
-
 Winter Olympics organisers resolve snow problem at ski site
Winter Olympics organisers resolve snow problem at ski site
-
Fuming Denmark summons US ambassador over Greenland envoy

-
 UK's street artist Banksy unveils latest mural in London
UK's street artist Banksy unveils latest mural in London
-
Rugby players lose order challenge in brain injury claim

-
 UK singer Chris Rea dies at 74, days before Christmas
UK singer Chris Rea dies at 74, days before Christmas
-
Last of kidnapped Nigerian pupils handed over, government says
-
 Zambia strike late to hold Mali in AFCON opener
Zambia strike late to hold Mali in AFCON opener
-
Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations

-
 Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank
Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank
-
Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros

-
 Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record
Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record
-
Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain

-
 McCullum wants to stay as England coach despite Ashes drubbing
McCullum wants to stay as England coach despite Ashes drubbing
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Italy fines Apple nearly 100 mn euros over app privacy feature
Italy fines Apple nearly 100 mn euros over app privacy feature
-
America's Cup switches to two-year cycle

-
 Jesus could start for Arsenal in League Cup, says Arteta
Jesus could start for Arsenal in League Cup, says Arteta
-
EU to probe Czech aid for two nuclear units

-
 Strauss says sacking Stokes and McCullum will not solve England's Ashes woes
Strauss says sacking Stokes and McCullum will not solve England's Ashes woes
-
Noel takes narrow lead after Alta Badia slalom first run

-
 Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Man City players face Christmas weigh-in as Guardiola issues 'fatty' warning

-
 German Christmas markets hit by flood of fake news
German Christmas markets hit by flood of fake news
-
Liverpool fear Isak has broken leg: reports

-
 West Indies captain says he 'let the team down' in New Zealand Tests
West Indies captain says he 'let the team down' in New Zealand Tests
-
Thailand says Cambodia agrees to border talks after ASEAN meet

-
 Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic
-
Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest

-
 Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says
-
Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win

-
 Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting
-
A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
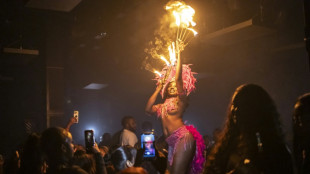
-
 US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official
-
CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform

-
 Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs
-
India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits

-
 McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride
-
Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey

-
 'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches
-
Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce

-
 As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
-
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
 Natural Products Expo West Introduces Inaugural CPG Innovation Summit for 2026 Edition
Natural Products Expo West Introduces Inaugural CPG Innovation Summit for 2026 Edition
-
HawkSearch Joins the National Association of Electrical Distributors as an Official Allied Partner

-
 Sannabis S.A.S., a Colombia Licensed Cannabis Operator, Addresses U.S. Marijuana Rescheduling and Potential Implications for International Medical Cannabis Travel and Trade
Sannabis S.A.S., a Colombia Licensed Cannabis Operator, Addresses U.S. Marijuana Rescheduling and Potential Implications for International Medical Cannabis Travel and Trade
-
LOANLEDGER AI SYSTEMS PTY LTD Confirms Official Registration and Initial Operational Phase of AI-Assisted Cryptocurrency Platform Has Been Passed


