
-
 EU must 'tear down barriers' to become 'global giant': von der Leyen
EU must 'tear down barriers' to become 'global giant': von der Leyen
-
US grand jury rejects bid to indict Democrats over illegal orders video

-
 Struggling brewer Heineken to cut up to 6,000 jobs
Struggling brewer Heineken to cut up to 6,000 jobs
-
Asian stock markets rise, dollar dips as traders await US jobs

-
 Britain's Harris Dickinson on John Lennon, directing and news overload
Britain's Harris Dickinson on John Lennon, directing and news overload
-
9 killed in Canada mass shooting that targeted school, residence

-
 Wembanyama scores 40 as Spurs rout Lakers, Pacers stun Knicks
Wembanyama scores 40 as Spurs rout Lakers, Pacers stun Knicks
-
UK's crumbling canals threatened with collapse

-
 Hong Kong convicts father of wanted activist over handling of funds
Hong Kong convicts father of wanted activist over handling of funds
-
Australia charges two Chinese nationals with foreign interference

-
 'Overloading' may have led to deadly Philippine ferry sinking
'Overloading' may have led to deadly Philippine ferry sinking
-
Bangladesh to vote on democratic reform charter

-
 China coach warns of 'gap' ahead of Women's Asian Cup title defence
China coach warns of 'gap' ahead of Women's Asian Cup title defence
-
Glitzy Oscar nominees luncheon back one year after LA fires

-
 Pacers outlast Knicks in overtime
Pacers outlast Knicks in overtime
-
9 killed in Canada mass shooting that targeted school, residence: police

-
 De Zerbi leaves Marseille 'by mutual agreement'
De Zerbi leaves Marseille 'by mutual agreement'
-
Netanyahu to push Trump on Iran missiles in White House talks

-
 England captain Stokes has surgery after being hit in face by ball
England captain Stokes has surgery after being hit in face by ball
-
Rennie, Joseph lead running to become next All Blacks coach

-
 Asian stock markets mixed as traders weigh US data, await jobs
Asian stock markets mixed as traders weigh US data, await jobs
-
Australian Olympic snowboarder airlifted to hospital with broken neck

-
 Moderna says US refusing to review mRNA-based flu shot
Moderna says US refusing to review mRNA-based flu shot
-
'Artists of steel': Japanese swords forge new fanbase

-
 New York model, carved in a basement, goes on display
New York model, carved in a basement, goes on display
-
Noisy humans harm birds and affect breeding success: study

-
 More American women holding multiple jobs as high costs sting
More American women holding multiple jobs as high costs sting
-
Charcoal or solar panels? A tale of two Cubas

-
 Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Notice of GM
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Notice of GM
-
Tocvan Announces Restart Of Exploration Drilling At The Gran Pilar Project South Block

-
 Corporate Treasury & Digital Infrastructure Note: The Active Management Divergence
Corporate Treasury & Digital Infrastructure Note: The Active Management Divergence
-
Several wounded in clashes at Albania opposition rally

-
 Chelsea's draw with Leeds 'bitter pill' for Rosenior
Chelsea's draw with Leeds 'bitter pill' for Rosenior
-
'On autopilot': US skate star Malinin nears more Olympic gold

-
 Carrick frustrated by Man Utd's lack of sharpness in West Ham draw
Carrick frustrated by Man Utd's lack of sharpness in West Ham draw
-
Frank confident of keeping Spurs job despite Newcastle defeat

-
 James's All-NBA streak ends as Lakers rule superstar out of Spurs clash
James's All-NBA streak ends as Lakers rule superstar out of Spurs clash
-
Anti-Khamenei slogans in Tehran on eve of revolution anniversary: social media footage

-
 Colombian senator kidnapped, president targeted in election run-up
Colombian senator kidnapped, president targeted in election run-up
-
Britney Spears sells rights to her music catalog: US media

-
 West Ham end Man Utd's winning run, Spurs sink to 16th
West Ham end Man Utd's winning run, Spurs sink to 16th
-
US skate star Malinin leads after short programme in Olympics

-
 Man Utd's Sesko strikes late to rescue West Ham draw
Man Utd's Sesko strikes late to rescue West Ham draw
-
Shiffrin flops at Winter Olympics as helmet row grows

-
 Celtics' Tatum practices with G League team but injury return uncertain
Celtics' Tatum practices with G League team but injury return uncertain
-
Gisele Pelicot publishes memoirs after rape trial ordeal

-
 Newcastle beat sorry Spurs to leave Frank on the brink
Newcastle beat sorry Spurs to leave Frank on the brink
-
'Outrage' as LGBTQ Pride flag removed from Stonewall monument

-
 Chappell Roan leaves agency headed by embattled 2028 Olympic chief
Chappell Roan leaves agency headed by embattled 2028 Olympic chief
-
Venezuelan authorities move Machado ally to house arrest


