-
 Russia is cracking down on WhatsApp and Telegram. Here's what we know
Russia is cracking down on WhatsApp and Telegram. Here's what we know
-
Stocks rise as all eyes on corporate earnings

-
 France bets on nuclear power to phase out fossil fuels
France bets on nuclear power to phase out fossil fuels
-
Italy bring in Pani for Brex to face Ireland in Six Nations

-
 Counting underway in first Bangladesh polls since deadly uprising
Counting underway in first Bangladesh polls since deadly uprising
-
Norway police search ex-PM Jagland's properties in probe over Epstein links

-
 Back flips and quads galore: US skater Malinin hits new heights in Milan
Back flips and quads galore: US skater Malinin hits new heights in Milan
-
'Madness': Ukrainians furious over Olympian ban for memorial helmet

-
 UEFA position on Russia ban 'has not changed', says Ceferin
UEFA position on Russia ban 'has not changed', says Ceferin
-
Cooper wins Olympic freestyle moguls gold after dramatic tie-break

-
 Italy's 'naval blockade' to stem migration too vague, critics say
Italy's 'naval blockade' to stem migration too vague, critics say
-
Turkey's central bank lifts 2026 inflation forecasts

-
 Tottenham 'not a big club' says Postecoglou after Frank sacking
Tottenham 'not a big club' says Postecoglou after Frank sacking
-
Belgian police raid EU commission in real estate probe

-
 Zelensky blasts Olympics ban for Ukrainian athlete over memorial helmet
Zelensky blasts Olympics ban for Ukrainian athlete over memorial helmet
-
Odermatt sets sights on Olympic giant slalom -- and gold

-
 Cinema's power to 'change the world' in focus at Berlin Film Fest
Cinema's power to 'change the world' in focus at Berlin Film Fest
-
France pick uncapped Brau-Boirie in new centre pairing for Wales

-
 Man Utd's Ratcliffe's apologises for 'language' on immigration
Man Utd's Ratcliffe's apologises for 'language' on immigration
-
UK economy struggles for growth in fresh blow to government

-
 EU vows swift reforms to confront challenge from China, US
EU vows swift reforms to confront challenge from China, US
-
UK nursery worker faces jail for serial child sex abuse

-
 Anti-racism body slams Man Utd co-owner for 'disgraceful' immigration comments
Anti-racism body slams Man Utd co-owner for 'disgraceful' immigration comments
-
Mercedes-Benz net profit nearly halves amid China, US woes

-
 Comeback queen Brignone wins super-G at Winter Olympics
Comeback queen Brignone wins super-G at Winter Olympics
-
Hermes sales rise despite US tariffs, currency headwinds

-
 Russia confirms ban on WhatsApp, says it failed to abide by law
Russia confirms ban on WhatsApp, says it failed to abide by law
-
Ukraine skeleton racer Heraskevych banned from Olympics over memorial helmet

-
 Pro-Kremlin accounts using Epstein files to push conspiracy: AFP research
Pro-Kremlin accounts using Epstein files to push conspiracy: AFP research
-
France picked uncapped Brau-Boirie at centre to face Wales

-
 Thomas Tuchel extends contract as England coach until Euro 2028
Thomas Tuchel extends contract as England coach until Euro 2028
-
England coach Tuchel set to sign new deal until 2028 - report

-
 Death toll in Madagascar cyclone rises to 35
Death toll in Madagascar cyclone rises to 35
-
Shanaka fireworks as Sri Lanka thrash Oman at T20 World Cup

-
 Sanofi says board has removed CEO Paul Hudson
Sanofi says board has removed CEO Paul Hudson
-
Struggling Nissan forecasts $4.2 bn full-year net loss

-
 Venezuela to debate historic amnesty bill for political prisoners
Venezuela to debate historic amnesty bill for political prisoners
-
Ukraine skeleton racer Heraskevych disqualified from Olympics over memorial helmet

-
 Markets mostly rise as stong US jobs data ease economy worries
Markets mostly rise as stong US jobs data ease economy worries
-
France jails three in gang rape case after mother saves evidence

-
 From 'Derry Girls' to 'heaven', Irish writer airs new comedy
From 'Derry Girls' to 'heaven', Irish writer airs new comedy
-
Asia markets mixed as stong US jobs data temper rate expectations

-
 Shanaka fireworks as Sri Lanka pile up 225-5 against Oman
Shanaka fireworks as Sri Lanka pile up 225-5 against Oman
-
Samsung starts mass production of next-gen AI memory chip

