
-
 Crash course: Vietnam's crypto boom goes bust
Crash course: Vietnam's crypto boom goes bust
-
Ahead of Oscars, Juliette Binoche hails strength of Cannes winners

-
 US cattle farmers caught between high costs and weary consumers
US cattle farmers caught between high costs and weary consumers
-
New York creatives squeezed out by high cost of living

-
 Lillard matches NBA 3-point contest mark in injury return
Lillard matches NBA 3-point contest mark in injury return
-
NBA mulling 'every possible remedy' as 'tanking' worsens

-
 Team USA men see off dogged Denmark in Olympic ice hockey
Team USA men see off dogged Denmark in Olympic ice hockey
-
'US-versus-World' All-Star Game divides NBA players

-
 Top seed Fritz beats Cilic to reach ATP Dallas Open final
Top seed Fritz beats Cilic to reach ATP Dallas Open final
-
Lens run riot to reclaim top spot in Ligue 1, Marseille slip up

-
 Last-gasp Zielinski effort keeps Inter at Serie A summit
Last-gasp Zielinski effort keeps Inter at Serie A summit
-
Vinicius bags brace as Real Madrid take Liga lead, end Sociedad run

-
 Liverpool beat Brighton, Man City oust Beckham's Salford from FA Cup
Liverpool beat Brighton, Man City oust Beckham's Salford from FA Cup
-
Australia celebrate best-ever Winter Olympics after Anthony wins dual moguls

-
 Townsend becomes a fan again as Scotland stun England in Six Nations
Townsend becomes a fan again as Scotland stun England in Six Nations
-
France's Macron urges calm after right-wing youth fatally beaten

-
 China's freeski star Gu recovers from crash to reach Olympic big air final
China's freeski star Gu recovers from crash to reach Olympic big air final
-
Charli XCX 'honoured' to be at 'political' Berlin Film Festival

-
 Relatives of Venezuela political prisoners begin hunger strike
Relatives of Venezuela political prisoners begin hunger strike
-
Trump's 'desire' to own Greenland persists: Danish PM

-
 European debate over nuclear weapons gains pace
European debate over nuclear weapons gains pace
-
Newcastle oust 10-man Villa from FA Cup, Man City beat Beckham's Salford

-
 Auger-Aliassime swats aside Bublik to power into Rotterdam final
Auger-Aliassime swats aside Bublik to power into Rotterdam final
-
French prosecutors announce special team for Epstein files

-
 Tuipulotu 'beyond proud' as Scotland stun England
Tuipulotu 'beyond proud' as Scotland stun England
-
Jones strikes twice as Scotland end England's unbeaten run in style

-
 American Stolz wins second Olympic gold in speed skating
American Stolz wins second Olympic gold in speed skating
-
Marseille start life after De Zerbi with Strasbourg draw

-
 ECB to extend euro backstop to boost currency's global role
ECB to extend euro backstop to boost currency's global role
-
Canada warned after 'F-bomb' Olympics curling exchange with Sweden

-
 Ultra-wealthy behaving badly in surreal Berlin premiere
Ultra-wealthy behaving badly in surreal Berlin premiere
-
250,000 at rally in Germany demand 'game over' for Iran's leaders

-
 UK to deploy aircraft carrier group to Arctic this year: PM
UK to deploy aircraft carrier group to Arctic this year: PM
-
Zelensky labels Putin a 'slave to war'

-
 Resurgent Muchova beats Mboko in Qatar final to end title drought
Resurgent Muchova beats Mboko in Qatar final to end title drought
-
Farrell hails Ireland's 'unbelievable character' in edgy Six Nations win

-
 Markram, Jansen lead South Africa to brink of T20 Super Eights
Markram, Jansen lead South Africa to brink of T20 Super Eights
-
Guehi scores first Man City goal to kill off Salford, Burnley stunned in FA Cup

-
 Swiss say Oman to host US-Iran talks in Geneva next week
Swiss say Oman to host US-Iran talks in Geneva next week
-
Kane brace helps Bayern widen gap atop Bundesliga

-
 Ireland hold their nerve to beat gallant Italy in Six Nations thriller
Ireland hold their nerve to beat gallant Italy in Six Nations thriller
-
European states say Navalny poisoned with dart frog toxin in Russian prison

-
 Braathen hails 'drastic' changes after Olympic gold
Braathen hails 'drastic' changes after Olympic gold
-
De Minaur eases past inconsistent Humbert into Rotterdam final

-
 Eurovision 70th anniversary live tour postponed
Eurovision 70th anniversary live tour postponed
-
Cuba cancels cigar festival amid economic crisis

-
 Son of Iran's last shah urges US action as supporters rally in Munich
Son of Iran's last shah urges US action as supporters rally in Munich
-
Jansen helps South Africa limit New Zealand to 175-7

