
-
 Akie Iwai leads, Canadian teen Deng in hunt at LPGA Canadian Open
Akie Iwai leads, Canadian teen Deng in hunt at LPGA Canadian Open
-
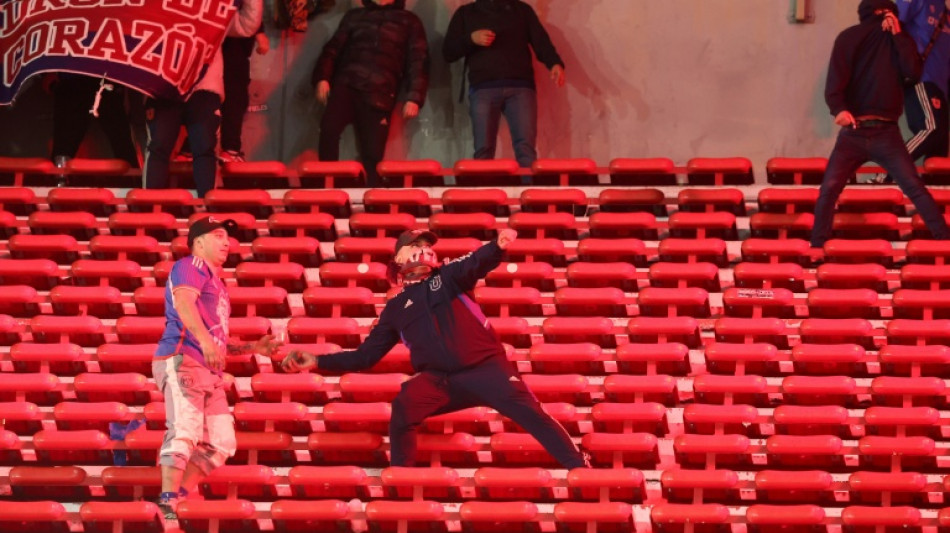
Chile, Argentina football fans trade blame over stadium violence

-
 Palestinian camps in Lebanon begin disarming
Palestinian camps in Lebanon begin disarming
-
Five dead as 'thunderous' bomb attack hits Colombian city

-
 Henley leads PGA Tour Championship with Scheffler in pursuit
Henley leads PGA Tour Championship with Scheffler in pursuit
-
US Supreme Court allows cuts in NIH diversity research grants

-
 Why fan violence still sullies Latin American football
Why fan violence still sullies Latin American football
-
Lil Nas X arrested after nearly naked nighttime stroll in LA

-
 Texas, California race to redraw electoral maps ahead of US midterms
Texas, California race to redraw electoral maps ahead of US midterms
-
US captain Zackary wants Eagles to soar against England in Women's Rugby World Cup opener

-
 Palace's Eze on verge of Arsenal move as he misses European tie
Palace's Eze on verge of Arsenal move as he misses European tie
-
Google to provide Gemini AI tools to US government

-
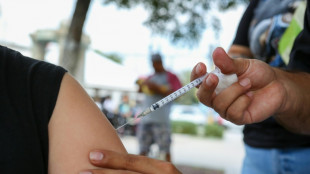 Canada measles cases pass 4,500, highest count in Americas
Canada measles cases pass 4,500, highest count in Americas
-
'Underdog' Jefferson-Wooden shrugs off Tokyo worlds pressure

-
 England's Jones relishing 'special occasion' at Women's Rugby World Cup after tragic year
England's Jones relishing 'special occasion' at Women's Rugby World Cup after tragic year
-
Alcaraz, Djokovic on US Open collision course

-
 US singer signs on for Russia's answer to Eurovision
US singer signs on for Russia's answer to Eurovision
-
Hundred-plus detained after fans 'lynched' during South America cup tie

-
 Trump hails 'total victory' as US court quashes $464 mn civil penalty
Trump hails 'total victory' as US court quashes $464 mn civil penalty
-
Stocks waver ahead of Fed speech but EU tariff deal lifts Europe

-
 Slot says Liverpool will only sign right player at right price amid Isak row
Slot says Liverpool will only sign right player at right price amid Isak row
-
Walmart expects better sales, earnings as shoppers squeezed by tariffs

-
 Malnourished Gaza children facing death without aid, says UN
Malnourished Gaza children facing death without aid, says UN
-
Autopsy rules out 'trauma' in Frenchman livestream death

-
 Liverpool's Frimpong out for several weeks with hamstring injury
Liverpool's Frimpong out for several weeks with hamstring injury
-
EU gets 15% US tariff for cars, but fails to get wine reprieve

-
 Leverkusen rebuild continues with Bade and Echeverri signings
Leverkusen rebuild continues with Bade and Echeverri signings
-
Ghana singer Shatta Wale held in US fraud probe over Lamborghini purchase

-
 Wales skipper Callender passed fit for Women's Rugby World Cup opener against Scotland
Wales skipper Callender passed fit for Women's Rugby World Cup opener against Scotland
-
Only goal is to win, says ever-competitive veteran Fraser-Pryce

