-
 YouTube star MrBeast buys youth-focused banking app
YouTube star MrBeast buys youth-focused banking app
-
French take surprise led over Americans in Olympic ice dancing

-
 Lindsey Vonn says has 'complex tibia fracture' from Olympics crash
Lindsey Vonn says has 'complex tibia fracture' from Olympics crash
-
US news anchor says 'hour of desperation' in search for missing mother

-
 Malen double lifts Roma level with Juventus
Malen double lifts Roma level with Juventus
-
'Schitt's Creek' star Catherine O'Hara died of blood clot in lung: death certificate

-
 'Best day of my life': Raimund soars to German Olympic ski jump gold
'Best day of my life': Raimund soars to German Olympic ski jump gold
-
US Justice Dept opens unredacted Epstein files to lawmakers

-
 Epstein taints European governments and royalty, US corporate elite
Epstein taints European governments and royalty, US corporate elite
-
Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico

-
 Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial
Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial
-
Winter Olympics organisers investigate reports of damaged medals

-
 Venezuela opposition figure freed, then rearrested after calling for elections
Venezuela opposition figure freed, then rearrested after calling for elections
-
Japan's Murase clinches Olympic big air gold as Gasser is toppled

-
 US athletes using Winter Olympics to express Trump criticism
US athletes using Winter Olympics to express Trump criticism
-
Japan's Murase clinches Olympic big air gold

-
 Pakistan to play India at T20 World Cup after boycott called off
Pakistan to play India at T20 World Cup after boycott called off
-
Emergency measures hobble Cuba as fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure

-
 UK king voices 'concern' as police probe ex-prince Andrew over Epstein
UK king voices 'concern' as police probe ex-prince Andrew over Epstein
-
Spanish NGO says govt flouting own Franco memory law

-
 What next for Vonn after painful end to Olympic dream?
What next for Vonn after painful end to Olympic dream?
-
Main trial begins in landmark US addiction case against Meta, YouTube

-
 South Africa open T20 World Cup campaign with Canada thrashing
South Africa open T20 World Cup campaign with Canada thrashing
-
Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony

-
 Discord adopts facial recognition in child safety crackdown
Discord adopts facial recognition in child safety crackdown
-
Some striking NY nurses reach deal with employers

-
 Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
-
EU chief backs Made-in-Europe push for 'strategic' sectors

-
 Machado ally 'kidnapped' after calling for Venezuela elections
Machado ally 'kidnapped' after calling for Venezuela elections
-
Epstein affair triggers crisis of trust in Norway

-
 AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
-
Iran steps up arrests while remaining positive on US talks

-
 Frank issues rallying cry for 'desperate' Tottenham
Frank issues rallying cry for 'desperate' Tottenham
-
South Africa pile up 213-4 against Canada in T20 World Cup

-
 Brazil seeks to restore block of Rumble video app
Brazil seeks to restore block of Rumble video app
-
Gu's hopes of Olympic triple gold dashed, Vonn still in hospital

-
 Pressure mounts on UK's Starmer as Scottish Labour leader urges him to quit
Pressure mounts on UK's Starmer as Scottish Labour leader urges him to quit
-
Macron backs ripping up vines as French wine sales dive

-
 Olympic freeski star Eileen Gu 'carrying weight of two countries'
Olympic freeski star Eileen Gu 'carrying weight of two countries'
-
Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June

-
 Tokyo stocks strike record high after Japanese premier wins vote
Tokyo stocks strike record high after Japanese premier wins vote
-
'I need to improve', says Haaland after barren spell

-
 Italian suspect questioned over Sarajevo 'weekend snipers' killings: reports
Italian suspect questioned over Sarajevo 'weekend snipers' killings: reports
-
Von Allmen at the double as Nef seals Olympic team combined gold

-
 Newlyweds, but rivals, as Olympic duo pursue skeleton dreams
Newlyweds, but rivals, as Olympic duo pursue skeleton dreams
-
Carrick sees 'a lot more to do' to earn Man Utd job

-
 Olympic star Chloe Kim calls for 'compassion' after Trump attack on US teammate
Olympic star Chloe Kim calls for 'compassion' after Trump attack on US teammate
-
'All the pressure' on Pakistan as USA out to inflict another T20 shock

-
 Starmer vows to remain as UK PM amid Epstein fallout
Starmer vows to remain as UK PM amid Epstein fallout
-
Howe would 'step aside' if right for Newcastle


