
-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
-
Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
-
 USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
-
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise

-
 Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
-
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record

-
 Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
-
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje

-
 Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
-
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up

-
 US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
-
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries

-
 India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
-
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz

-
 Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through

-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'

-
 Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
-
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot

-
 'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
-
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall

-
 Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
-
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time

-
 Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
-
Griezmann 'will continue' with Atletico despite MLS option: sporting director

-
 Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
-
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France

-
 Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
-
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels

-
 Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
-
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes


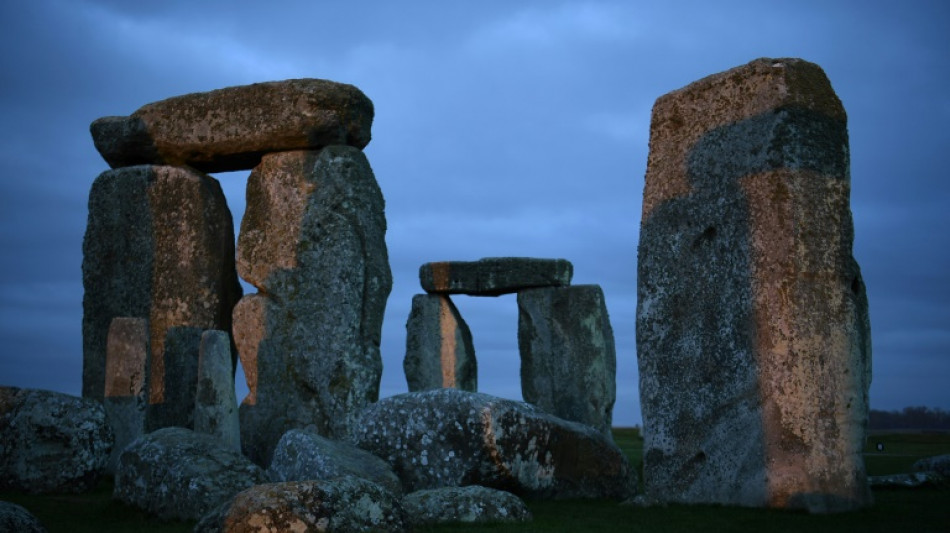
Stonehenge mystery deepens as altar traced to Scotland
A central stone of the famous Stonehenge monument in southwest England came from 750 kilometres away in northeast Scotland, surprised scientists said Wednesday, solving one mystery but raising another: how did its prehistoric builders move the huge slab so far?
The Neolithic circle of giant stones has been a source of wonder and mystery for nearly 5,000 years -- in the Middle Ages, the wizard Merlin of Arthurian legend was said to have stolen the monument from Ireland.
More recently, scientists have determined that the site's upright sandstones came from relatively nearby Marlborough, while the bluestones arrayed near its centre came from Wales.
But the origin of the Altar Stone, a unique six-tonne slab laying on its side at the heart of the circle, remained elusive.
It was long thought to have also come from Wales, but tests along those lines always "drew a blank," said Richard Bevins, a professor from Aberystwyth University, mid-Wales, and co-author of a new study.
This prompted a team of British and Australian researchers to broaden their horizons -- and in turn discover something "quite sensational", he told AFP.
Using chemical analysis, they determined that the Altar Stone came from Scotland's Orcadian Basin, which is at least 750 kilometres (460 miles) from Stonehenge, according to the study in the journal Nature.
- 'Genuinely shocking' -
The researchers were stunned.
"This is a genuinely shocking result," study co-author Robert Ixer of University College London said in a statement.
The "astonishing" distance was the longest recorded journey for any stone at the time, said fellow co-author Nick Pearce of Aberystwyth University.
Whether people around 2,500 BC were capable of transporting such huge stones from Wales had already been a matter of heated debate among archaeologists and historians.
That a five-by-one-metre (16-by-three-feet) stone made the trip across much of the length of the UK suggests that the British isles were home to a highly organised and well-connected society at the time, the researchers said.
They called for further research to find out exactly where in Scotland the stone came from -- and how it made its way to Stonehenge.
One theory is that the stone was brought to southern England not by humans but by naturally moving ice flows.
However research has shown that ice would actually have carried such stones "northwards, away from Stonehenge", lead study author Anthony Clarke from Australia's Curtin University told a news conference.
Another option was that the Neolithic builders moved the stones over land -- though this would have been extraordinarily difficult.
Dense forest, marshy bogs and mountains all formed "formidable barriers" for prehistoric movers, Clarke said.
- 'Incredibly important' -
Another option is that the stone was transported by sea.
There is evidence of an "extensive network of Neolithic shipping," which moved pottery and gems around the region, Clarke said.
To work out where it came from, the researchers fired laser beams into the crystals of a thin slice of the Altar Stone.
The ratio of uranium and lead in these crystals act as "miniature clocks" for rocks, providing their age, said study co-author Chris Kirkland of Curtin University.
The team then compared the stone's age to other rocks across the UK and found "with a high degree of certainty" that it came from the Orcadian Basin, Kirkland said.
Susan Greaney, an archaeologist at the UK's University of Exeter not involved in the study, said it established the first "direct link" between southern England and northern Scotland during this time.
"The placement of this stone at the heart of the monument, on the solstice axis, shows that they thought this stone, and by implication, the connection with the area to the north, was incredibly important," she told AFP.
F.Pedersen--AMWN



