
-
 'War is back in vogue,' Pope Leo says
'War is back in vogue,' Pope Leo says
-
Storms pummel northern Europe causing travel mayhem and power cuts

-
 France has right to say 'no' to US, Paris says
France has right to say 'no' to US, Paris says
-
TikTok drives 'bizarre' rush to Prague library's book tower

-
 EU countries override France to greenlight Mercosur trade deal
EU countries override France to greenlight Mercosur trade deal
-
Russia joins Chinese, Iran warships for drills off S.Africa

-
 Stocks rise ahead of US jobs data and key tariffs ruling
Stocks rise ahead of US jobs data and key tariffs ruling
-
'All are in the streets': Iranians defiant as protests grow

-
 Kurdish fighters refuse to leave Syria's Aleppo after truce
Kurdish fighters refuse to leave Syria's Aleppo after truce
-
Grok turns off AI image generation for non-payers after nudes backlash

-
 Germany factory output jumps but exports disappoint
Germany factory output jumps but exports disappoint
-
Defiant Khamenei insists 'won't back down' in face of Iran protests

-
 Russian strikes cut heat to Kyiv, mayor calls for temporary evacuation
Russian strikes cut heat to Kyiv, mayor calls for temporary evacuation
-
Switzerland holds day of mourning after deadly New Year fire

-
 Hundreds of thousands without power as storms pummel Europe
Hundreds of thousands without power as storms pummel Europe
-
Man City win race to sign forward Semenyo

-
 Experts say oceans soaked up record heat levels in 2025
Experts say oceans soaked up record heat levels in 2025
-
'Would be fun': Alcaraz, Sinner tease prospect of teaming up in doubles

-
 Man City win race to sign Semenyo
Man City win race to sign Semenyo
-
Chinese AI unicorn MiniMax soars 109 percent in Hong Kong debut

-
 Iran rocked by night of protests despite internet blackout: videos
Iran rocked by night of protests despite internet blackout: videos
-
Swiatek romps to United Cup victory in 58 minutes

-
 Procession of Christ's icon draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
Procession of Christ's icon draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
-
Every second counts for Japan's 'King Kazu' at 58

-
 Syria announces ceasefire with Kurdish fighters in Aleppo
Syria announces ceasefire with Kurdish fighters in Aleppo
-
Russia hits Ukraine with hypersonic missile after rejecting peacekeeping plan

-
 Asian stocks mixed ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
Asian stocks mixed ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
-
Scores without power as Storm Goretti pummels Europe

-
 Sabalenka gets revenge over Keys in repeat of Australian Open final
Sabalenka gets revenge over Keys in repeat of Australian Open final
-
Fresh from China, South Korea president to visit Japan

-
 Injured Kimmich to miss icy Bundesliga return for Bayern
Injured Kimmich to miss icy Bundesliga return for Bayern
-
Rybakina has little hope of change to tennis schedule
-
 Osimhen, Nigeria seek harmony with Algeria up next at AFCON
Osimhen, Nigeria seek harmony with Algeria up next at AFCON
-
US immigration agent's fatal shooting of woman leaves Minneapolis in shock

-
 After fire tragedy, small Swiss town mourns 'decimated generation'
After fire tragedy, small Swiss town mourns 'decimated generation'
-
Switzerland mourns Crans-Montana fire tragedy

-
 Russia bombards Kyiv after rejecting peacekeeping plan
Russia bombards Kyiv after rejecting peacekeeping plan
-
Crunch time for EU's long-stalled Mercosur trade deal

-
 Asian stocks rally ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
Asian stocks rally ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
-
'Sever the chain': scam tycoons in China's crosshairs

-
 Bulls-Heat NBA game postponed over 'moisture' on court
Bulls-Heat NBA game postponed over 'moisture' on court
-
Arsenal's Martinelli 'deeply sorry' for shoving injured Bradley

-
 Christ icon's procession draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
Christ icon's procession draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
-
Moleiro shining as Villarreal make up La Liga ground after cup failures

-
 New Chelsea boss Rosenior faces FA Cup test
New Chelsea boss Rosenior faces FA Cup test
-
Vietnam shrugs off Trump tariffs as US exports surge

-
 Syrian government announces ceasefire in Aleppo after deadly clashes
Syrian government announces ceasefire in Aleppo after deadly clashes
-
New Zealand's rare flightless parrot begins breeding again

-
 Age no barrier for rampant Australia but future uncertain
Age no barrier for rampant Australia but future uncertain
-
Ex-delivery driver gives voice to China's precarious gig workers


