
-
 Liverpool's set play transformation a return to 'normal' for Slot
Liverpool's set play transformation a return to 'normal' for Slot
-
Man City win to close on Arsenal as Liverpool hit five

-
 Kane bags brace as Bayern end Dortmund's title hopes
Kane bags brace as Bayern end Dortmund's title hopes
-
Semenyo sinks Leeds as Man City close gap on Arsenal

-
 Last-gasp Lukaku saves Napoli's blushes at rock-bottom Verona
Last-gasp Lukaku saves Napoli's blushes at rock-bottom Verona
-
Could the US-Israel war on Iran drag on?

-
 Iranians abroad jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
Iranians abroad jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
-
Pakistan 'have underperformed' says Agha after T20 World Cup exit

-
 Under-strength Toulouse overpower Montauban in Top 14
Under-strength Toulouse overpower Montauban in Top 14
-
Vietnam AI law takes effect, first in Southeast Asia

-
 Brazil's Lula visits flood zone as death toll from landslides hits 70
Brazil's Lula visits flood zone as death toll from landslides hits 70
-
New Zealand into T20 World Cup semis as Sri Lanka avoid big Pakistan loss

-
 Medvedev wins Dubai title as Griekspoor withdraws
Medvedev wins Dubai title as Griekspoor withdraws
-
First Yamal hat-trick helps Liga leaders Barcelona beat Villarreal

-
 Liverpool hit five past West Ham, Haaland-less City face Leeds test
Liverpool hit five past West Ham, Haaland-less City face Leeds test
-
Van der Poel romps to cobbled classic win

-
 Republicans back Trump, Democrats attack 'illegal' Iran war
Republicans back Trump, Democrats attack 'illegal' Iran war
-
Madonna is surprise attraction at Dolce & Gabbana Milan show

-
 Farhan keeps Pakistan hopes alive as they post 212-8 against Sri Lanka
Farhan keeps Pakistan hopes alive as they post 212-8 against Sri Lanka
-
Afghanistan says civilians killed in Pakistan air strikes

-
 Tug of war: how US presidents battle Congress for military powers
Tug of war: how US presidents battle Congress for military powers
-
Residents flee as Iran missiles stun peaceful Gulf cities

-
 Streets empty and shops close as US strikes confirm Iranian fears
Streets empty and shops close as US strikes confirm Iranian fears
-
Israelis shelter underground as Iran fires missiles

-
 Bournemouth held by Sunderland in blow to European bid
Bournemouth held by Sunderland in blow to European bid
-
VAR expanded to include second bookings and corners for World Cup

-
 Iranians in Istanbul jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
Iranians in Istanbul jittery but jubilant at US, Israeli strikes
-
Congo-Brazzaville president vows to keep power as campaign kicks off

-
 US, Israel launch strikes on Iran, Tehran hits back across region
US, Israel launch strikes on Iran, Tehran hits back across region
-
Germany's Aicher wins women's super-G in Soldeu

-
 Fight against terror: Trump threatens Tehran's mullahs
Fight against terror: Trump threatens Tehran's mullahs
-
US and Israel launch strikes on Iran, explosions reported across region

-
 Iran's Khamenei: ruthless revolutionary at apex of Islamic republic
Iran's Khamenei: ruthless revolutionary at apex of Islamic republic
-
In Iran attack, Trump seeks what he foreswore -- regime change
-
 Climate change forces facelift for Michelangelo masterpiece
Climate change forces facelift for Michelangelo masterpiece
-
Trump says US aims to destroy Iran's military, topple government
-
 Acosta wins season-opening MotoGP sprint after Marquez penalty
Acosta wins season-opening MotoGP sprint after Marquez penalty
-
US and Israel launch strikes against Iran

-
 Afghanistan says Pakistan fighter jet down as cross-border strikes flare
Afghanistan says Pakistan fighter jet down as cross-border strikes flare
-
Kerr says only '85 percent' fit for Women's Asian Cup

-
 Messi's Inter Miami to visit White House: US media
Messi's Inter Miami to visit White House: US media
-
Thunder beat Nuggets in overtime on Gilgeous-Alexander's return

-
 'It's surreal': Zimbabwe superfans revel in unexpected ride to India
'It's surreal': Zimbabwe superfans revel in unexpected ride to India
-
New 'Wuthering Heights' film unleashes fresh wave of Bronte-mania

-
 US backs Pakistan's 'right to defend itself' after strikes on Afghanistan
US backs Pakistan's 'right to defend itself' after strikes on Afghanistan
-
Bezzecchi beats Marquez to pole at season-opening Thailand MotoGP

