-
 Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'
Paul Thomas Anderson wins top director prize for 'One Battle After Another'
-
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums

-
 NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences
NFL embraces fashion as league seeks new audiences
-
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?

-
 Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up
Real Madrid can wait - Siraj's dream night after late T20 call-up
-
Castle's monster night fuels Spurs, Rockets rally to beat Thunder

-
 Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate
Japan votes in snow-hit snap polls as Takaichi eyes strong mandate
-
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents

-
 Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo
Berlin's crumbling 'Russian houses' trapped in bureaucratic limbo
-
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya

-
 Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl
Super Bowl set for Patriots-Seahawks showdown as politics swirl
-
Sengun shines as Rockets rally to beat NBA champion Thunder

-
 Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back
Matsuyama grabs PGA Phoenix Open lead with Hisatsune one back
-
Washington Post CEO out after sweeping job cuts

-
 Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM
Haiti's transitional council hands power to PM
-
N. Korea to hold party congress in February, first since 2021

-
 Thailand votes after three leaders in two years
Thailand votes after three leaders in two years
-
Swiss joy as Von Allmen wins first gold of Winter Olympics

-
 George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales
George backs England to 'kick on' after Six Nations rout of Wales
-
Malinin upstaged as Japan keep pressure on USA in skating team event

-
 Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
Vail's golden comets Vonn and Shiffrin inspire those who follow
-
Veteran French politician loses culture post over Epstein links

-
 Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
Japan's Kimura wins Olympic snowboard big air gold
-
Arteta backs confident Gyokeres to hit 'highest level'

-
 Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
Hojlund the hero as Napoli snatch late win at Genoa
-
England's Arundell 'frustrated' despite hat-trick in Wales romp

-
 Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Winter Olympics on her birthday
-
Arundell hat-trick inspires England thrashing of Wales in Six Nations opener

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Rosenior hails 'unstoppable' Palmer after treble tames Wolves

-
 French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
French ex-minister offers resignation from Paris cultural hub over Epstein links
-
New NBA dunk contest champ assured and shooting stars return

-
 Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
Shiffrin says will use lessons learnt from Beijing flop at 2026 Games
-
Takaichi tipped for big win as Japan votes

-
 Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
Lens return top of Ligue 1 with win over Rennes
-
Shiffrin learning from Beijing lessons ahead of Milan-Cortina bow

-
 Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
Demonstrators in Berlin call for fall of Iran's Islamic republic
-
'Free the mountains!": clashes at Milan protest over Winter Olympics

-
 Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
Townsend accepts pressure will mount on him after Italy defeat
-
BMW iX3 new style and design

-
 Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
Suryakumar's 84 leads India to opening win over USA in T20 World Cup
-
Lollobrigida skates to first Italian gold of Milan-Cortina Games

-
 Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
Barca beat Mallorca to extend Liga lead
-
Gyokeres lifts Arsenal nine clear as Man Utd pile pressure on Frank

-
 Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga
Late Guirassy winner for Dortmund trims Bayern's lead atop Bundesliga
-
'Free the mountains!": protest in Milan over Winter Olympics

-
 Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead
Gyokeres double helps Arsenal stretch Premier League lead
-
New Skoda Epiq: modern with range

-
 Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland
Six Nations misery for Townsend as Italy beat sorry Scotland
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain


