
-
 Godolphin in full bloom as Desert Flower wins 1000 Guineas
Godolphin in full bloom as Desert Flower wins 1000 Guineas
-
Almeida wins Tour de Romandie as Evenepoel claims closing time-trial

-
 Bolsonaro leaves hospital three weeks after abdominal surgery
Bolsonaro leaves hospital three weeks after abdominal surgery
-
Man Utd crash at Brentford, Isak rescues Newcastle

-
 Romanians vote in tense presidential rerun as far right eyes win
Romanians vote in tense presidential rerun as far right eyes win
-
Lyon see off Racing to set up Challenge Cup final against Bath

-
 Kolkata survive Parag's six-hitting blitz to clinch IPL thriller
Kolkata survive Parag's six-hitting blitz to clinch IPL thriller
-
Israel vows retaliation against Yemen's Huthis over airport attack

-
 Mbappe maintains Real Madrid Liga dream in Celta thriller
Mbappe maintains Real Madrid Liga dream in Celta thriller
-
UNESCO says Nicaragua quitting over press prize award

-
 Church donation box goes digital in Greece
Church donation box goes digital in Greece
-
Germans mark liberation of Ravensbrueck Nazi camp

-
 Missile hits Israel airport area in Huthi-claimed attack
Missile hits Israel airport area in Huthi-claimed attack
-
DeChambeau eyes PGA Championship battle after South Korea LIV win

-
 Chinese president to visit Russia on May 7-10: Kremlin
Chinese president to visit Russia on May 7-10: Kremlin
-
'We don't care': weddings go on in Pakistan's Kashmir border

-
 Missile hits Israel airport area in attack claimed by Yemen's Huthis
Missile hits Israel airport area in attack claimed by Yemen's Huthis
-
Mexican mayor arrested in probe of alleged drug cartel ranch: govt source

-
 Seven Iranians among eight arrested in UK counterterrorism probes
Seven Iranians among eight arrested in UK counterterrorism probes
-
Israel says area of airport hit after Yemen missile launch

-
 Romanians return to polls as far right hopes to win presidential rerun
Romanians return to polls as far right hopes to win presidential rerun
-
4 Iranians among 5 arrested in UK for 'terrorism offences': police

-
 'Two million' throng Lady Gaga concert at Rio's Copacabana
'Two million' throng Lady Gaga concert at Rio's Copacabana
-
India-Pakistan gunfire triggers terror of past conflict

-
 UK hard right sets sights high after local election triumphs
UK hard right sets sights high after local election triumphs
-
Sexual abuse of nuns: one of the Catholic Church's last taboos

-
 West German foothold of far-right AfD shows challenge for Merz
West German foothold of far-right AfD shows challenge for Merz
-
Maldives president holds record 15-hour press conference

-
 'Accept me': Near Ukraine front, a haven for outcasts
'Accept me': Near Ukraine front, a haven for outcasts
-
Canelo Alvarez unifies super middleweight titles on Saudi Arabia debut

-
 Canelo Alvarez unifes super middleweight titles on Saudi Arabia debut
Canelo Alvarez unifes super middleweight titles on Saudi Arabia debut
-
US Fed expected to pause cuts again and wait for clarity on tariffs

-
 Ex-Liverpool star Firmino 'proud' after more Champions League history
Ex-Liverpool star Firmino 'proud' after more Champions League history
-
Australian PM basks in win, vows 'orderly' government

-
 Qataris hooked on traditional fishing competition
Qataris hooked on traditional fishing competition
-
Mozart chocolate row leaves bitter taste in Austria

-
 US solar tariffs could drive Asia transition boom
US solar tariffs could drive Asia transition boom
-
Four-try Hurricane Sullivan says revenge fuelled Chiefs upset

-
 Nuggets rout Clippers to advance in NBA playoffs
Nuggets rout Clippers to advance in NBA playoffs
-
Scheffler shines in dark for eight-shot CJ Cup Byron Nelson lead

-
 Romania returns to polls after annulled presidential vote
Romania returns to polls after annulled presidential vote
-
Easy vote turns Musk's dreams for Starbase city in Texas into reality

-
 Messi and Miami bounce back with 4-1 crushing of Red Bulls
Messi and Miami bounce back with 4-1 crushing of Red Bulls
-
US researchers seek to legitimize AI mental health care

-
 Ryu clings to two-shot lead at LPGA Black Desert Championship
Ryu clings to two-shot lead at LPGA Black Desert Championship
-
Ledecky, Walsh cap Pro Swim meet with world records