-
 OpenAI strikes Pentagon deal with 'safeguards' as Trump dumps Anthropic
OpenAI strikes Pentagon deal with 'safeguards' as Trump dumps Anthropic
-
Oscar-nominated 'F1' sound engineers recreate roar of racetrack

-
 15 dead as cash-packed military plane crashes in Bolivia
15 dead as cash-packed military plane crashes in Bolivia
-
Costa Rica's Grynspan pledges reform in bid for UN chief job


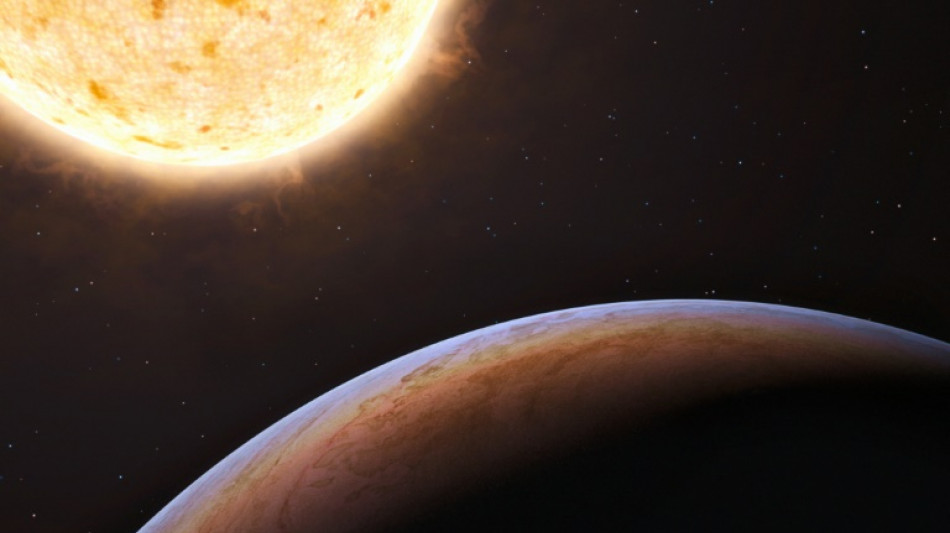
Huge planet discovered orbiting tiny star puzzles scientists
Astronomers announced Wednesday they have discovered a massive planet orbiting a tiny star, a bizarre pairing that has stumped scientists.
Most of the stars across the Milky Way are small red dwarfs like TOI-6894, which has only 20 percent the mass of our Sun.
It had not been thought possible that such puny, weak stars could provide the conditions needed to form and host huge planets.
But an international team of astronomers have detected the unmistakable signature of a gas giant planet orbiting the undersized TOI-6894, according to a study in the journal Nature Astronomy.
This makes the star the smallest star yet known to host a gas giant.
The planet has a slightly larger radius than Saturn, but only half its mass. It orbits its star in a little over three days.
The astronomers discovered the planet when searching through more than 91,000 low-mass red dwarfs observed by NASA's TESS space telescope.
Its existence was then confirmed by ground-based telescopes, including Chile's Very Large Telescope.
"The fact that this star hosts a giant planet has big implications for the total number of giant planets we estimate exist in our galaxy," study co-author Daniel Bayliss of the UK's Warwick University said in a statement.
Another co-author, Vincent Van Eylen, of University College London, said it was an "intriguing discovery".
"We don't really understand how a star with so little mass can form such a massive planet!" he said.
"This is one of the goals of the search for more exoplanets. By finding planetary systems different from our solar system, we can test our models and better understand how our own solar system formed."
- How do you make a planet? -
The most prominent theory for how planets form is called core accretion.
The process begins when a ring of gas and dust -- called a protoplanetary disc -- which surrounds a newly formed star builds up into a planetary core. This core attracts more gas that forms an atmosphere, eventually snowballing into a gas giant.
Under this theory, it is difficult for low-mass stars to host giant planets because there is not enough gas and dust to begin building a core in the first place.
A rival theory proposes that these planets instead form when their protoplanetary disc becomes gravitationally unstable and breaks up, with the collapsing gas and dust forming a planet.
However neither theory seems to explain the existence of the newly discovered planet, TOI-6894b, the researchers said.
The planet also interests scientists because it is strangely cold.
Most of the gas giants discovered outside our Solar System so far have been what are known as "hot Jupiters", where temperatures soar well over 1,000 degrees Celsius.
But the newly discovered planet appears to be under 150C, the researchers said.
"Temperatures are low enough that atmospheric observations could even show us ammonia, which would be the first time it is found in an exoplanet atmosphere," said study co-author Amaury Triaud of Birmingham University.
The James Webb space telescope is scheduled to turn its powerful gaze towards the planet in the next year, which could help uncover some more mysteries of this strange planet.
A.Jones--AMWN


