
-
 Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
Russell tops final practice in Melbourne as Antonelli crashes heavily
-
Vibes war? Trump pitches Iran conflict on 'feeling'

-
 Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
Nepal's rapper-turned-politician looks set for landslide win
-
Tatum's 'emotional' return sparks Celtics over Mavs

-
 Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
Rising US fuel prices risk sparking domestic wildfire for Trump
-
Questions over AI capability as tech guides Iran strikes

-
 Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
Trump convenes Latin American leaders to curb crime, immigration
-
Venezuela inflation hit 475% in 2025, the world's highest level

-
 Only Iran's 'unconditional surrender' can end war: Trump
Only Iran's 'unconditional surrender' can end war: Trump
-
Former 100m champion Kerley banned two years over whereabouts failures

-
 Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
Sabalenka opens Indian Wells bid with dominant win
-
Doris relieved Ireland's slim title hopes intact after 'scrappy' win over Welsh

-
 Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
Man City aren't a 'complete team' admits Guardiola
-
Arteta warns Arsenal to preserve reputation in Mansfield clash

-
 Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
Timothee Chalamet taken to task over opera, ballet dig
-
Ireland keep title hopes alive in thrilling win over Wales

-
 Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
Hungary has not returned cash seized from bank workers, Kyiv says
-
Napoli secure first Serie A home win since January

-
 Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
Valverde strikes late as Real Madrid beat Celta Vigo
-
PSG beaten by Monaco ahead of Chelsea Champions League showdown

-
 Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
Liverpool tame Wolves to reach FA Cup quarter-finals
-
Kane-less Bayern brush aside Gladbach to continue title march

-
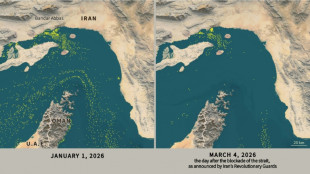 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Berger extends lead midway through Arnold Palmer Invitational

-
 Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
Paralympics open with Russian athletes booed in ceremony
-
Cuba 'next' on agenda, after Iran: Trump
-
 Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
Zverev leads way into Indian Wells third round
-
NASA defense test kicked asteroid off course -- and changed its orbit around the sun

-
 Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
Anthropic vows court fight in Pentagon row
-
'Harder path': Obama attacks Trump at Jesse Jackson memorial

-
 Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
Amber Glenn says will not visit White House to celebrate Olympic gold
-
Russian athletes booed as they parade under own flag at Paralympics opening

-
 Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
Trump to attend return of six US troops killed in Iran war
-
Tom Brady flag football event moved from Saudi to Los Angeles: reports

-
 UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
UN chief slams 'unlawful attacks', says Mideast could spiral out of control
-
Middle East war a new shock for financial markets

-
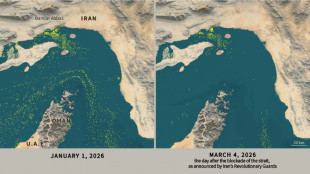 Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
Only nine commercial ships detected crossing the Hormuz Strait since Monday
-
Mexico unveils 100,000-strong security deployment for World Cup

-
 Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
Trump's Iran war violates international law, experts say
-
Swiss eyeing fewer F-35 fighters, reshaping defence set-up

-
 UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
UK police question three women in Al-Fayed probe
-
Oil prices surge as Mideast war rages, stocks fall on US jobs

-
 Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
Dupont says France must forget Six Nations title talk against Scotland
-
Voices from Iran: protests, fear and scarcity

-
 Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
Champions League ambitions encourage Barca gamble in Bilbao
-
This is how Ukraine has countered Russia's Iran-designed drones

-
 Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
Dybala out for six weeks as Roma battle for top-four spot
-
Sleepless Iranians count cost of war as damage mounts

-
 Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
Itoje tells faltering England to 'take the game to Italy' in Six Nations
-
Leading satellite firm to hold back Gulf state images


