-
 New Ypsilon and Ypsilon hf
New Ypsilon and Ypsilon hf
-
The Cupra Raval will be launched in 2026

-
 New id.Polo comes electric
New id.Polo comes electric
-
Iran defies US threats to insist on right to enrich uranium

-
 Seifert powers New Zealand to their record T20 World Cup chase
Seifert powers New Zealand to their record T20 World Cup chase
-
Naib's fifty lifts Afghanistan to 182-6 against New Zealand

-
 Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'
Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'
-
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums

-
 NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences
NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences
-
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?

-
 Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up
Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up
-
Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder

-
 Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate
Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate
-
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents

-
 Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo
Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo
-
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya

-
 Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl
Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl
-
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder

-
 Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back
-
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts

-
 Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM
-
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021

-
 Thailand votes after three leaders in two years
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years
-
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics

-
 George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales
-
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event

-
 Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
-
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links

-
 Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
-
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'

-
 Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
-
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
-
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves

-
 French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
-
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return

-
 Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
-
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes

-
 Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
-
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow

-
 Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
-
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics

-
 Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
-
BMW iX3 new style and design

-
 Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
-
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games

-
 Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
-
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank


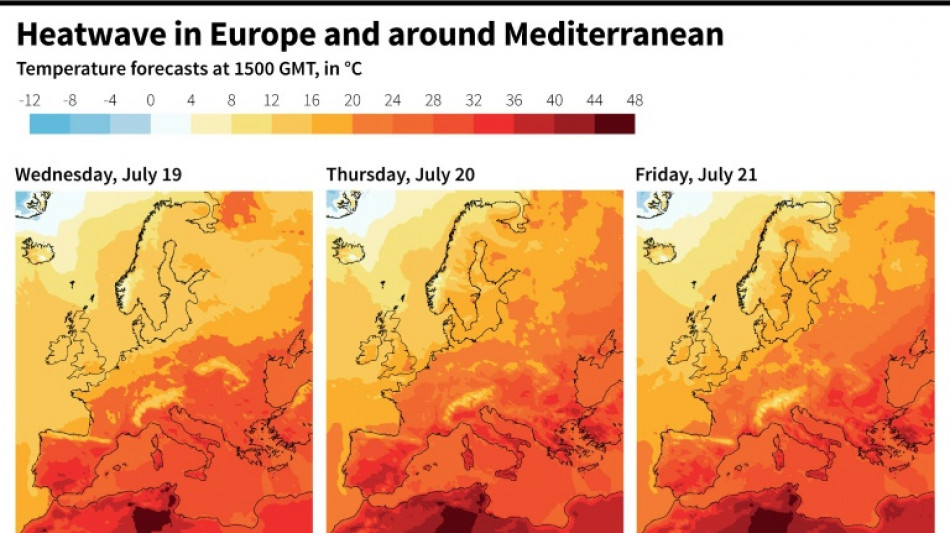
Heat-struck Mediterranean is climate change 'hot spot'
Struck by near-record temperatures and wildfires during this week's heatwave, the Mediterranean region is ranked as a climate-change "hot spot" by scientists.
The beaches, seafood and heritage sites in the region spanning parts of southern Europe, northern Africa and western Asia are under threat.
Here are five key threats to the region flagged by the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Its reports are the most comprehensive summary of scientific knowledge on global warming.
- Deadly heatwaves -
Like parts of the United States and Asia, the Med has been hit by extreme heat in recent weeks. The Italian islands of Sardinia and Sicily are forecast to possibly top a continent-wide record of 48.8C (119.8F).
"Heatwaves are increasing due to climate change in the Mediterranean, and are amplified in cities due to urbanisation practices," causing illness and death, the IPCC said in its 2022 report on impacts of climate change and how to adapt to them.
One study published in 2010 led by scientists at the University of Bern calculated that the intensity, length and number of heatwaves in the eastern Mediterranean had increased by about six or seven times since the 1960s.
- Wheat and olives -
A drought in North Africa has left farmers bracing for a terrible harvest. "We've never seen a drought this bad," Tunisian wheat farmer Tahar Chaouachi told AFP. "It's been dry for the last four years but we expected some rain this season. Instead, it's become worse."
With hotter weather drying up groundwater for irrigating farms, the IPCC said that with global warming of more than 1.5C olive yields could fall by a fifth in the northern Mediterranean. The world has warmed more than 1.1C since the 19th century.
Researchers at Stanford University found "the Mediterranean experiencing significant adverse impacts on most crops".
- Water and politics -
A drought in Spain has raised political tensions over water management ahead of a general election on July 23. The European Drought Observatory said groundwater tables across half the Mediterranean region were running low already in June.
The IPCC report warned climate change will worsen water shortages "in most locations" in the region. Lakes and reservoirs are expected to decline by up to 45 percent this century, and surface water availability by up to 55 percent in North Africa.
Meanwhile "terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems are impacted by climate change in the Mediterranean, resulting in loss of habitats and biodiversity," it added.
- Rising seas -
The sea level in the Mediterranean basin has risen 2.8mm a year over recent decades, threatening shorelines and cities such as Venice, which regularly suffers tidal floods.
"Sea level rise already impacts extreme coastal waters around the Mediterranean and it is projected to increase coastal flooding, erosion and salinisation risks," said the IPCC.
"These impacts would affect agriculture, fisheries and aquaculture, urban development, port operations, tourism, cultural sites and many coastal ecosystems."
- Invasive species -
As well as its cherished beaches, climate change threatens the Mediterranean sea and the food produced by its fisheries.
"A shift in Mediterranean marine ecosystems, characterised by biodiversity decline and invasive species, has occurred since the 1980s" due to climate change and other human impacts, the IPCC said.
With global warming of more than 1.5C, more than 20 percent of exploited fish and invertebrates in the Eastern Mediterranean could become locally extinct by 2060 and fishing revenues could decrease up to 30 percent by 2050, it said.
L.Davis--AMWN