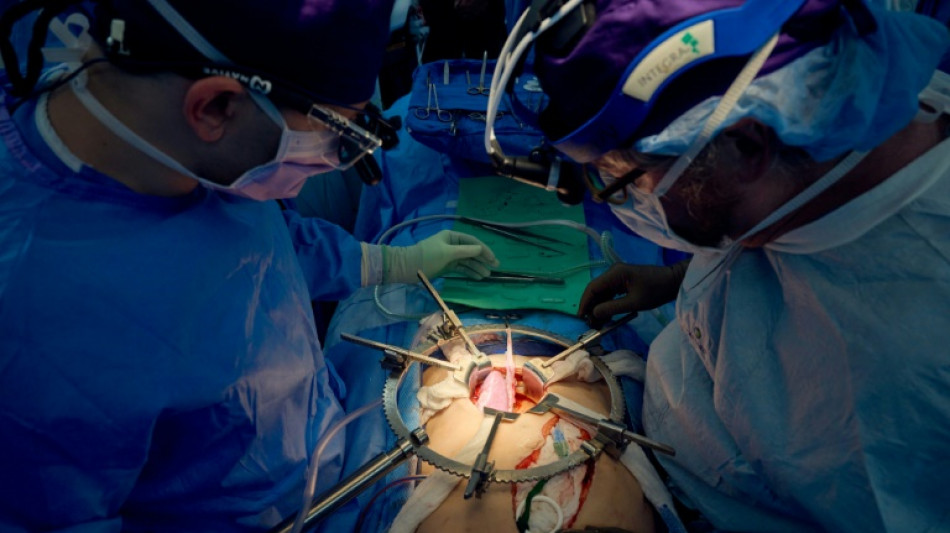
US surgeons say pig kidney functional in human for more than a month
US surgeons who transplanted a genetically-modified pig kidney into a brain dead patient said Wednesday it was still working well after a record 32 days -- a significant step in the quest to close the organ donation gap.
The latest experimental procedure is part of a growing field of research aimed at advancing cross-species transplants, using bodies that have been donated for science.
There are more than 103,000 people waiting for organs in the United States, 88,000 of whom need kidneys.
"We have a genetically-edited pig kidney surviving for over a month in a human," Robert Montgomery, director of the NYU Langone Transplant Institute, told reporters. "I think there's a very compelling story that exists at this point that I think should give further assurances about starting some initial studies... in living humans."
Montgomery carried out the first genetically modified pig kidney transplant to a human in September 2021, followed by a similar procedure in November 2021. There have since been a handful of other cases, with all the experiments running for two or three days.
While previous transplants have involved up to 10 genetic modifications, the latest saw just one: in the gene involved in the so-called "hyperacute rejection," which would otherwise occur within minutes of an animal organ being connected to a human circulatory system.
By "knocking out" the gene responsible for a biomolecule called alpha-gal -- a prime target for roving human antibodies -- the NYU Langone team were able to stop immediate rejection.
"We've now gathered more evidence to show that, at least in kidneys, just eliminating the gene that triggers a hyperacute rejection may be enough along with clinically approved immunosuppressive drugs to successfully manage the transplant in a human for optimal performance -- potentially in the long-term," said Montgomery.
They also embedded the pig's thymus gland -- which lies around the neck and is responsible for educating the immune system -- in the kidney's outer layer.
Adam Griesemer, of the NYU Grossman School of Medicine, added this allowed immune cells in the host's body to learn to recognize the pig's cells as its own, preventing a more delayed rejection.
Both of the patient's own kidneys were removed, then one pig kidney was transplanted, and started immediately producing urine.
Monitoring showed that levels of creatinine, a waste product, were at optimal levels, and there was no evidence of rejection.
- No evidence of pig virus -
Crucially, no evidence of porcine cytomegalovirus -- which may trigger organ failure -- have been detected, and the team plan to continue monitoring for another month.
The research was made possible by the family of the 57-year-old male patient, Maurice "Mo" Miller, who was found unresponsive in his bathroom in July. Doctors determined he had an aggressive form of brain cancer, and would not wake up.
"Though my brother cannot be here, I can say with confidence he would be proud of the fact in the tragedy of his death, his legacy will be helping many people live," his sister Mary Miller-Duffy told reporters.
In January 2022, surgeons at the University of Maryland Medical School carried out the world's first pig-to-human transplant on a living patient. He died two months after the milestone, with the presence of porcine cytomegalovirus in the organ later blamed.
The donor pig came from a herd from Virginia-based biotech company Revivicor. The herd was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a source of meat for people with hypersensitivity to the alpha-gal molecule, an allergy caused by tick bites.
These pigs are bred, not cloned, meaning the process can be more easily scaled.
Early xenotransplantation research focused on harvesting organs from primates -- for example, a baboon heart was transplanted into a newborn known as "Baby Fae" in 1984, but she survived only 20 days.
Current efforts focus on pigs, which are thought to be ideal donors because of their organ size, their rapid growth and large litters, and the fact they are already raised as a food source.
O.Johnson--AMWN



