
-
 Bulgaria adopts euro amid fear and uncertainty
Bulgaria adopts euro amid fear and uncertainty
-
Giannis triumphant in NBA return as Spurs win streak ends

-
 How company bets on bitcoin can backfire
How company bets on bitcoin can backfire
-
Touadera on path to third presidential term as Central African Republic votes

-
 'Acoustic hazard': Noise complaints spark Vietnam pickleball wars
'Acoustic hazard': Noise complaints spark Vietnam pickleball wars
-
Iraqis cover soil with clay to curb sandstorms

-
 Australia's Head backs struggling opening partner Weatherald
Australia's Head backs struggling opening partner Weatherald
-
'Make emitters responsible': Thailand's clean air activists

-
 Zelensky looks to close out Ukraine peace deal at Trump meet
Zelensky looks to close out Ukraine peace deal at Trump meet
-
MCG curator in 'state of shock' after Ashes Test carnage

-
 Texans edge Chargers to reach NFL playoffs
Texans edge Chargers to reach NFL playoffs
-
Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw

-
 Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round
Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round
-
How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not

-
 Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family
Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family
-
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought

-
 Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania
Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania
-
Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea

-
 Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine
Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine
-
Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit

-
 Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota
Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota
-
Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo

-
 Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck
-
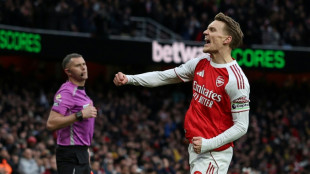
Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
-
 Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role
Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role
-
UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles

-
 Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects
Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects
-
'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year

-
 Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes
Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes
-
Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday

-
 US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says
US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says
-
Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest

-
 Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth
Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth
-
Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit

-
 Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
-
Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power

-
 Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
-
Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win

-
 What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
-
Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'

-
 England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire

-
 Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
-
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
-
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan

-
 Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
-
New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television


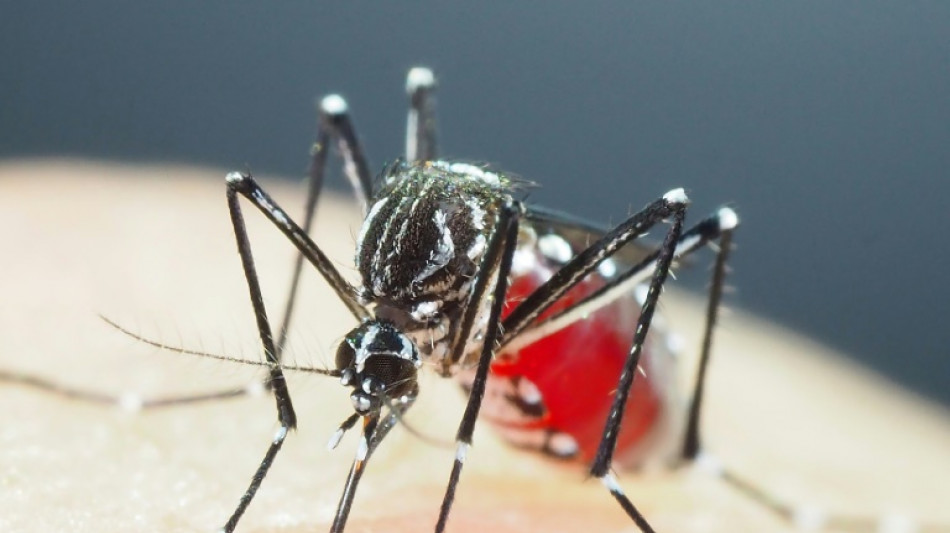
Super-resistant mosquitoes in Asia pose growing threat: study
Mosquitoes that transmit dengue and other viruses have evolved growing resistance to insecticides in parts of Asia, and novel ways to control them are desperately needed, new research warns.
Health authorities commonly fog mosquito-infested areas with clouds of insecticide, and resistance has long been a concern, but the scale of the problem was not well understood.
Japanese scientist Shinji Kasai and his team examined mosquitos from several countries in Asia as well as Ghana and found a series of mutations had made some virtually impervious to popular pyrethroid-based chemicals like permethrin.
"In Cambodia, more than 90 percent of Aedes aegypti mosquitoes have the combination of mutations that results in an extremely high level of resistance," Kasai told AFP.
He found some mosquito strains had 1,000-fold resistance, compared to the 100-fold seen previously.
That meant insecticide levels that would normally kill almost 100 percent of mosquitoes in a sample killed only around seven percent of the insects.
Even a dose 10 times stronger killed just 30 percent of the super-resistant mosquitoes.
"The resistance level that we found in mosquitos in Cambodia and Vietnam is totally different," said Kasai, director of the Department of Medical Entomology at Japan's National Institute of Infectious Diseases.
Dengue can cause hemorrhagic fever and infects an estimated 100 to 400 million people a year, although over 80 percent of cases are mild or asymptomatic, according to the World Health Organization.
Several dengue vaccines have been developed, and researchers have also used a bacteria that sterilises mosquitoes to tackle the virus.
But neither option is yet close to eradicating dengue, and Aedes aegypti mosquitoes carry other diseases, including zika and yellow fever.
- New formulas needed -
Resistance was also detected in another type of mosquito, Aedes albopictus, though at lower levels -- possibly because it tends to feed outdoors, often on animals, and may be exposed to insecticides less than its human-loving Aedes aegypti counterparts.
The research found several genetic changes were linked with resistance, including two that occur close to the part of mosquitoes targeted by pyrethroid and several other insecticides.
Resistance levels differed, with mosquitos from Ghana as well as parts of Indonesia and Taiwan still relatively susceptible to existing chemicals, particularly at higher doses.
But the research shows "commonly employed strategies may no longer be effective," said Cameron Webb, an associate professor and mosquito researcher at NSW Health Pathology and the University of Sydney.
"There is growing evidence that there may not be a place for current insecticide formulations in controlling populations of key mosquito pests," Webb told AFP.
He said new chemicals are needed, but authorities and researchers also need to think of other ways to protect communities, including vaccines.
"We have to think about rotating insecticides... that have different target sites," added Kasai, whose research was published last month in the journal Science Advances.
"The problem is that we don't have so many different kinds that we can use."
Other options include more efforts to remove breeding sites.
When and where the mutations for resistance emerged is still a mystery, but Kasai is now expanding the research elsewhere in Asia and examining more recent samples from Cambodia and Vietnam to see if anything has changed from the 2016-2019 study period.
"We are worried that the mosquitoes with the mutations that we found in this study will spread to the rest of the world in the near future," he said.
"Before that, we have to think of a solution."
A.Mahlangu--AMWN