-
 Benin's lovers less row-mantic as apps replace waterway rendezvous
Benin's lovers less row-mantic as apps replace waterway rendezvous
-
Geneva opera house selling off thousands of extravagant costumes

-
 Non-alcoholic wine: a booming business searching for quality
Non-alcoholic wine: a booming business searching for quality
-
Greece's Cycladic islands swept up in concrete fever

-
 Grieving Canada town holds vigil for school shooting victims
Grieving Canada town holds vigil for school shooting victims
-
Israel president says at end of visit antisemitism in Australia 'frightening'


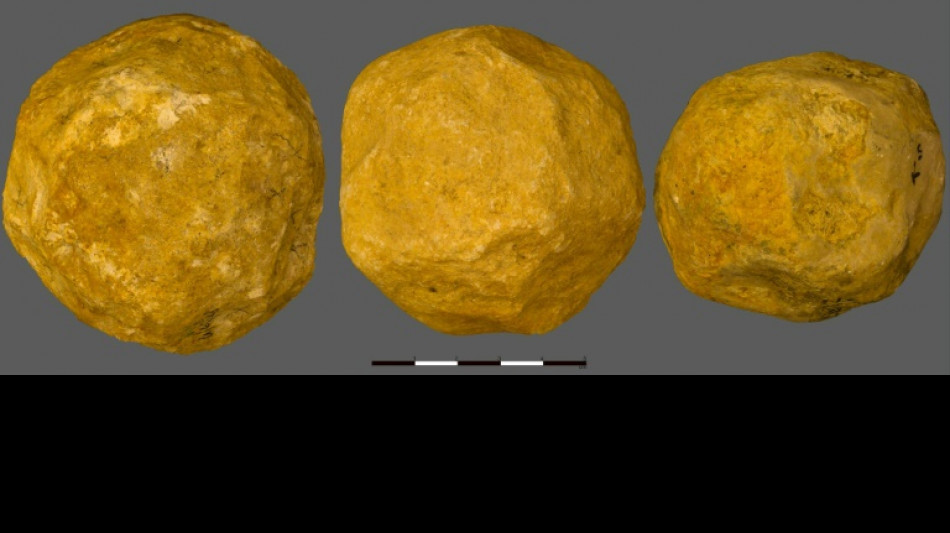
Early humans deliberately made mysterious stone 'spheroids'
The early ancestors of humans deliberately made stones into spheres 1.4 million years ago, a study said on Wednesday, though what prehistoric people used the balls for remains a mystery.
Archaeologists have long debated exactly how the tennis ball-sized "spheroids" were created.
Did early hominins intentionally chip away at them with the aim of crafting a perfect sphere, or were they merely the accidental by-product of repeatedly smashing the stones like ancient hammers?
New research led by the Hebrew University of Jerusalem suggests that our ancestors knew what they were doing.
The team of scientists examined 150 limestone spheroids dating from 1.4 million years ago which were found at the 'Ubeidiya archaeological site, in the north of modern-day Israel.
Using 3D analysis to reconstruct the geometry of the stones, the researchers determined that their sphericalness was "likely to have been produced intentionally".
The early hominins -- exactly which human lineage they belonged to remains unknown -- had "attempted to achieve the Platonic ideal of a sphere", they said.
While the spheroids were being made, the stones did not become smoother, but did become "markedly more spherical," said the study in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
This is important because while nature can make pebbles smoother, such as those in a river or stream, "they almost never approach a truly spherical shape," the study said.
Julia Cabanas, an archaeologist at France's Natural History Museum not involved in the research, told AFP that this means the hominins had a "mentally preconceived" idea of what they were doing.
That in turn indicates that our ancient relatives had the cognitive capacity to plan and carry out such work.
Cabanas said the same technique could be used on other spheroids. For example, it could shed light on the oldest known spheroids, which date back two million years and were found in the Olduvai Gorge of modern-day Tanzania.
But exactly why our ancestors went to the effort of crafting spheres remains a mystery.
Possible theories include that the hominins were trying to make a tool that could extract marrow from bones, or grind up plants.
Some scientists have suggested that the spheroids could have been used as projectiles, or that they may have had a symbolic or artistic purpose.
"All hypotheses are possible," Cabanes said.
"We will probably never know the answer."
P.Stevenson--AMWN
