-
 Fly-half Jalibert ruled out of France side to face Italy
Fly-half Jalibert ruled out of France side to face Italy
-
Russell restart try 'big moment' in Scotland win, says Townsend

-
 Kane helps Bayern extend Bundesliga lead as Dortmund held by Leipzig
Kane helps Bayern extend Bundesliga lead as Dortmund held by Leipzig
-
Liga leaders Real Madrid stung by late Osasuna winner

-
 Ilker Catak's 'Yellow Letters' wins Golden Bear at Berlin film festival
Ilker Catak's 'Yellow Letters' wins Golden Bear at Berlin film festival
-
England's Genge says thumping Six Nations loss to Ireland exposes 'scar tissue'

-
 Thousands march in France for slain far-right activist
Thousands march in France for slain far-right activist
-
Imperious Alcaraz storms to Qatar Open title

-
 Klaebo makes Olympic history as Gu forced to wait
Klaebo makes Olympic history as Gu forced to wait
-
Late Scotland try breaks Welsh hearts in Six Nations

-
 Lens lose, giving PSG chance to reclaim Ligue 1 lead
Lens lose, giving PSG chance to reclaim Ligue 1 lead
-
FIFA's Gaza support 'in keeping' with international federation - IOC

-
 First all-Pakistani production makes history at Berlin film fest
First all-Pakistani production makes history at Berlin film fest
-
Gu forced to wait as heavy snow postpones Olympic halfpipe final

-
 NASA chief rules out March launch of Moon mission over technical issues
NASA chief rules out March launch of Moon mission over technical issues
-
Dutch double as Bergsma and Groenewoud win Olympic speed skating gold

-
 At least three dead as migrant boat capsizes off Greek island
At least three dead as migrant boat capsizes off Greek island
-
Struggling Juventus' woes deepen with home loss to Como

-
 Chelsea, Aston Villa held in blow to Champions League hopes
Chelsea, Aston Villa held in blow to Champions League hopes
-
Thousands march in France for slain far-right activist under heavy security

-
 Kane nets double as Bundesliga leaders Bayern beat Frankfurt
Kane nets double as Bundesliga leaders Bayern beat Frankfurt
-
Canada beat USA to take bronze in Olympic women's curling

-
 Hunger and belief key to Ireland's win, says Sheehan
Hunger and belief key to Ireland's win, says Sheehan
-
Pegula sees off Svitolina to win Dubai WTA 1000 title

-
 Trump hikes US global tariff rate to 15%
Trump hikes US global tariff rate to 15%
-
AI revolution looms over Berlin film fest

-
 Gibson-Park guides Ireland to record-breaking win in England
Gibson-Park guides Ireland to record-breaking win in England
-
Defence the priority for France against Italy, says Dupont

-
 Juventus end bad week with 2-0 loss against Como
Juventus end bad week with 2-0 loss against Como
-
Libya's Ramadan celebrations tempered by economic woes

-
 Norway's cross-country king Klaebo wins sixth gold of Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics
Norway's cross-country king Klaebo wins sixth gold of Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics
-
Iranian students chant anti-government slogans, as US threats loom

-
 Hezbollah vows resistance after deadly Israeli strike
Hezbollah vows resistance after deadly Israeli strike
-
'Stormy seas' of Gaza row overshadow Berlin film fest finale

-
 Pakistan-New Zealand Super Eights clash delayed by rain
Pakistan-New Zealand Super Eights clash delayed by rain
-
Werder Bremen cancel US tour citing 'political reasons'

-
 South Africa's De Kock says handling pressure key in India clash
South Africa's De Kock says handling pressure key in India clash
-
French volunteer bakes for Ukraine amid frosts and power outages

-
 Mexico's Del Toro wins stage to take overall UAE Tour lead
Mexico's Del Toro wins stage to take overall UAE Tour lead
-
Brook says a 'shame' if Pakistan players snubbed for Hundred

-
 Gu shoots for elusive gold as Klaebo makes Olympic history
Gu shoots for elusive gold as Klaebo makes Olympic history
-
France win Olympic ski mountaineering mixed relay

-
 Norway's Klaebo wins sixth gold of Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics
Norway's Klaebo wins sixth gold of Milan-Cortina Winter Olympics
-
Global summit calls for 'secure, trustworthy and robust AI'

-
 Macron urges 'calm' ahead of tense rally for slain far-right activist
Macron urges 'calm' ahead of tense rally for slain far-right activist
-
Rain go away: Brook says England ready for Sri Lanka disruption

-
 Impact of Israeli-Palestinian conflict plays out on screen in Berlin
Impact of Israeli-Palestinian conflict plays out on screen in Berlin
-
Macron urges 'calm' ahead of rally for slain far-right activist

-
 Venezuela grants amnesty to 379 political prisoners
Venezuela grants amnesty to 379 political prisoners
-
Austria turns Hitler's home into a police station