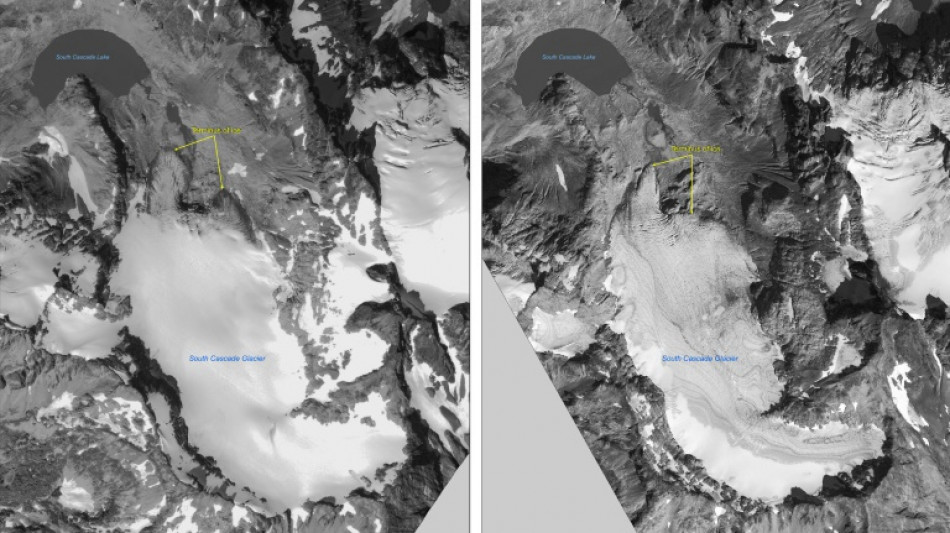
In US Northwest, South Cascade is where glacier science grew up
For nearly 70 years scientists have been probing, measuring, drilling and generally getting to know South Cascade Glacier in the US Northwest, developing and honing skills now used worldwide.
Generations of glaciologists have studied the slow-moving ice mass in Washington state, which is one of five so-called "benchmark" US glaciers, keeping tabs on how they are changing as human activity warms the Earth.
While glaciers have been studied in Europe since at least the 19th century, what scientists learned here has been invaluable.
"A lot of the scientific methods that we use to measure glaciers were developed here," said Andrew Fountain, professor emeritus at Portland State University, who specializes in glaciers and climate change.
That includes the use of ice radar, which allowed researchers to see just how thick the ice is in a spot where a glacier has probably existed for upwards of a million years.
- Ideal for studying -
South Cascade Glacier sits in a basin at the head of the South Fork of the Cascade river, which flows down ultimately into Puget Sound.
The size of the basin -- more than 2 square miles (over 6 square kilometers) -- along with its straightforward geometry made it ideal to study for scientists wanting to know how these dynamic bodies are faring in the changing world.
A glacier is a perennial accumulation of snow and ice that is always on the move, abrading the rocks underneath and -- over a long enough period of time -- carving valleys.
Measurements began at the site in 1958, according to the US Geological Survey, the government body that studies the natural environment.
The following year, the USGS began what is known as a "continuous mass balance" measurement project that keeps a running tally of streamflow runoff, precipitation, air temperature, barometric pressure, snow thickness and density, ice ablation, surface speed and surface altitude.
- Retreating -
The data collected here, as well as from the four other benchmark glaciers -- three in Alaska and one in Montana -- provides a continuous record, capturing their seasonal variations and their year-to-year changes.
Over nearly seven decades, glaciologists have been able "to track how the glacier is responding to climate."
And what they are seeing is not good, says Fountain.
"As you can imagine, it's been retreating like crazy" and is now about half the size it was when measurements started.
With a very complete record of the conditions, it's clear that the rising temperatures of the industrial age are to blame, said Fountain.
A warmer atmosphere reduces the amount of precipitation that falls as snow, and increases the ambient air temperature so what snow does fall, doesn't hang around.
While people may find it difficult to discern any long-term trends from the wildly differing amounts of snow a region can experience from year to year, a shrinking glacier is an obvious sign that the balance of nature is off.
"We can understand very viscerally that the climate is warming," he said.
Since President Donald Trump -- a climate change skeptic -- came to power, he and billionaire adviser Elon Musk have set about slashing government spending, eliminating tens of thousands of government jobs, including scientists.
This week, researchers at the Environmental Protection Agency -- which tackles environmental issues including pollution, clean water and climate change -- were put in the firing line.
For Fountain, whatever the reason a government has for diminishing the work of scientists, they should not be ignored.
About two percent of the world's water is stored in glaciers, and if they all melt, it will run eventually into the oceans, further raising sea levels and imperiling human settlements along tens of thousands of miles (kilometers) of coastlines worldwide.
That, amongst other reasons, is why the science of glaciology that came of age at South Cascade Glacier is invaluable, said Fountain.
"Just because we don't want to hear a message doesn't mean it isn't happening," he said.
P.Santos--AMWN


