
-
 Iranian in possible prisoner exchange faces 'terrorism' verdict in France
Iranian in possible prisoner exchange faces 'terrorism' verdict in France
-
'Street-smart' New Zealand can topple England to make T20 semis: coach

-
 Iran-US talks begin in push to avert war
Iran-US talks begin in push to avert war
-
Merz says Germany, China must overcome trade gaps 'together'

-
 Automaker Stellantis posts massive loss, pivots from EV
Automaker Stellantis posts massive loss, pivots from EV
-
US, Ukraine to meet in Geneva after overnight Russian strikes

-
 Snake-like robot unveiled for Fukushima debris removal
Snake-like robot unveiled for Fukushima debris removal
-
'Public lynching': Senegal cracks down on LGBTQ+ community

-
 Hong Kong sentences father of wanted activist to 8 months in jail
Hong Kong sentences father of wanted activist to 8 months in jail
-
The woman fighting to reclaim her face from Albania's 'AI minister'

-
 Bulgaria ski station becomes refuge for digital nomads
Bulgaria ski station becomes refuge for digital nomads
-
Thai runner-up party seeks criminal case against election officials

-
 North Korea's Kim shuns South but could 'get along' with US
North Korea's Kim shuns South but could 'get along' with US
-
Spurs win 10th straight, Pistons silence Thunder in battle of NBA's best

-
 Germany's Merz visits China AI hub hoping for business deals
Germany's Merz visits China AI hub hoping for business deals
-
Post-uprising polls won't shake Nepal's delicate India-China balance

-
 S.Korea's Park Chan-wook to head Cannes festival jury
S.Korea's Park Chan-wook to head Cannes festival jury
-
Australian ex-PM says 'more important than ever' to ditch UK monarchy

-
 Dressed for succession? Kim Jong Un, daughter fuel speculation with matching coats
Dressed for succession? Kim Jong Un, daughter fuel speculation with matching coats
-
US-Ukraine talks to open in Geneva after overnight Russian strikes

-
 Export ban sparks rush to process lithium in Zimbabwe
Export ban sparks rush to process lithium in Zimbabwe
-
Pakistani sculptor turns scrap into colossal metal artworks

-
 Epstein files reveal links to cash, women, power in Africa
Epstein files reveal links to cash, women, power in Africa
-
Where are Southeast Asia's data centres?

-
 Where AI lives: Southeast Asia's data centre boom
Where AI lives: Southeast Asia's data centre boom
-
Seoul hits fresh record on mixed day for Asia markets

-
 Kyiv residents pool together for solar panels and batteries amid Russian strikes
Kyiv residents pool together for solar panels and batteries amid Russian strikes
-
North Korea's Kim says could 'get along' with US but shuns South

-
 Cuba kills four on US-registered speedboat trying to 'infiltrate'
Cuba kills four on US-registered speedboat trying to 'infiltrate'
-
UK Labour party threatened by hard-right, leftists in heartland

-
 Australian PM sorry after saying sexual assault survivor 'difficult'
Australian PM sorry after saying sexual assault survivor 'difficult'
-
Kim Jong Un spurns olive branch from 'hostile' South Korea

-
 DR Congo sanctuary resists bloody forest sell-off
DR Congo sanctuary resists bloody forest sell-off
-
North Korea looking to replicate youth success at Women's Asian Cup

-
 Deal or no deal: What's the state of Trump's tariffs?
Deal or no deal: What's the state of Trump's tariffs?
-
Hillary Clinton to testify in US House panel's Epstein probe

-
 African migrants won legal protections - then Trump deported them
African migrants won legal protections - then Trump deported them
-
US women's ice hockey captain responds to 'distasteful' Trump remark

-
 US presses missile issue as new Iran talks to open in Geneva
US presses missile issue as new Iran talks to open in Geneva
-
US government accused of major 'cover-up' over Trump sex abuse claims

-
 US eases Cuba oil embargo but demands 'dramatic' change
US eases Cuba oil embargo but demands 'dramatic' change
-
IMF urges US to work with partners to ease trade restrictions

-
 Brumbies not getting carried away by emphatic Super Rugby start
Brumbies not getting carried away by emphatic Super Rugby start
-
Dr. Angela Zeng's TEDx Talk on Supporting Children's Mental Health Without Medication Goes Live

-
 Truly Good Foods Unveils Golden Hour(TM) Snack Bars
Truly Good Foods Unveils Golden Hour(TM) Snack Bars
-
Renee Is Transforming AI Therapy, And It's Just Getting Started

-
 Eagle Plains Increases Saskatchewan Gold Royalty Portfolio
Eagle Plains Increases Saskatchewan Gold Royalty Portfolio
-
Innovation Holds Key to Future Growth, New Research from Ipsos, Alchemy-RX and Market Logic Finds
-
 Forecast Change for The 2025/2026 Fiscal Year
Forecast Change for The 2025/2026 Fiscal Year
-
Banyan Gold Continues to Intersect Visible Gold and High-Grade Mineralization in Powerline, Yukon, Canada