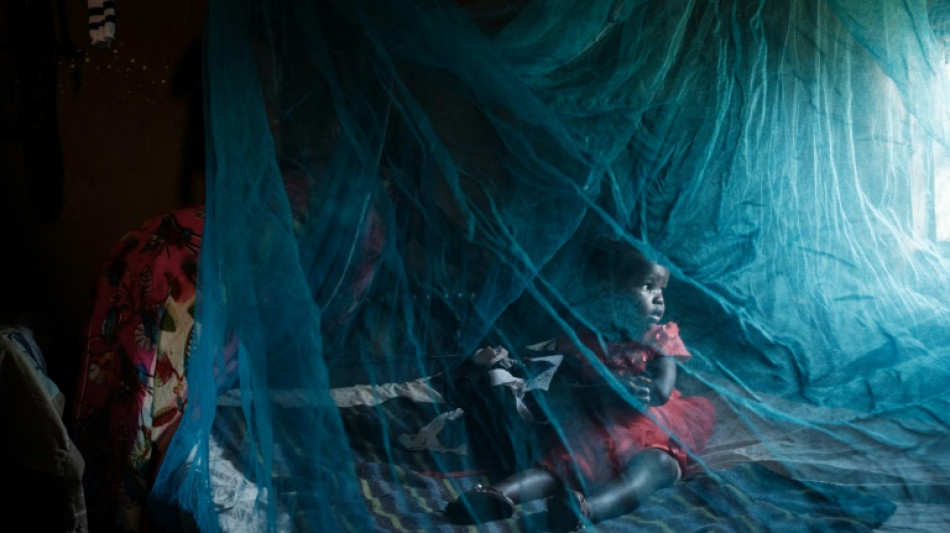
Urban mosquito sparks malaria surge in East Africa
The spread of a mosquito in East Africa that thrives in urban areas and is immune to insecticide is fuelling a surge in malaria that could reverse decades of progress against the disease, experts say.
Africa accounted for about 95 percent of the 249 million malaria cases and 608,000 deaths worldwide in 2022, according to the most recent data from the World Health Organization (WHO), which said children under five accounted for 80 percent of deaths in the region.
But the emergence of an invasive species of mosquito on the continent could massively increase those numbers.
Anopheles stephensi is native to parts of South Asia and the Middle East but was spotted for the first time in the tiny Horn of Africa state of Djibouti in 2012.
Djibouti had all but eradicated malaria only to see it make a slow but steady return over the following years, hitting more than 70,000 cases in 2020.
Then stephensi arrived in neighbouring Ethiopia and WHO says it is key to an "unprecedented surge", from 4.1 million malaria cases and 527 deaths last year to 7.3 million cases and 1,157 deaths between January 1 and October 20, 2024.
Unlike other species which are seasonal and prefer rural areas, stephensi thrives year-round in urban settings, breeding in man-made water storage tanks, roof gutters or even air conditioning units.
It appears to be highly resistant to insecticides, and bites earlier in the evening than other carriers. That means bed nets -- up to now the prime weapon against malaria -- may be much less effective.
"The invasion and spread of Anopheles stephensi has the potential to change the malaria landscape in Africa and reverse decades of progress we've made towards malaria control," Meera Venkatesan, malaria division chief for USAID, told AFP.
- 'More research is needed' -
The fear is that stephensi will infest dense cities like Mombasa on Kenya's Indian Ocean coast and Sudan's capital Khartoum, with one 2020 study warning it could eventually reach 126 million city-dwellers across Africa.
Only last month, Egypt was declared malaria-free by WHO after a century-long battle against the disease -- a status that could be threatened by stephensi's arrival.
Much remains unknown, however.
Stephensi was confirmed as present in Kenya in late 2022, but has so far stayed in hotter, dryer areas without reaching the high-altitude capital, Nairobi.
"We don't yet fully understand the biology and behaviour of this mosquito," Charles Mbogo, president of the Pan-African Mosquito Control Association, told AFP.
"Possibly it is climate-driven and requires high temperatures, but much more research is needed."
He called for increased funding for capturing and testing mosquitos, and for educating the public on prevention measures such as covering water receptacles.
- Multiplying threats -
The spread of stephensi could dovetail with other worrying trends, including increased evidence of drug resistant malaria recorded in Uganda, Rwanda, Tanzania and Eritrea.
"The arrival of resistance is imminent," said Dorothy Achu, WHO's head of tropical and vector-borne diseases in Africa.
WHO is working with countries to diversify treatment programmes to delay resistance, she said.
A new malaria variant is also evading tests used to diagnose the disease.
"The increased transmission that stephensi is driving could potentially help accelerate the spread of other threats, such as drug resistance or another mutation in the parasite that leads it to be less detectable by our most widely-used diagnostics," said Venkatesan at USAID.
Another added challenge is the lack of coordination between African governments.
Achu said WHO is working on "a more continental approach".
But Mbogo in Kenya said "more political will" was needed.
"We share information as scientists with colleagues in neighbouring countries," he said"But we need to reach the higher level. We need cross-border collaborations, data-sharing."
P.Santos--AMWN


