
-
 Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
Sri Lanka hospital releases 22 rescued Iranian sailors
-
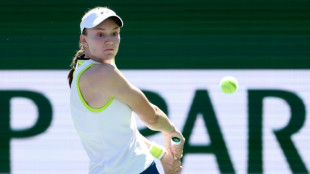
Andreeva powers into Indian Wells third round with 6-0, 6-0 rout
-
 USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
USA rout Britain after nervy start in World Baseball Classic
-
Young Chinese parents tighten belts as childcare costs rise

-
 Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
Sony faces $2.7 bn class action from UK PlayStation users
-
Thunder secure 50th win as Gilgeous-Alexander nears record

-
 Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
Nepal's rapper-led centrist party heads for poll landslide
-
White House UFC event to be headlined by Topuria-Gaethje

-
 Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
Philippines' 'Cockroach Lord' goes to bat for misunderstood bugs
-
Piastri out of Australian Grand Prix after crashing in lead-up

-
 US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
US court voids mass layoffs at Voice of America parent
-
Explosion at US embassy in Oslo, no injuries

-
 India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
India's economy is booming, but uneven growth clouds ascent
-
German state election a test for Chancellor Merz

-
 Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
Israeli strike kills four at Beirut hotel: Lebanon
-
Alcaraz cruises into Indian Wells third round as Djokovic fights through

-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
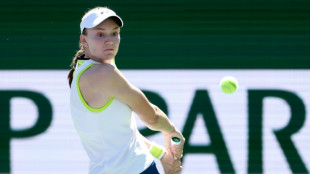
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'

-
 Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
-
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot

-
 'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
-
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall

-
 Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
-
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time

-
 Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
-
Griezmann 'will continue' with Atletico despite MLS option: sporting director

-
 Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
-
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France

-
 Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
-
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels

-
 Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
-
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes


Scientists pinpoint dino-killing asteroid's origin: past Jupiter
An intense debate surrounding the cosmic rock that killed the dinosaurs has stirred scientists for decades, but a new study has revealed some important -- and far-out -- data about the impactor's origin story.
Researchers, whose findings were published Thursday in the journal Science, used an innovative technique to demonstrate that the apocalyptic culprit which slammed into the Earth's surface 66 million years ago, causing the most recent mass extinction, had formed beyond Jupiter's orbit.
They also refute the idea that it was a comet.
The new insights into the apparent asteroid that cratered into Chicxulub, in what is present-day Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula, could improve the understanding of celestial objects that have struck our planet.
"Now we can, with all this knowledge... say that this asteroid initially formed beyond Jupiter," Mario Fischer-Godde, lead author of the study and a geochemist at the University of Cologne, told AFP.
The conclusions are particularly notable, given how rarely this type of asteroid collides with Earth.
Such information may well prove useful in assessing future threats, or determining how water arrived on this planet, Fischer-Godde said.
- Samples -
The new findings are based on analysis of sediment samples formed at the period between the Cretaceous and Paleogene eras, the time of the asteroid's cataclysmic impact.
Researchers measured the isotopes of the element ruthenium, not uncommon on asteroids but extremely rare on Earth. So by inspecting the deposits in multiple geological layers that mark the debris from the impact at Chicxulub, they could be sure that the ruthenium studied came "100 percent from this asteroid."
"Our lab in Cologne is one of the rare labs that can do these measurements," and it was the first time such study techniques were used on impact debris layers, Fischer-Godde said.
Ruthenium isotopes can be used to distinguish between the two main groups of asteroids: C-type, or carbonaceous, asteroids that formed in the outer solar system, and S-type silicate asteroids from the inner solar system, nearer the sun.
The study affirms that the asteroid that triggered a mega-earthquake, precipitated a global winter and wiped out the dinosaurs and most other life, was a C-type asteroid that formed beyond Jupiter.
Studies from two decades ago had already made such an assumption, but with far less certainty.
The conclusions are striking, because most meteorites -- pieces of asteroids that fall to Earth -- are S-types, Fischer-Godde pointed out.
Does that mean the Chicxulub impactor formed beyond Jupiter and made a beeline for our planet? Not necessarily.
"We cannot be really sure where the asteroid was kind of hiding just before it impacted on Earth," Fischer-Godde said, adding that after its formation, it may have made a stopover in the asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter and where most meteorites originate.
- Not a comet -
The study also dismisses the idea that the destructive impactor was a comet, an amalgam of icy rock from the very edge of the solar system. Such a hypothesis was put forward in a much-publicized study in 2021, based on statistical simulations.
Sample analyses now show that the celestial object was far different in composition from a subset of meteorites which are believed to have been comets in the past. It is therefore "unlikely" the impactor in question was a comet, Fischer-Godde said.
As to the wider usefulness of his findings, the geochemist offered two suggestions.
He believes that more accurately defining the nature of asteroids that have struck Earth since its beginnings some 4.5 billion years ago could help solve the enigma of the origin of our planet's water.
Scientists believe water may have been brought to Earth by asteroids, likely of the C-type like the one that struck 66 million years ago, even though they are less frequent.
Studying past asteroids also allows humanity to prepare for the future, Fischer-Godde said.
"If we find that earlier mass extinction events could also be related to C-type asteroid impacts, then... if there's ever going to be C-type asteroid on an Earth-crossing orbit, we have to be very careful," he said, "because it might be the last one we witness."
D.Moore--AMWN



