
-
 A rough guide to F1 rule changes for 2026
A rough guide to F1 rule changes for 2026
-
At least 25 killed at Pakistan's pro-Iran weekend protests

-
 Israel kills 31 in Lebanon, vows to expand strikes after Hezbollah fire
Israel kills 31 in Lebanon, vows to expand strikes after Hezbollah fire
-
Myanmar grants amnesty to over 7,000 convicted of 'terrorist group' support

-
 Riyadh's King Fahd stadium to host 2027 Asian Cup final
Riyadh's King Fahd stadium to host 2027 Asian Cup final
-
'Superman Sanju' toast of India after T20 World Cup heroics

-
 Travel chaos, but F1 season-opener in Australia 'ready to go'
Travel chaos, but F1 season-opener in Australia 'ready to go'
-
Lunar New Year heartache for Chinese team at Women's Asian Cup

-
 El Nino may return in 2026 and make planet even hotter
El Nino may return in 2026 and make planet even hotter
-
Somaliland's Israel deal could put Berbera port at risk

-
 Texas primaries launch midterm battle with Trump agenda at stake
Texas primaries launch midterm battle with Trump agenda at stake
-
How a Syrian refugee chef met Britain's King Charles

-
 Bangladesh tackle gender barriers to reach Women's Asian Cup
Bangladesh tackle gender barriers to reach Women's Asian Cup
-
Argentina's Milei says wants US 'strategic alliance' to be state policy

-
 'Sinners' wins top prize at Screen Actors Guild awards
'Sinners' wins top prize at Screen Actors Guild awards
-
New rules, same old suspects as F1 revs up for 2026 season

-
 World Cup tickets: Huge demand and sky-high prices
World Cup tickets: Huge demand and sky-high prices
-
List of key Actor Award winners

-
 Trump hunkers down after Iran strikes
Trump hunkers down after Iran strikes
-
China's leaders gather for key strategy session as challenges grow

-
 UK toughens asylum rules to discourage migration
UK toughens asylum rules to discourage migration
-
Israel hits Lebanon after Hezbollah fire, expanding Iran war

-
 CBS in turmoil as US media feels pressure under Trump
CBS in turmoil as US media feels pressure under Trump
-
Messi bags double as Miami battle back to down Orlando

-
 Greenland is 'open for business' -- kind of, says business leader
Greenland is 'open for business' -- kind of, says business leader
-
Canada's Carney to mend rift, boost trade as he meets India's Modi

-
 Crude soars, stocks drop after US strikes on Iran
Crude soars, stocks drop after US strikes on Iran
-
Iran war spreads across region as US, Israel suffer losses

-
 Miriam Margolyes tackles aging in Oscar-nominated short
Miriam Margolyes tackles aging in Oscar-nominated short
-
Recognition, not competition, for Oscar-nominated foreign filmmakers

-
 Israel, Hezbollah trade fire: latest developments in Iran war
Israel, Hezbollah trade fire: latest developments in Iran war
-
Israel strikes Tehran: latest developments in Iran war

-
 Trump vows to avenge first US deaths as Iran war intensifies
Trump vows to avenge first US deaths as Iran war intensifies
-
MWC 2026: Amdocs Unveils CES26, an Agent-driven BSS-OSS-Network Suite, powered by the Amdocs aOS Cognitive Core

-
 MWC 2026: Amdocs Launches Global eSIM Traveler Solution, Enabling Telcos to Reclaim the Roaming Journey
MWC 2026: Amdocs Launches Global eSIM Traveler Solution, Enabling Telcos to Reclaim the Roaming Journey
-
Empire Joins Western Australia Delegation

-
 InterContinental Hotels Group PLC Announces Transaction in Own Shares - March 02
InterContinental Hotels Group PLC Announces Transaction in Own Shares - March 02
-
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Receipt of First Tranche of Grant

-
 Lowry collapses late again, Echavarria snatches victory in Cognizant Classic
Lowry collapses late again, Echavarria snatches victory in Cognizant Classic
-
Aubameyang strikes twice as Marseille edge Lyon in Ligue 1

-
 Infantino says players who cover mouths when speaking could be sent off
Infantino says players who cover mouths when speaking could be sent off
-
Bolsonaro son rallies the right as thousands protest Brazil government

-
 Juve stay in Champions League hunt with last-gasp Roma draw
Juve stay in Champions League hunt with last-gasp Roma draw
-
Maersk suspends vessel transit through Strait of Hormuz

-
 France, Germany, UK ready to take 'defensive action' against Iran
France, Germany, UK ready to take 'defensive action' against Iran
-
Knicks halt Spurs' 11-game NBA winning streak

-
 EU warns against long war, urges 'credible transition' in Iran
EU warns against long war, urges 'credible transition' in Iran
-
Bored of peace? Trump keeps choosing war

-
 Arteta embraces Arsenal's 'Set-Piece FC' label after corners sink Chelsea
Arteta embraces Arsenal's 'Set-Piece FC' label after corners sink Chelsea
-
Sevilla rescue derby draw to deal Betis top four setback


