
-
 Australia's Head backs struggling opening partner Weatherald
Australia's Head backs struggling opening partner Weatherald
-
'Make emitters responsible': Thailand's clean air activists

-
 Zelensky looks to close out Ukraine peace deal at Trump meet
Zelensky looks to close out Ukraine peace deal at Trump meet
-
MCG curator in 'state of shock' after Ashes Test carnage

-
 Texans edge Chargers to reach NFL playoffs
Texans edge Chargers to reach NFL playoffs
-
Osimhen and Mane score as Nigeria win to qualify, Senegal draw

-
 Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round
Osimhen stars as Nigeria survive Tunisia rally to reach second round
-
How Myanmar's junta-run vote works, and why it might not

-
 Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family
Watkins wants to sicken Arsenal-supporting family
-
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Villa as Wirtz ends drought

-
 Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania
Late penalty miss denies Uganda AFCON win against Tanzania
-
Watkins stretches Villa's winning streak at Chelsea

-
 Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine
Zelensky stops in Canada en route to US as Russia pummels Ukraine
-
Arteta salutes injury-hit Arsenal's survival spirit

-
 Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota
Wirtz scores first Liverpool goal as Anfield remembers Jota
-
Mane rescues AFCON draw for Senegal against DR Congo

-
 Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck
Arsenal hold off surging Man City, Wirtz breaks Liverpool duck
-
Arsenal ignore injury woes to retain top spot with win over Brighton
-
 Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role
Sealed with a kiss: Guardiola revels in Cherki starring role
-
UK launches paid military gap-year scheme amid recruitment struggles

-
 Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects
Jota's children join tributes as Liverpool, Wolves pay respects
-
'Tired' Inoue beats Picasso by unanimous decision to end gruelling year

-
 Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes
Thailand and Cambodia declare truce after weeks of clashes
-
Netanyahu to meet Trump in US on Monday

-
 US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says
US strikes targeted IS militants, Lakurawa jihadists, Nigeria says
-
Cherki stars in Man City win at Forest

-
 Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth
Schwarz records maiden super-G success, Odermatt fourth
-
Russia pummels Kyiv ahead of Zelensky's US visit

-
 Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
Smith laments lack of runs after first Ashes home Test loss for 15 years
-
Russian barrage on Kyiv kills one, leaves hundreds of thousands without power

-
 Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
Stokes, Smith agree two-day Tests not a good look after MCG carnage
-
Stokes hails under-fire England's courage in 'really special' Test win

-
 What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
What they said as England win 4th Ashes Test - reaction
-
Hong Kongers bid farewell to 'king of umbrellas'

-
 England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
England snap 15-year losing streak to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test
-
Thailand and Cambodia agree to 'immediate' ceasefire

-
 Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
Closing 10-0 run lifts Bulls over 76ers while Pistons fall
-
England 77-2 at tea, need 98 more to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
Somalia, African nations denounce Israeli recognition of Somaliland
-
England need 175 to win chaotic 4th Ashes Test

-
 Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
Cricket Australia boss says short Tests 'bad for business' after MCG carnage
-
Russia lashes out at Zelensky ahead of new Trump talks on Ukraine plan

-
 Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
Six Australia wickets fall as England fight back in 4th Ashes Test
-
New to The Street Show #710 Airs Tonight at 6:30 PM EST on Bloomberg Television

-
 Dental Implant Financing and Insurance Options in Georgetown, TX
Dental Implant Financing and Insurance Options in Georgetown, TX
-
Man Utd made to 'suffer' for Newcastle win, says Amorim

-
 Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
Morocco made to wait for Cup of Nations knockout place after Egypt advance
-
Key NFL week has playoff spots, byes and seeds at stake

-
 Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
Morocco forced to wait for AFCON knockout place after Mali draw
-
Dorgu delivers winner for depleted Man Utd against Newcastle