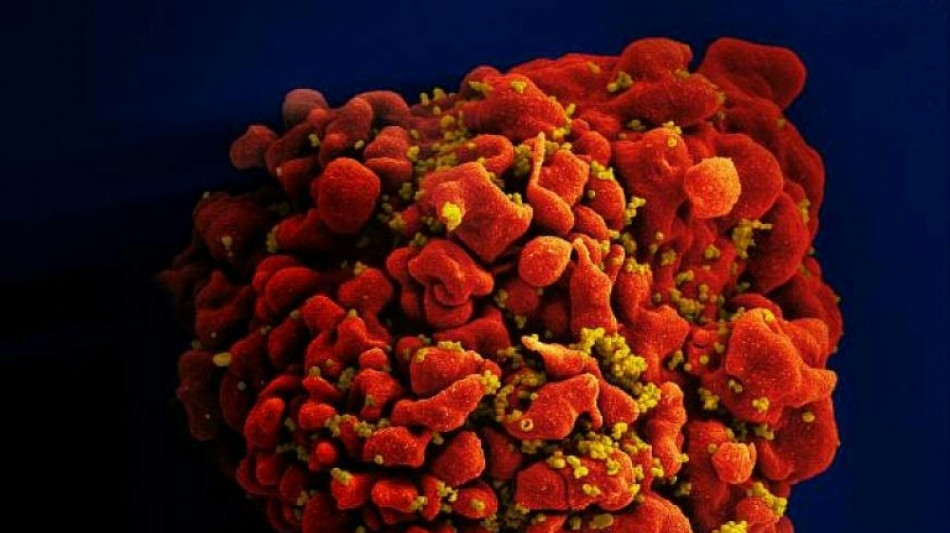
New 'highly virulent' HIV strain discovered in the Netherlands
Oxford researchers announced Thursday the discovery of a highly virulent strain of HIV that has been lurking in the Netherlands for decades, but because of the effectiveness of modern treatments, is "no cause for alarm."
Their analysis, published Thursday in the journal "Science," showed that patients infected with what they call the "VB variant" had 3.5 to 5.5 times higher levels of the virus in their blood than those infected with other variants, as well as a more rapidly fading immune system.
However, the study also found that after starting treatment, individuals with the VB variant had similar immune system recovery and survival to individuals with other HIV variants.
"There's no cause for alarm with this new viral variant," said Oxford epidemiologist Chris Wymant, the lead author on the paper, in an interview with AFP.
The variant likely arose in the late 1980s and early 1990s in the Netherlands, according to the researchers, but began to decline around 2010.
Since modern interventions still seem to work on the variant, the research team believes that widespread HIV treatment in the Netherlands did not contribute to the virus's evolution, and that early detection and treatment are paramount.
"Our findings emphasize the importance of World Health Organization guidance that individuals at risk of acquiring HIV have access to regular testing to allow early diagnosis, followed by immediate treatment," said co-author Christophe Fraser, also an Oxford researcher, in a press release announcing the findings.
The work also supports the theory that viruses can evolve to become more virulent, a widely-hypothesized idea for which few real-world examples have been found.
The Delta variant of the novel coronavirus was another recent example.
The discovery of the HIV variant should therefore "be a warning that we should never be overconfident about saying viruses will just evolve to become milder," said Wymant to AFP.
In total, the team found 109 people infected with the VB variant, with only four living outside the Netherlands, but still in western Europe.
- 500 mutations -
The HIV virus is constantly evolving, so much so that each person infected has a slightly different version.
The VB variant, however, was found to have over 500 mutations.
"Finding a new variant is normal, but finding a new variant with unusual properties is not -- especially one with increased virulence," Wyman explained.
The research team first identified the VB variant in 17 HIV positive individuals by parsing a broad data set from the BEEHIVE project, a data collection and analysis initiative in Europe and Uganda.
Because 15 of the 17 were from the Netherlands, they further studied data from 6,700 HIV-positive Dutch individuals, identifying 92 others.
The earliest appearance of the VB variant in their data was found in someone diagnosed in 1992 who had an early version of the variant, and the most recent in 2014.
Other researchers have since found other individuals with the variant diagnosed after 2014.
Doctors usually measure HIV's deterioration of the immune system by monitoring the decline of CD4 T-cells, which are targeted by the HIV virus and pivotal for protecting the body against infections.
In patients infected with the VB variant, CD4 decline occurred twice as fast compared to other variants, "placing them at risk of developing AIDS much more rapidly," the researchers said.
In addition to its increased impact on the immune system, the team also found the VB variant to be more highly transmissible.
They came to that conclusion after comparing the different versions of the VB variant drawn from infected patients.
The fact that they were so similar suggests that the virus passed rapidly to someone else before it could accumulate many mutations.
- 'Critical' to diagnose and treat early -
"Because the VB variant causes a more rapid decline in immune system strength, this makes it critical that individuals are diagnosed early and start treatment as soon as possible," the press statement noted.
"This limits the amount of time HIV can damage an individual's immune system and jeopardize their health," added Fraser.
Fraser is also the principal investigator of the BEEHIVE project, which was launched in 2014 to gather data on how mutations in the HIV virus can lead to varying degrees of severity among patients.
Those differences have previously been thought to mostly relate to the strength of individuals' own immune systems.
The researchers said they could not identify which genetic mutation in the VB variant caused its virulence, but they hope future studies will be able to.
B.Finley--AMWN

