
-
 Fears of Mideast war as US-Iran conflict flares
Fears of Mideast war as US-Iran conflict flares
-
Guardiola expects short absence for injured Haaland

-
 Liverpool's set play transformation a return to 'normal' for Slot
Liverpool's set play transformation a return to 'normal' for Slot
-
Man City win to close on Arsenal as Liverpool hit five

-
 Kane bags brace as Bayern end Dortmund's title hopes
Kane bags brace as Bayern end Dortmund's title hopes
-
Semenyo sinks Leeds as Man City close gap on Arsenal

-
 Last-gasp Lukaku saves Napoli's blushes at rock-bottom Verona
Last-gasp Lukaku saves Napoli's blushes at rock-bottom Verona
-
Could the US-Israel war on Iran drag on?

-
 Iranians abroad jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
Iranians abroad jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
-
Pakistan 'have underperformed' says Agha after T20 World Cup exit

-
 Under-strength Toulouse overpower Montauban in Top 14
Under-strength Toulouse overpower Montauban in Top 14
-
Vietnam AI law takes effect, first in Southeast Asia

-
 Brazil's Lula visits flood zone as death toll from landslides hits 70
Brazil's Lula visits flood zone as death toll from landslides hits 70
-
New Zealand into T20 World Cup semis as Sri Lanka avoid big Pakistan loss

-
 Medvedev wins Dubai title as Griekspoor withdraws
Medvedev wins Dubai title as Griekspoor withdraws
-
First Yamal hat-trick helps Liga leaders Barcelona beat Villarreal

-
 Liverpool hit five past West Ham, Haaland-less City face Leeds test
Liverpool hit five past West Ham, Haaland-less City face Leeds test
-
Van der Poel romps to cobbled classic win

-
 Republicans back Trump, Democrats attack 'illegal' Iran war
Republicans back Trump, Democrats attack 'illegal' Iran war
-
Madonna is surprise attraction at Dolce & Gabbana Milan show

-
 Farhan keeps Pakistan hopes alive as they post 212-8 against Sri Lanka
Farhan keeps Pakistan hopes alive as they post 212-8 against Sri Lanka
-
Afghanistan says civilians killed in Pakistan air strikes

-
 Tug of war: how US presidents battle Congress for military powers
Tug of war: how US presidents battle Congress for military powers
-
Residents flee as Iran missiles stun peaceful Gulf cities

-
 Streets empty and shops close as US strikes confirm Iranian fears
Streets empty and shops close as US strikes confirm Iranian fears
-
Israelis shelter underground as Iran fires missiles

-
 Bournemouth held by Sunderland in blow to European bid
Bournemouth held by Sunderland in blow to European bid
-
VAR expanded to include second bookings and corners for World Cup

-
 Iranians in Istanbul jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
Iranians in Istanbul jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
-
Congo-Brazzaville president vows to keep power as campaign kicks off

-
 US, Israel launch strikes on Iran, Tehran hits back across region
US, Israel launch strikes on Iran, Tehran hits back across region
-
Germany's Aicher wins women's super-G in Soldeu

-
 Fight against terror: Trump threatens Tehran's mullahs
Fight against terror: Trump threatens Tehran's mullahs
-
US and Israel launch strikes on Iran, explosions reported across region

-
 Iran's Khamenei: ruthless revolutionary at apex of Islamic republic
Iran's Khamenei: ruthless revolutionary at apex of Islamic republic
-
In Iran attack, Trump seeks what he foreswore -- regime change
-
 Climate change forces facelift for Michelangelo masterpiece
Climate change forces facelift for Michelangelo masterpiece
-
Trump says US aims to destroy Iran's military, topple government
-
 Acosta wins season-opening MotoGP sprint after Marquez penalty
Acosta wins season-opening MotoGP sprint after Marquez penalty
-
US and Israel launch strikes against Iran

-
 Afghanistan says Pakistan fighter jet down as cross-border strikes flare
Afghanistan says Pakistan fighter jet down as cross-border strikes flare
-
Kerr says only '85 percent' fit for Women's Asian Cup

-
 Messi's Inter Miami to visit White House: US media
Messi's Inter Miami to visit White House: US media
-
Thunder beat Nuggets in overtime on Gilgeous-Alexander's return

-
 'It's surreal': Zimbabwe superfans revel in unexpected ride to India
'It's surreal': Zimbabwe superfans revel in unexpected ride to India
-
New 'Wuthering Heights' film unleashes fresh wave of Bronte-mania

-
 US backs Pakistan's 'right to defend itself' after strikes on Afghanistan
US backs Pakistan's 'right to defend itself' after strikes on Afghanistan
-
Bezzecchi beats Marquez to pole at season-opening Thailand MotoGP

-
 OpenAI strikes Pentagon deal with 'safeguards' as Trump dumps Anthropic
OpenAI strikes Pentagon deal with 'safeguards' as Trump dumps Anthropic
-
Oscar-nominated 'F1' sound engineers recreate roar of racetrack