-
 Maresca adamant Fofana 'very happy' at Chelsea
Maresca adamant Fofana 'very happy' at Chelsea
-
Record EU wildfires burnt more than 1 mn hectares in 2025: AFP analysis

-
 Hurricane Erin brings coastal flooding to N. Carolina, Virginia
Hurricane Erin brings coastal flooding to N. Carolina, Virginia
-
Stocks slide as investors await key Fed speech

-
 EU gets 15% US tariff for cars, fails to secure wine reprieve
EU gets 15% US tariff for cars, fails to secure wine reprieve
-
Russian fuel prices surge after Ukraine hits refineries

-
 Maguire feels it will be 'silly' to leave Man Utd now
Maguire feels it will be 'silly' to leave Man Utd now
-
Ukrainian suspect arrested in Italy over Nord Stream blasts

-
 England include ex-skipper Knight in Women's World Cup squad as Cross misses out
England include ex-skipper Knight in Women's World Cup squad as Cross misses out
-
Walmart lifts outlook for sales, earnings despite tariffs

-
 UK sees record asylum claims as row brews over housing
UK sees record asylum claims as row brews over housing
-
Swiss international Okafor move to Leeds heralds new EPL record

-
 Microsoft re-joins handheld gaming fight against Nintendo's Switch
Microsoft re-joins handheld gaming fight against Nintendo's Switch
-
McReight to captain Wallabies against Springboks

-
 Taiwanese boxer Lin agrees to gender test for world championships
Taiwanese boxer Lin agrees to gender test for world championships
-
Stocks slip as investors await key Fed speech

-
 Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai's 'punditry' not criminal: lawyer
Hong Kong mogul Jimmy Lai's 'punditry' not criminal: lawyer
-
Bournemouth sign 'proven winner' Adli from Leverkusen

-
 Israel pounds Gaza City as military takes first steps in offensive
Israel pounds Gaza City as military takes first steps in offensive
-
First security guarantees, then Putin summit, Zelensky says


Why fan violence still sullies Latin American football
Images of a fan jumping from the stands to escape a beating as bottles, rocks and seats fly through the air at a game between Chilean and Argentine clubs in Buenos Aires on Wednesday highlight the enduring problem of violence in Latin American football.
Over 100 people were arrested over the bloody battles between supporters of Universidad de Chile and Argentina's Independiente, which left 19 people injured, three seriously.
From Mexico to Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Chile and Ecuador, stadium violence continues to mar the beautiful game in football-mad Latin America.
Here is a quick overview of the situation:
- What causes the violence? -
Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Honduras, Ecuador, Peru and Uruguay have all enacted laws over the past two decades to tackle hooliganism, including, in some cases, with prison sentences.
But the violence continues unabated.
So far this year in Chile, twelve matches were suspended due to violence, according to the players' union.
In April, two fans died during a stampede outside a Santiago stadium before a Copa Libertadores match between local side Colo Colo and Brazil's Fortaleza.
In Argentina, more than 100 people have died in the last 20 years, 157 in Brazil between 2009 and 2019, and 170 died in Colombia between 2001 and 2019, according to academic and NGO studies.
There's an idea "that stadiums are spaces where it's legitimate to commit acts of violence, not just physical violence, but also racism and homophobia," Argentine sociologist Diego Murze, author of the book "Football, Violence, and the State," told AFP.
According to Murze, there's a "tribal logic that has always prevailed in football," including a culture of provocation between fans that has "re-emerged in recent years."
For many fans, "football is a channel for frustration," says Colombian sociologist German Gomez, author of the book "Football and Hooligans, an Urban Phenomenon."
Gomez attributed it to "a poeticization of what a team's victory means in the lives of these fans, which leads to that loss of emotional control when a match is won, and even when it is lost."
- Has tighter scrutiny worked?
Security has been stepped up at stadiums around the continent, with some requiring biometric identification for entry and installing video surveillance of the stands.
"In Argentina, they monitor you more in a soccer stadium than at the airport," Murze said,
But the technology, while useful to identify banned offenders, is often powerless to prevent violence by hitherto unknown individuals with masked faces.
The Colombian sociologist accused Conmebol, South America's football governing body, of being lax on violence, saying it doesn't "issue exemplary sanctions against soccer clubs because... closing a soccer club can mean significant financial losses."
- What more can be done? -
In Argentina, visiting fans are not allowed at local first division games.
Several clubs in the World Cup title holder, as well as in Chile and Uruguay, were forced to play behind closed doors last year as punishment for fan violence.
Murze argued that clubs need to professionalize their security apparatus, as they currently "rely entirely on what the state and the police can do."
Following the deaths of the two fans in Chile in April, the Chilean government ended the "Safe Stadium" program, an initiative created in 2011 to combat football violence, without success.
The program prohibited drums and banners from stadiums and left stadium security in the hands of private individuals.
The government has pledged to replace it with new rules for all mass events.
"Mitigating football violence in South America must be driven by actions that promote education and football culture," said Gomez.
S.Gregor--AMWN