The secret to living to 110? Bad record-keeping, researcher says
Most of what we know about humans living to very old age is based on faulty data, including the science behind the "blue zones" famous for having a high proportion of people over 100, according to one researcher.
The desire to live as long as possible has driven a booming lifestyle industry selling supplements, books, tech and tips to those wanting to learn the secrets of the world's oldest people.
But Saul Justin Newman, a researcher at University College London's Centre for Longitudinal Studies, told AFP that most extreme old age data "is junk to a really shocking degree".
Newman's research, which is currently being peer-reviewed, looked at data about centenarians and supercentenarians -- people who live to 100 and 110 -- in the United States, Italy, England, France and Japan.
Contrary to what one might expect, he found that supercentenarians tended to come from areas with poor health, high levels of poverty -- and bad record-keeping.
The true secret to extreme longevity seems to be to "move where birth certificates are rare, teach your kids pension fraud and start lying", Newman said as he accepted an Ig Nobel prize, a humorous version of the Nobel, in September.
Just one of many examples is Sogen Kato, who was thought to be Japan's oldest living person until his mummified remains were discovered in 2010.
It turned out he had been dead since 1978. His family was arrested for collecting three decades of pensions payments.
The government then launched a review which found that 82 percent of Japan's centenarians -- 230,000 people -- were missing or dead.
"Their paperwork is in order, they're just dead," Newman said.
This illustrates the problem Newman has sought to shine a light on -- that confirming ages in this field involves triple-checking very old documents that could have been wrong from the start.
The industry that has popped up around blue zones is one "symptom" of this problem, he said.
- 'Only alive on pension day' -
Blue zones are regions around the world where people are said to live disproportionately longer and healthier lives.
The term was first used in 2004 by researchers referring to the Italian island of Sardinia.
The following year, National Geographic reporter Dan Buettner wrote a story that added the Japanese islands of Okinawa and the Californian city of Loma Linda.
Buettner admitted to the New York Times in October that he only included Loma Linda because his editor told him: "you need to find America's blue zone".
The reporter teamed up with some demographers to create the Blue Zones lifestyle brand, and they added Costa Rica's Nicoya Peninsula and the Greek island of Ikaria to the list.
However, as seen in Japan, later government records have cast doubt on old age data in these regions.
In Costa Rica, 2008 research showed that 42 percent of centenarians had "lied about their age" in an earlier census, Newman said.
For Greece, he found 2012 data suggesting that 72 percent of the country's centenarians were dead or imaginary.
"They're only alive on pension day," Newman said.
Several prominent blue zone researchers wrote a rebuttal earlier this year, calling Newman's work "ethically and academically irresponsible".
They accused Newman of referring to broader regions of Japan and Sardinia when the blue zones were smaller areas.
The demographers also emphasised they had "meticulously validated" the ages of supercentenarians in blue zones, double-checking historical records and registries dating back to the 1800s.
Newman said this argument illustrated his point.
"If you start with a birth certificate that's wrong, that gets copied to everything, and you get perfectly consistent, perfectly wrong records," he said.
- A clock to measure age -
The only "way out of this quagmire" is to physically measure people's ages, Newman said.
Steve Horvath, an ageing researcher at the University of California, told AFP he had created a new technique called a methylation clock "for the express purpose of validating claims of exceptional longevity".
The clock can "reliably detect instances of severe fraud", such as when a child assumes their parent's identity, but cannot yet tell the difference between a 115- and 120-year-old, he said.
Horvath has offered to test a DNA sample of France's Jeanne Calment, who died at 122 in 1997 and holds the record for the oldest confirmed age.
Newman's analysis "appears to be both rigorous and convincing", Horvath said, adding that several blue zones are overseen by rigorous scientists.
"I suspect both opinions hold some truth," he said.
So what can people at home take away from this debate?
"If you want to live a long time, step number one: don't buy anything," Newman said.
"Listen your GP (doctor), do some exercise, don't drink, don't smoke -- that's it."
Y.Kobayashi--AMWN

