-
 Thailand says Cambodia agrees to border talks after ASEAN meet
Thailand says Cambodia agrees to border talks after ASEAN meet
-
Alleged Bondi shooters conducted 'tactical' training in countryside, Australian police say

-
 Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant
-
Knicks' Brunson scores 47, Bulls edge Hawks epic

-
 Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026
Global nuclear arms control under pressure in 2026
-
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease

-
 Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest
Jailed Malaysian ex-PM Najib loses bid for house arrest
-
Banned film exposes Hong Kong's censorship trend, director says

-
 Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win
Duffy, Patel force West Indies collapse as NZ close in on Test series win
-
Australian state pushes tough gun laws, 'terror symbols' ban after shooting

-
 A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
A night out on the town during Nigeria's 'Detty December'
-
US in 'pursuit' of third oil tanker in Caribbean: official

-
 CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform
CO2 soon to be buried under North Sea oil platform
-
Steelers edge Lions as Bears, 49ers reach playoffs

-
 India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits
India's Bollywood counts costs as star fees squeeze profits
-
McCullum admits errors in Ashes preparations as England look to salvage pride

-
 Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey
Pets, pedis and peppermints: When the diva is a donkey
-
'A den of bandits': Rwanda closes thousands of evangelical churches

-
 Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce
Southeast Asia bloc meets to press Thailand, Cambodia on truce
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Heirs Energies Agrees $750m Afreximbank Financing to Drive Long-Term Growth

-
 Black Book Poll: "Governed AI" Emerges as the Deciding Factor in 2026 NHS Procurement
Black Book Poll: "Governed AI" Emerges as the Deciding Factor in 2026 NHS Procurement
-
Hemogenyx Pharmaceuticals PLC Announces Update on Admission of Shares

-
 Pantheon Resources PLC Announces Shareholder Letter and Corporate Update on Dubhe-1
Pantheon Resources PLC Announces Shareholder Letter and Corporate Update on Dubhe-1
-
Tocvan Begins Trenching Material for the Pilot Mine and Pushes Ahead With Infrastructure Development

-
 Steelers receiver Metcalf strikes Lions fan
Steelers receiver Metcalf strikes Lions fan
-
Morocco coach 'taking no risks' with Hakimi fitness

-
 Gang members given hundreds-years-long sentences in El Salvador
Gang members given hundreds-years-long sentences in El Salvador
-
Chargers, Bills edge closer to playoff berths

-
 Gang members given hundred-years-long sentences in El Salvador
Gang members given hundred-years-long sentences in El Salvador
-
Hosts Morocco off to winning start at Africa Cup of Nations

-
 No jacket required for Emery as Villa dream of title glory
No jacket required for Emery as Villa dream of title glory
-
Amorim fears United captain Fernandes will be out 'a while'

-
 Nigerian government frees 130 kidnapped Catholic schoolchildren
Nigerian government frees 130 kidnapped Catholic schoolchildren
-
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear in Bundesliga

-
 Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear
Captain Kane helps undermanned Bayern go nine clear
-
Rogers stars as Villa beat Man Utd to boost title bid

-
 Barca strengthen Liga lead at Villarreal, Atletico go third
Barca strengthen Liga lead at Villarreal, Atletico go third
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 Third day of Ukraine settlement talks to begin in Miami
Third day of Ukraine settlement talks to begin in Miami
-
Barcelona's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win

-
 Macron, on UAE visit, announces new French aircraft carrier
Macron, on UAE visit, announces new French aircraft carrier
-
Barca's Raphinha, Yamal strike in Villarreal win

-
 Gunmen kill 9, wound 10 in South Africa bar attack
Gunmen kill 9, wound 10 in South Africa bar attack
-
Allegations of new cover-up over Epstein files

-
 Atletico go third with comfortable win at Girona
Atletico go third with comfortable win at Girona
-
Schwarz breaks World Cup duck with Alta Badia giant slalom victory

-
 Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
Salah unaffected by Liverpool turmoil ahead of AFCON opener - Egypt coach
-
Goggia eases her pain with World Cup super-G win as Vonn takes third