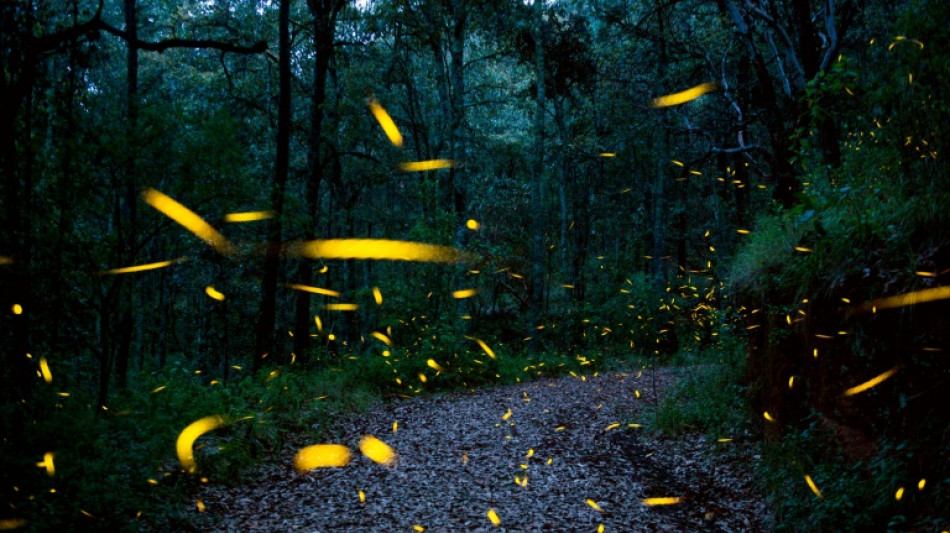
From robot fireflies to okra plasters: 2022's nature-inspired solutions
Even as animals and plants face widespread extinction from human-driven causes like climate change, the natural world continues to inspire scientific discovery in unexpected ways.
"Nature has spent hundreds of millions of years optimising elegant solutions to extremely complicated problems," said Alon Gorodetsky, a biomedical engineer at the University of California, Irvine.
"So if we look to nature, we can shortcut our development process and get to a valuable solution right away," he told AFP.
From squid-skin food warmers to a lubricant made of cow mucus, here is a selection of this year's scientific work inspired by nature.
- Okra plasters stop bleeding hearts -
Stopping the bleeding hearts and livers of dogs and rabbits without stitches may now be possible with a biodegradable plaster made of sticky okra gel.
Okra is a fuzzy green vegetable with a slimy texture that inspired Malcolm Xing from Canada's University of Manitoba to turn it into a medical adhesive.
"Okra is a fantastic material," said Xing.
In the July study published in Advanced Healthcare Materials, researchers discovered that refining okra in a juicer and then drying it into a powder creates an effective bioadhesive that quickly creates a physical barrier and starts the blood clotting process.
The researchers plan to test this plaster on humans in the coming years.
- Cow mucus lubricant -
Snot may invoke feelings of disgust, but laboratory tests found that a lubricant made of cow mucus showed promise at curtailing the spread of certain sexually transmitted infections.
The study, published in Advanced Science in September, is very preliminary, however. It has not yet been tested on humans and should not replace other forms of protection, like condoms.
Researchers extracted the mucus from the salivary glands of cows and turned it into a gel that binds to and constrains viruses. Mucus is made of a protein called mucin that might have antiviral properties.
It is also both a solid and a liquid.
"Being a solid, it can trap bacteria or viruses in the body. Being a liquid, it can clear those pathogens from the body," said study co-author Hongji Yan from Sweden's KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm.
- Robot fireflies -
Fireflies that light up the night sky inspired scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to create tiny, bug-sized robots that emit light when they fly.
The glowing artificial muscles help the honey bee-sized robots communicate with each other, which may make them useful for search and rescue missions some day.
Though the robots can only operate in a laboratory environment so far, the researchers are excited at their potential future uses.
- Cancer-sniffing ants -
There are an estimated 20 quadrillion ants in the world, and researchers have discovered that one species might be able to sniff out cancer in human breasts.
In a study conducted at Sorbonne Paris Nord University and published on the preprint server bioRxiv, which has not yet been peer-reviewed, scientists used a sugar-water reward to train ants to smell the difference between mouse urine implanted with, and without, human tumours.
While dogs can be trained to use their super noses to detect cancer, this is expensive and takes time.
Ants might provide a cheaper, albeit less cute, alternative.
- Squid-skin tea cosies -
The strange skin of squids has inspired a packaging material that can keep coffee and food warm for as long, or as little, as wanted, according to a March study published in Nature Sustainability.
Squids have miniature organs called chromatophores that can drastically change size, and also help them change colour.
To mimic "these pigment-filled organs", study co-author Alon Gorodetsky, from the University of California, Irvine, said they developed "little metal islands that you could move apart" and contract.
The heat level can then be controlled by how much the material is stretched.
"If you put it around a warm object -- for example, a coffee-filled cup or a hot sandwich -- you can control the rate at which it cools down," he said.
"Nature really is the epitome of innovation and engineering," Gorodetsky added.
L.Miller--AMWN