-
 Braathen wins unique Winter Olympic gold for Brazil, Malinin seeks answers
Braathen wins unique Winter Olympic gold for Brazil, Malinin seeks answers
-
Relatives of Venezuela political prisoners begin hunger strike after 17 freed


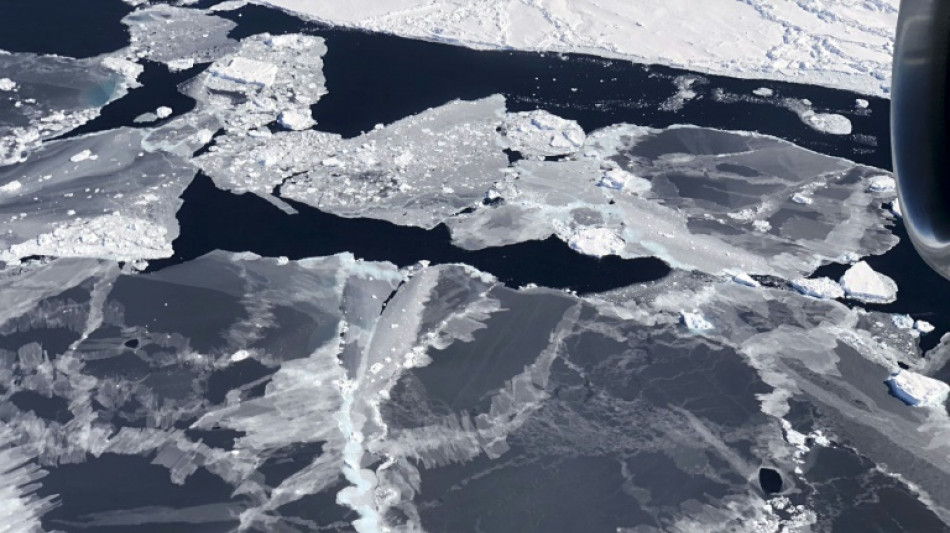
Emperor penguin populations declining faster than expected
Emperor penguin populations in Antarctica have shrunk by almost a quarter as global warming transforms their icy habitat, according to new research on Tuesday that warned the losses were far worse than previously imagined.
Scientists monitoring the world's largest penguin species used satellites to assess sixteen colonies in the Antarctic Peninsula, Weddell Sea and Bellingshausen Sea, representing nearly a third of the global emperor penguin population.
What they found was "probably about 50-percent worse" than even the most pessimistic estimate of current populations using computer modelling, said Peter Fretwell, who tracks wildlife from space at the British Antarctic Survey (BAS).
Researchers know that climate change is driving the losses but the speed of the declines is a particular cause for alarm.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications: Earth & Environment, found that numbers declined 22 percent in the 15 years to 2024 for the colonies monitored.
This compares with an earlier estimate of a 9.5-percent reduction across Antarctica as a whole between 2009 and 2018.
Warming is thinning and destabilising the ice under the penguins' feet in their breeding grounds.
In recent years some colonies have lost all their chicks because the ice has given way beneath them, plunging hatchlings into the sea before they were old enough to cope with the freezing ocean.
Fretwell said the new research suggests penguin numbers have been declining since the monitoring began in 2009.
That is even before global warming was having a major impact on the sea ice, which forms over open water adjacent to land in the region.
But he said the culprit is still likely to be climate change, with warming driving other challenges for the penguins, such as higher rainfall or increasing encroachment from predators.
"Emperor penguins are probably the most clear-cut example of where climate change is really showing its effect," said Fretwell.
"There's no fishing. There's no habitat destruction. There's no pollution which is causing their populations to decline.
"It's just the temperatures in the ice on which they breed and live, and that's really climate change."
- 'Worrying result" -
Emperor penguins, aka Aptenodytes forsteri, number about a quarter of a million breeding pairs, all in Antarctica, according to a 2020 study.
A baby emperor penguin emerges from an egg kept warm in winter by a male, while the female in a breeding pair embarks on a two-month fishing expedition.
When she returns to the colony, she feeds the hatchling by regurgitating.
To survive on their own, chicks must develop waterproof feathers, a process that typically starts in mid-December.
Fretwell said there is hope that the penguins may go further south in the future but added that it is not clear "how long they're going to last out there".
Computer models have projected that the species will be near extinction by the end of the century if humans do not slash their planet-heating emissions.
The latest study suggests the picture could be even worse.
"We may have to rethink those models now with this new data," said Fretwell.
"We really do need to look at the rest of the population to see if this worrying result transfers around the continent," he added.
But he stressed there was still time to reduce the threat to the penguins.
"We've got this really depressing picture of climate change and falling populations even faster than we thought but it's not too late," he said.
We're probably going to lose a lot of emperor penguins along the way but if people do change, and if we do reduce or turn around our climate emissions, then then we will save the emperor penguin."
G.Stevens--AMWN