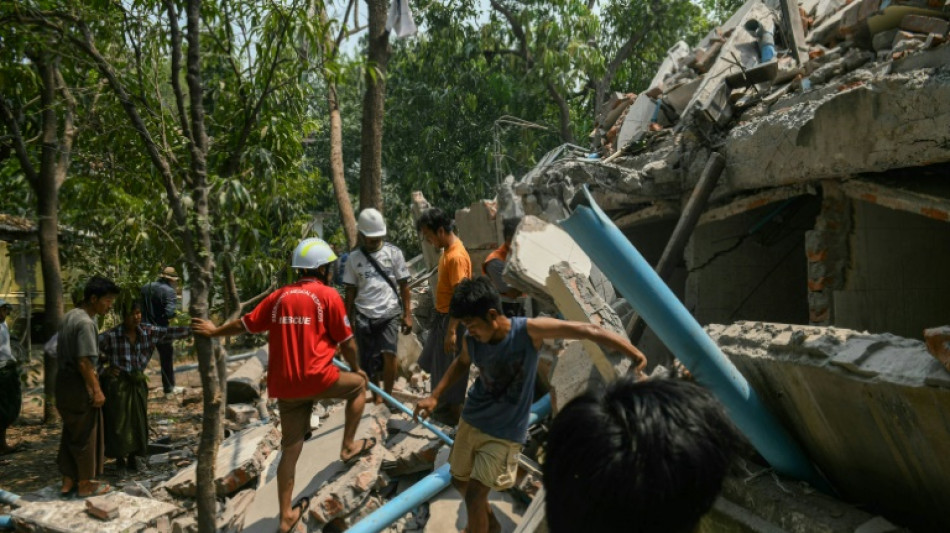
Scientists explain why Myanmar quake was so deadly
Experts say that the devastating earthquake in Myanmar on Friday was likely the strongest to hit the country in decades, with disaster modelling suggesting thousands could be dead.
Automatic assessments from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) said the shallow 7.7-magnitude quake northwest of the central Myanmar city of Sagaing triggered a red alert for shaking-related fatalities and economic losses.
"High casualties and extensive damage are probable and the disaster is likely widespread," it said, locating the epicentre near the central Myanmar city of Mandalay, home to more than a million people.
Myanmar's ruling junta said on Saturday morning that the number killed had passed 1,000, with more than 2,000 injured.
However, the USGS analysis said there was a 35 percent chance that possible fatalities could be in the range of 10,000-100,000 people.
The USGS offered a similar likelihood that the financial damage could total tens of thousands of millions of dollars, warning that it might exceed the GDP of Myanmar.
Weak infrastructure will complicate relief efforts in the isolated, military-ruled state, where rescue services and the healthcare system have already been ravaged by four years of civil war sparked by a military coup in 2021.
- Dangerous fault -
Bill McGuire, emeritus professor of geophysical and climate hazards at University College London (UCL), said it was "probably the biggest earthquake on the Myanmar mainland in three-quarters of a century".
A 6.7-magnitude aftershock struck minutes after the first and McGuire warned that "more can be expected".
Rebecca Bell, a tectonics expert at Imperial College London (ICL), suggested it was a side-to-side "strike-slip" of the Sagaing Fault.
This is where the Indian tectonic plate, to the west, meets the Sunda plate that forms much of Southeast Asia -- a fault similar in scale and movement to the San Andreas Fault in California.
"The Sagaing fault is very long, 1,200 kilometres (745 miles), and very straight," Bell said. "The straight nature means earthquakes can rupture over large areas -- and the larger the area of the fault that slips, the larger the earthquake."
Earthquakes in such cases can be "particularly destructive", Bell added, explaining that since the quake takes place at a shallow depth, its seismic energy has dissipated little by the time it reaches populated areas above.
That causes "a lot of shaking at the surface", Bell said.
- Building boom -
Myanmar has been hit by powerful quakes in the past.
There have been more than 14 earthquakes with a magnitude of 6 or above in the past century, including a magnitude 6.8 earthquake near Mandalay in 1956, said Brian Baptie, a seismologist with the British Geological Survey.
Ian Watkinson, from the department of earth sciences at Royal Holloway University of London, said what had changed in recent decades was the "boom in high-rise buildings constructed from reinforced concrete".
Myanmar has been riven by years of conflict and there is a low level of building design enforcement.
"Critically, during all previous magnitude 7 or larger earthquakes along the Sagaing Fault, Myanmar was relatively undeveloped, with mostly low-rise timber-framed buildings and brick-built religious monuments," Watkinson said.
"Today's earthquake is the first test of modern Myanmar's infrastructure against a large, shallow-focus earthquake close to its major cities."
Baptie said that at least 2.8 million people in Myanmar were in hard-hit areas where most lived in buildings "constructed from timber and unreinforced brick masonry" that are vulnerable to earthquake shaking.
"The usual mantra is that 'earthquakes don't kill people; collapsing infrastructure does'," said Ilan Kelman, an expert in disaster reduction at UCL.
"Governments are responsible for planning regulations and building codes. This disaster exposes what governments of Burma/Myanmar failed to do long before the earthquake, which would have saved lives during the shaking."
- Skyscraper checks -
Strong tremors also rocked neighbouring Thailand, where a 30-storey skyscraper under construction was reduced to a pile of dusty concrete, trapping workers in the debris.
Christian Malaga-Chuquitaype, from ICL's civil and environmental engineering department, said the nature of the ground in Bangkok contributed to the impact on the city, despite being some 1,000 kilometres (620 miles) from the epicentre in Myanmar.
"Even though Bangkok is far from active faults, its soft soil amplifies the shaking," he said. "This affects especially tall buildings during distant earthquakes."
Malaga-Chuquitaype said the construction techniques in Bangkok favouring "flat slabs" -- where floors are held only by columns without using strengthening beams, like a table supported only by legs -- were a "problematic design".
He said that initial video analysis of the collapsed tower block in Bangkok suggested this type of construction technique had been used.
Roberto Gentile, a catastrophe risk modelling expert from UCL, said the "dramatic collapse" of the Bangkok tower block meant that "other tall buildings in the city may require a thorough assessment".
Bangkok city authorities said they will deploy more than 100 engineers to inspect buildings for safety after receiving more than 2,000 reports of damage.
P.Silva--AMWN

