face already made huge efforts to clean data -- sometimes jettisoning as much as 90 percent.
He hoped that web users would help clear up the internet by simply not engaging with generated content.
"I strongly believe that humans will see the effects and catch generated data way before models will," he said.
J.Williams--AMWN