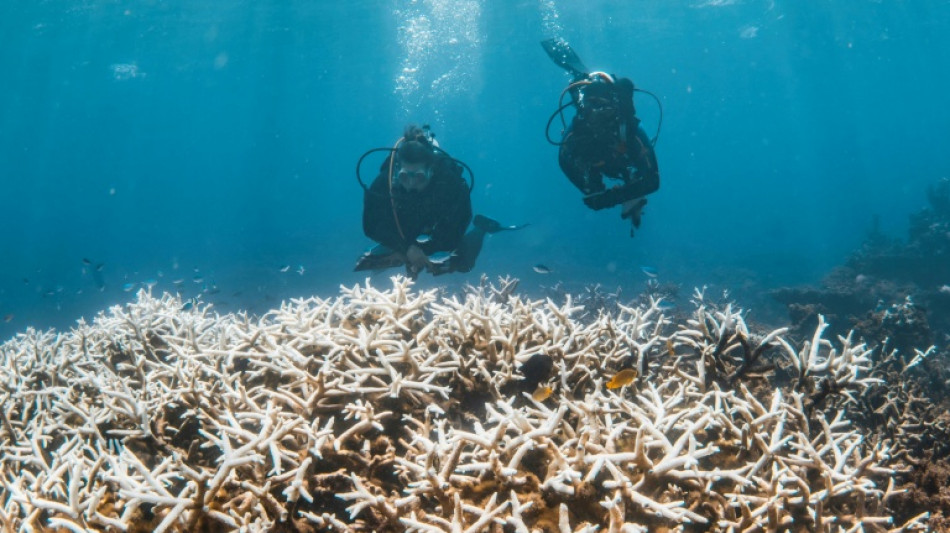
Coral frozen in time throws lifeline for Great Barrier Reef
Rows of tanks filled with liquid nitrogen sit in temperature-controlled chambers at Sydney's Taronga zoo, cradling parts of the Great Barrier Reef's diverse and magnificent corals frozen in time.
The world's largest store of cryogenically frozen coral is a frosty Noah's Ark for an ecosystem that scientists warn could be the first to disappear if climate change is not combatted fast enough.
Trillions of cells from dozens of key coral species on the Great Barrier Reef (GBR) -— collected each year during mass spawning -- offer the chance to regenerate damaged and diminished corals now and into the future.
"Essentially, a pause button has been pressed on their biological clocks," said Justine O'Brien, manager of conservation science at Taronga Conservation Society Australia.
"I hope our collective efforts can help to retain the reef's beautiful diversity," she told AFP.
Since the coral programme began in 2011, Taronga's CryoDiversity Bank has been intruding annually on the GBR's spawning, when corals send eggs and sperm into the waters for breeding.
Scientists collect the sperm and mix it with cryoprotectants, which remove water as the samples freeze, and protect internal cell structures.
Eggs contain too much water and fat to be frozen without damage using current techniques, so for now cannot be similarly banked, but other cells are also harvested and frozen for research.
The samples are placed into liquid nitrogen and stored at -196 degrees Celsius (-320 Fahrenheit). Strict measures ensure the temperature never changes.
"We can keep them alive indefinitely," O'Brien said.
"You could thaw them out a few years from now, a few decades from now or hundreds of years from now and they will have retained the same fertilising potential that existed when they were initially collected and frozen."
- Coral disease, death -
So far the bank has 34 species of the approximately 400 kinds of hard corals on the GBR, prioritising those most essential to reef structure and function, with plans to expand.
In addition to reproduction, the samples can be used for research and record-keeping, helping track the effects of warming seas, overfishing and pollution that threaten coral reefs globally.
Scientists forecast that at 1.5 Celsius (34.7 Fahrenheit) of warming, some 70 to 90 percent of the world's coral reefs could disappear -- a disastrous prospect for people and the planet.
Coral reefs support not just marine life but hundreds of millions of people living in coastal communities by providing food, protection from storms and livelihoods through fishing and tourism.
Warming oceans cause coral to expel the algae that provides not just their characteristic colour but also their food. Once bleached, they are exposed to disease and death by starvation.
A global coral bleaching event has been unfolding since 2023, spreading to 84 percent of the world's reefs, across the Pacific, Indian and Atlantic oceans.
Live coral cover has halved since the 1950s due to climate change and environmental damage, the International Coral Reef Initiative, a global conservation partnership, said this year.
Next week, nations will meet in France for a UN oceans summit where they will be under pressure to deliver action and much-needed funds to better protect the world's overexploited and polluted seas.
But the third UN Ocean Conference may struggle to find global consensus and raise money given ongoing disagreements over deep-sea mining, plastic trash and overfishing.
- 'Window closing' -
O'Brien warns the GBR is under pressure, despite the resilience it has already shown.
"We know the frequency and severity of impacts that are now occurring are not giving the reef enough recovery time," she said.
The cryobank, one of just a handful around the world, offers a glimmer of hope.
Last year, Taronga and Australian Institute of Marine Science researchers successfully thawed frozen coral sperm to fertilise fresh eggs, producing viable coral larvae that were placed back onto the reef.
It was a world-first for the GBR and preliminary surveys show the transplants have grown well.
These efforts -- part of a broader programme looking at everything from shading corals to transplanting more heat-tolerant varieties -- are a "small part of the solution to the global coral reef crisis," said WWF-Australia's head of oceans Richard Leck.
But he warned that more needs to be done to ensure the long-term survival of coral.
"Reefs are incredibly resilient and they do bounce back remarkably quickly after major disturbances," he told AFP.
"There is certainly a window to get reefs through climate change, but it is clear that that window is closing."
Ch.Havering--AMWN