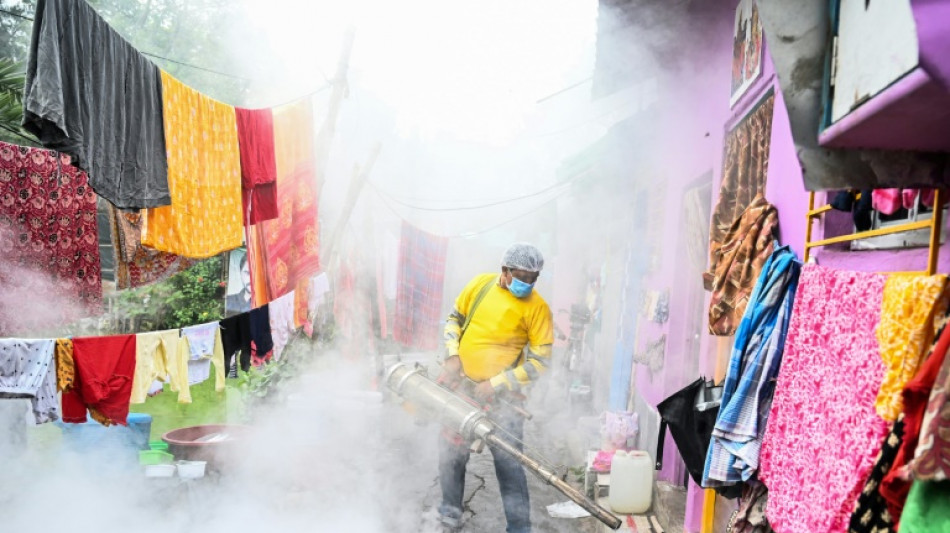
Dengue treatment advances in animal trials
A new dengue treatment that could become the first to prevent and treat the virus has proven effective in initial trials in monkeys, according to new research.
Dengue is transmitted by mosquitoes and affects tens of millions each year, producing brutal symptoms that have earned it the moniker "breakbone fever".
It is endemic in dozens of countries, but no treatment exists, and two vaccines that have been developed are not yet universally approved.
Two years ago, researchers published work showing a compound could effectively prevent the virus from replicating in cell cultures and mice by preventing the interaction between two proteins.
Now the team has refined the compound and tested it in both mice and monkeys, with "very encouraging" results, said Marnix Van Loock, lead for emerging pathogens at the Janssen Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a drug company.
In rhesus macaques, a high dose of the compound known as JNJ-1802 "completely blocked viral replication", he told AFP, while in control animals viral RNA was detected between day three and seven after infection.
In monkeys, the compound was tested against the two most prevalent of the four strains of dengue, and only for its preventative properties, rather than for treatment.
But it was tested for both treatment and prevention in mice, against all four types of dengue, with successful outcomes, Van Loock said.
Dengue can cause intense flu-like symptoms, and sometimes develops into a severe form which can be fatal.
Because there are four different strains, getting infected by one does not protect against another, and catching dengue a second time is often more serious.
Researchers have warned that a warmer, wetter climate which is more hospitable to mosquitoes is likely to increase the prevalence of viruses passed on by the insect.
With no treatment available, efforts currently focus on reducing transmission -- including by infecting mosquitoes with a bacteria.
A vaccine called Dengvaxia is approved for use only in some countries and is effective against a single strain.
A second vaccine, Qdenga, was approved last December for use by the European Union, and it has also been greenlighted by Britain and Indonesia.
There are still questions to answer about the treatment however, including whether it could increase vulnerability to reinfection.
When people contract dengue, the presence of the virus in their blood generally stimulates a potent immune response that protects them from future infection.
But in some people, the immune response is weaker and that leaves them vulnerable to reinfection, which can produce more serious symptoms.
It is not yet clear whether preventing or reducing viral replication could produce that same vulnerability to reinfection.
The researchers will need to submit safety data from their current phase of testing before moving ahead with further trials involving humans, including field studies in areas affected by dengue.
Van Loock was reluctant to speculate on when a treatment might realistically be deployable.
"We are guided by the science and the data that we generate to really answer that question," he said.
P.Martin--AMWN