-
 Sovereignty rules in 151st Kentucky Derby
Sovereignty rules in 151st Kentucky Derby
-
New to The Street Acquires 15% Equity Stake in CommercialVille, Launches National Media Campaign Featuring Patent-Backed Platform

-
 Prometheus Laboratories Presents Novel Data on Precision-Guided Care in IBD at DDW(R) 2025
Prometheus Laboratories Presents Novel Data on Precision-Guided Care in IBD at DDW(R) 2025
-
McLaughlin-Levrone sets world's fastest of year in 400m hurdles


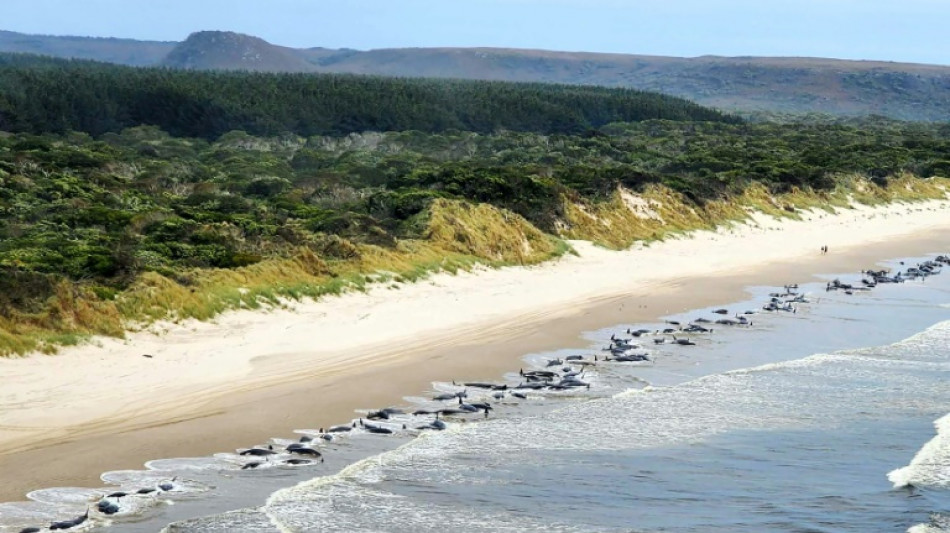
Whale strandings: Five questions answered
The death of about 200 pilot whales at a Tasmanian beach has renewed questions about what causes such mass strandings and whether they can be prevented.
With the help of Karen Stockin, a whale stranding expert at New Zealand's Massey University, here are the answers to five key questions:
What causes mass strandings?
Scientists are still trying to work that out. They do know that there are multiple types of stranding events, with several explanations that can overlap. The causes can be natural, based on bathymetry -- the shape of the ocean floor -- or they can be species-specific.
Pilot whales and several smaller dolphin species are known to regularly mass strand, especially in the southern hemisphere, according to Stockin. In some instances, a sick whale headed towards shore and a full group unwittingly followed them.
Does it happen in certain areas?
There are a few global hotspots. In the southern hemisphere, Tasmania and New Zealand's Golden Bay have seen several instances, and in the northern hemisphere, the United States bay of Cape Cod, Massachusetts, is another hotspot.
In those areas, there are similarities between the topography of the beaches and environmental conditions. For example, Cape Cod and Golden Bay share a prominent narrow coastal land feature and shallow water with large tidal variations. Some people call such areas "whale traps" because of the speed at which the tide can recede.
Are strandings becoming more common?
Possibly. Strandings are natural phenomena and have been documented since the days of Aristotle. The health of the oceans has, however, deteriorated in recent decades.
Strandings could become more common as human use of the seas, shipping traffic and chemical pollution all increase.
Epizootic diseases -- outbreaks of sickness that affect a specific animal species -- could also lead to more. But there is still much to understand about the phenomenon, Stockin said.
Is climate change a factor?
Research on how climate change is affecting marine mammals is still in its infancy. Experts know that climate change can give rise to changes in prey and predator distribution. For some species, this may result in whales coming closer to shore.
For example, recent research based on current climate prediction models suggests that by the year 2050, the distribution of sperm whales and blue whales in New Zealand could vary considerably.
Can strandings be prevented?
Not really. As strandings occur for a multitude of reasons, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. But Stockin said that by better understanding whether and how human-induced changes are causing more mass strandings, solutions could be found.
D.Cunningha--AMWN