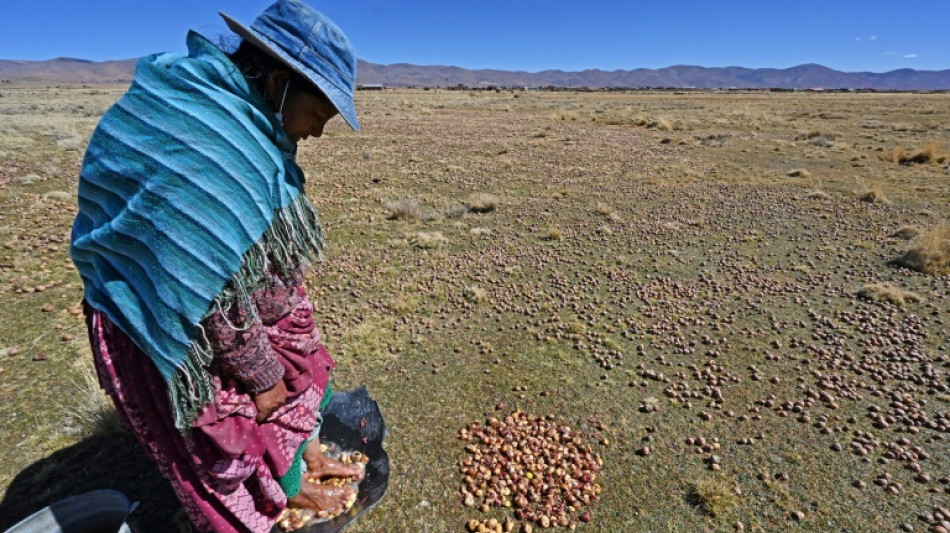
Study reveals potato's secret tomato past
You say potato, I say tomato?
Turns out one helped create the other: Natural interbreeding between wild tomatoes and potato-like plants in South America gave rise to the modern day spud around nine million years ago, according to a new study published Thursday in the journal Cell.
Co-author Loren Rieseberg, a professor at the University of British Columbia, told AFP the findings point to a "profound shift" in evolutionary biology, as scientists increasingly recognize the role of ancient hybridization events in shaping the Tree of Life.
While it was once thought that random mutations were by far the biggest driver of new species, "we now agree that the creative role of hybridization has been underestimated," he said.
Simple, affordable and versatile, the humble potato is now one of the world's most important crops. But its origins have long puzzled scientists.
Modern potato plants closely resemble three species from Chile known as Etuberosum. However, these plants do not produce tubers -- the large underground structures, like those found in potatoes and yams, that store nutrients and are the parts we eat.
On the other hand, genetic analysis has revealed a surprising closeness to tomatoes.
"This is known as discordance, and indicates something interesting is going on!" co-author Sandra Knapp, a research botanist at Britain's Natural History Museum, told AFP.
To solve the mystery, an international team of researchers analyzed 450 genomes from cultivated potatoes and 56 wild potato species.
Lead author Zhiyang Zhang, of the Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, said in a statement: "Wild potatoes are very difficult to sample, so this dataset represents the most comprehensive collection of wild potato genomic data ever analysed."
- 'Wow' moment -
The analysis revealed that modern potatoes carry a balanced genetic legacy from two ancestral species -- roughly 60 percent from Etuberosum and 40 percent from tomatoes.
"My wow moment was when the Chinese team showed that ALL potatoes, wild species as well as land races, had basically the same proportion of tomato genes and Etuberosum genes," said Knapp.
"That really points to an ancient hybridization event rather than various events of gene exchange later on," she added. "It is so clear cut! Beautiful."
One gene called SP6A, a signal for tuberization, came from the tomato lineage. But it only enabled tuber formation when paired with the IT1 gene from Etuberosum, which controls underground stem growth.
The divergence between Etuberosum and tomatoes is thought to have begun 14 million years ago -- possibly due to off-target pollination by insects -- and completed nine million years ago.
This evolutionary event coincided with the rapid uplift of the Andes mountain range, providing ideal conditions for the emergence of tuber-bearing plants that could store nutrients underground.
Another key feature of tubers is their ability to reproduce asexually, sprouting new buds without the need for seeds or pollination -- a trait that helped them spread across South America, and through later human exchange, around the globe.
Co-author Sanwen Huang, a professor at the Agricultural Genomics Institute at Shenzhen, told AFP that his lab is now working on a new hybrid potato that can be reproduced by seeds to accelerate breeding.
This study suggests that using the tomato "as a chassis of synthetic biology" is a promising route for creating this new potato, he said.
D.Kaufman--AMWN