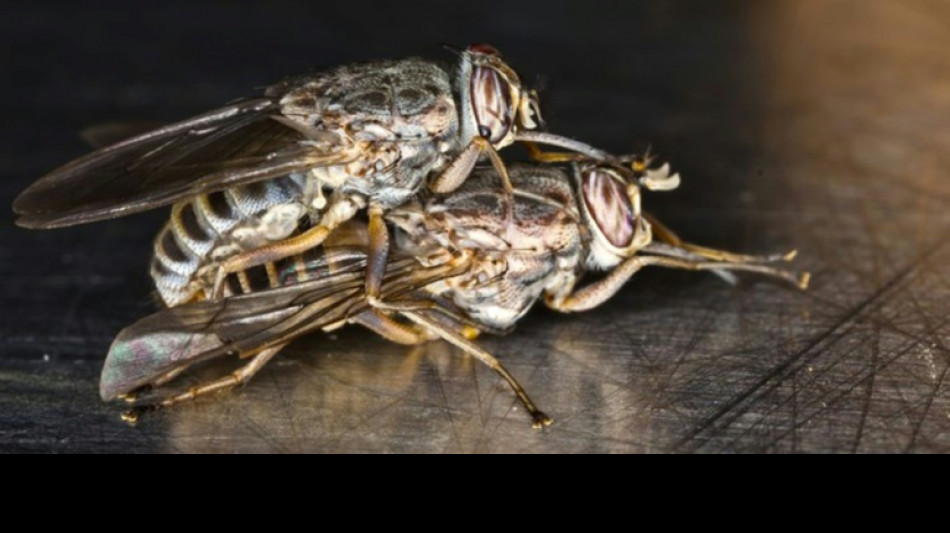
Discovery of tsetse fly mating behavior may help curb sleeping sickness
Researchers have identified chemicals in tsetse flies that control their mating behavior, a discovery that may well aid the fight against the disease-causing insects in sub-Saharan Africa.
"It could be used in traps to make them more effective in trapping tsetse flies," said John Carlson, a biology professor at Yale University and one of the authors of a study published Thursday in the journal Science.
Trypanosomiasis, also known as sleeping sickness, is caused by parasites transmitted by the tsetse fly. It affects humans and domestic animals.
The disease threatens millions of people in dozens of countries in sub-Saharan Africa.
Animal trypanosomiasis, known as Nagana, kills some three million cattle each year, an annual cost of $1.2 billion, according to a companion article in Science.
It is considered a major cause of rural poverty and the authors warned that the geographic range of the tsetse fly is expected to grow as a result of climate change.
For the study, the researchers focused on pheromones, chemical compounds an animal releases that affect the behavior of others of the same species.
Pheromones allow insects to identify each other in an environment where there are potentially thousands of other species.
The Yale researchers identified volatile sex pheromones that had not previously been isolated in tsetse flies despite more than a century of study.
Pheromones are currently used to control a wide variety of other insect pests such as moths.
Pantry moths, for example, can be caught using sticky traps baited with a plastic disc soaked with an attractive pheromone.
- 'The flies stop moving' -
For the study, the researchers soaked tsetse flies in liquid and then used a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer to identify specific chemicals.
One of them, methyl palmitoleate (MPO), acted as an aphrodisiac, attracting male tsetse flies.
In tests, male tsetse flies were attracted to decoys -- knots in yarn doused with MPO -- and, unusually, to females of another tsetse fly species.
Olfactory neurons on the antennae of the flies were found to increase their firing rates in response to MPO.
"Not only is MPO an attractant, but it causes tsetse flies to freeze -- the flies stop moving," Carlson said.
Current traps for tsetse flies use animal odors but MPO tends to last longer and could "enhance the effectiveness of traps," he said.
Carlson said field tests using MPO were getting underway in Kenya.
The type of pheromone identified in the study may not be effective against all types of tsetse flies, however.
The study focused on the species Glossina morsitans, a major vector of the disease in cattle, not on Glossina fuscipes, which causes the most human cases of the disease.
But Carlson said he was optimistic that the research methods used could lead to identifying pheromones from other tsetse species.
L.Miller--AMWN