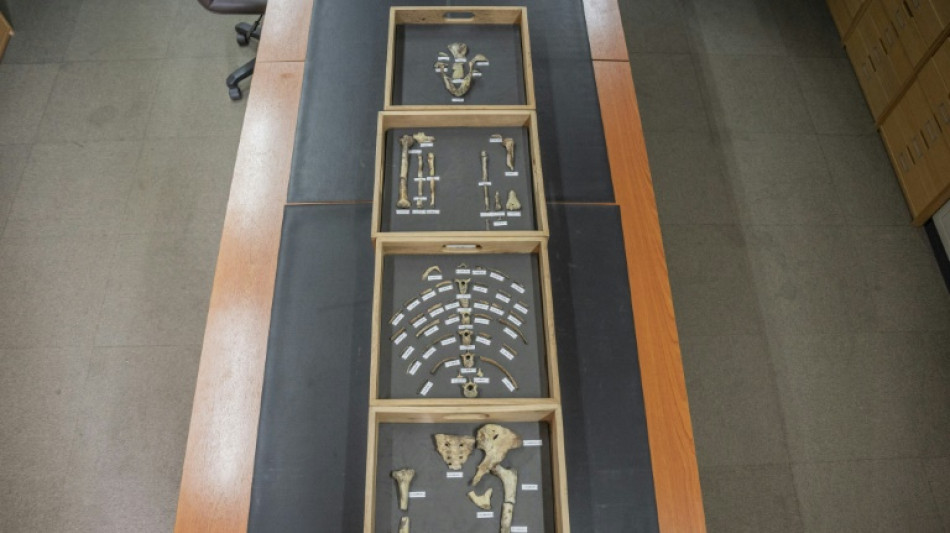
Human ancestor Lucy still has secrets 50 years after discovery
She was, for a while, the oldest known member of the human family. Fifty years after the discovery of Lucy in Ethiopia, the remarkable remains continue to yield theories and questions.
In a non-descript room in the National Museum of Ethiopia, the 3.18-million-year-old bones are delicately removed from a safe and placed on a long table.
They consist of fossilised dental remains, skull fragments, parts of the pelvis and femur that make up the world's most famous Australopithecus afarensis, Lucy.
The hominid was discovered on November 24, 1974, in the Afar region of northeast Ethiopia by a team of scientists led by Maurice Taieb, Yves Coppens, Donald Johanson, Jon Kalb, and Raymonde Bonnefille.
The 52 bone fragments, amounting to some 40 percent of Lucy's skeleton, was, at the time, the most complete ever found, and revolutionised the understanding of our ancestors.
The skeleton was initially called A.L-288-1, in reference to Afar and its geolocation.
But the researchers nicknamed it Lucy after The Beatles' song "Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds", which they listened to after celebrating their discovery.
Lucy walked on two legs and is thought to have died aged between 11 and 13 -- considered an adult for this species. She was 1.10 metres tall (3.6 feet) and weighed 29 kg (64 pounds).
For Sahleselasie Melaku, the 31-year-old head of the palaeontology department, Lucy's discovery represented an emergence from a "dark age" in our understanding of human ancestors.
"The impact of the discovery was very big in the discipline and even the whole world," he told AFP.
Lucy showed that members of the human family existed beyond three million years ago, and she also provided a template for fitting together later bone discoveries.
The amount of information that can be gleaned from the bones has allowed some highly detailed theories about Lucy's life.
A slightly deformed vertebra, for instance, "means she probably had back problems", said Melaku.
- 'Exceptional' -
Jean-Renaud Boisserie, a paleonthologist specialised in Ethiopia and the research director at the French National Centre for Scientific Research said it was an "exceptional" breakthrough for the discipline.
"We basically knew very little about the period of three million years ago, and we had nothing as complete," he said.
Lucy was often described as "the grandmother of humanity", but more recent discoveries suggest she may have been more like an aunt or a cousin, experts say.
Skeletal finds in places like Ethiopia, South Africa and Kenya have complicated the picture and led to much debate about when different species of hominid emerged and which should be classified as part of the human or chimpanzee families.
The discovery of "Toumai" in Chad in 2001 -- a skull dated to six or seven million years old -- suggested the human family may go much further back than previously thought.
Meanwhile, Lucy has yet to reveal all her secrets.
A study published in 2016 argued she spent a third of her time in trees, where she nested, and had highly developed upper limbs.
Another study that year in the American journal Plos One theorised that she died after falling from a tree.
A 2022 study in Nature, focused on Lucy's pelvis, concluded that newborn members of Australopithecus had a very immature brain, like human newborns today, and required parental support to survive.
"There are a lot of unanswered questions," said Melaku with a smile. "Especially, we don't know much more about the early livelihoods of these early human ancestors."
The museum receives frequent requests to study it, but the iconic skeleton no longer leaves Ethiopia.
Wider scientific progress and advanced equipment are opening up new avenues for research.
"The studies that can be carried out on her, on her peers, pose the scientific questions of tomorrow," said Boisserie.
"Material as exceptional as this plays a driving role in the evolution of research."
L.Mason--AMWN



